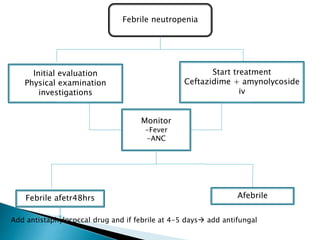
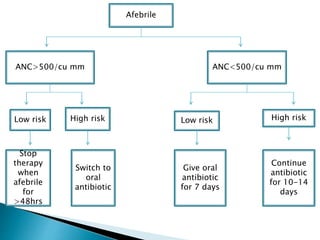
This document discusses neutropenia and febrile neutropenia in children. It defines neutropenia as a decrease in absolute neutrophil count and describes different levels of severity from mild to profound. It outlines common causes of infection in febrile neutropenic children including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Risk factors for serious infection are described. Guidelines are provided for evaluation, treatment including antibiotic and antifungal selection, and risk stratification of febrile neutropenic children.