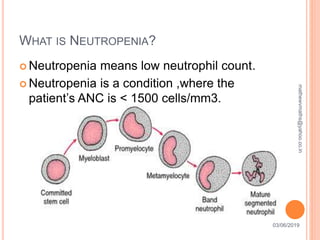
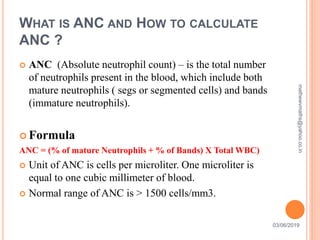
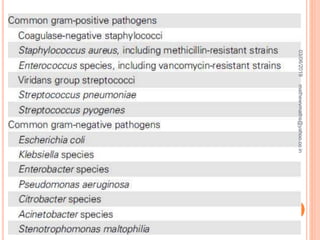
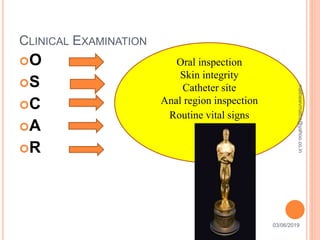
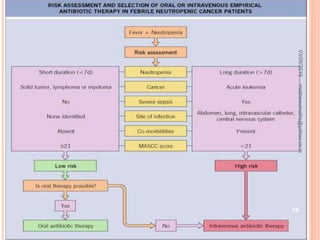
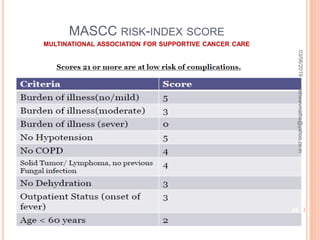
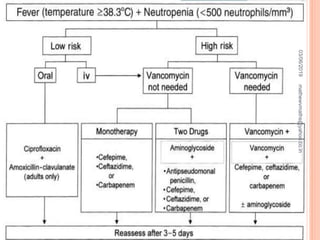
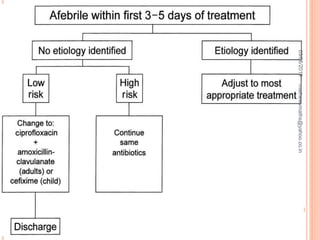
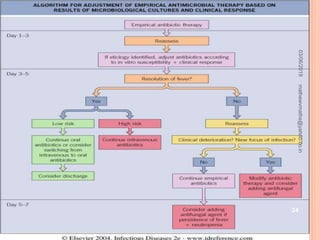
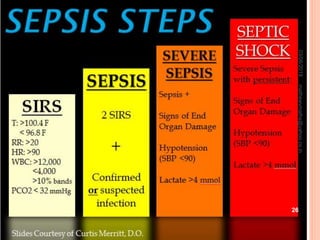
Febrile neutropenia is a common oncological emergency seen in patients undergoing chemotherapy. It is defined as a fever over 38.3°C along with a low absolute neutrophil count under 500 cells/mm3. The highest risk is in patients with hematological malignancies undergoing chemotherapy, where febrile neutropenia is a leading cause of mortality. Nurses play an important role in early recognition of infection and rapid administration of first-line antibiotics to treat potential neutropenic sepsis.