The document discusses fault tolerance techniques in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). It first reviews WSNs and types of failures that can occur, such as energy depletion, hardware failure, and communication link errors. It then covers approaches to fault detection including centralized (Sympathy, Secure Locations) and distributed (node self-detection, clustering). Fault recovery techniques like relay node placement, hop-by-hop TCP, and data aggregation are also summarized. The document aims to provide an overview of key aspects of fault tolerance in WSNs.





![Sympathy[4]
Using a message-flooding approach to pool event data and current
states (metrics) from sensor node
Nodes periodically send metrics back to a sink to detect failures and
cause of failure
Given sensor hardware and network limitations, these transmitted
metrics must be minimized
Insufficient data at the sink implies failure; sufficient data at the sink
implies acceptable network behavior
Based on these metrics, it detects which nodes or components have
not delivered sufficient data and infers the causes of failures
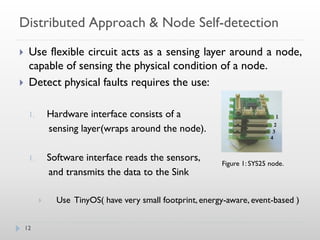
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faulttoleranceinwsn-121004082836-phpapp01/85/Fault-tolerance-in-wsn-6-320.jpg)
![Secure Locations[5]
Work on location-aware sensor networks
Introduces a scalable trust-based routing protocol (TRANS)
Select trusted paths that do not include misbehaving
nodes by identifying the insecure locations and routing
Include two parts:
1. trust routing
2. insecure location discovery and isolation
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faulttoleranceinwsn-121004082836-phpapp01/85/Fault-tolerance-in-wsn-7-320.jpg)







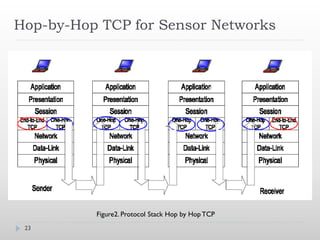
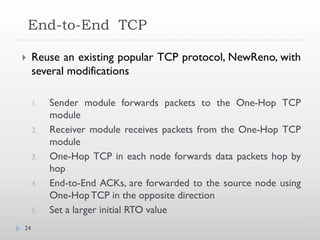


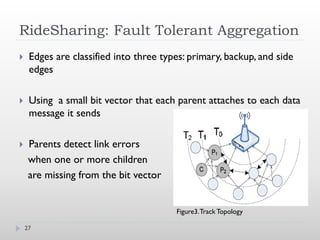

![References
[1] Hai Liu, Amiya Nayak, and Ivan Stojmenovi ' Fault-Tolerant Algorithms/Protocols in
Wireless Sensor Networks' Department of Computer Science, Hong Kong Baptist
University, Springer-Verlag London Limited 2009
[2] M.Yu, H.Mokhtar, and M.Merabti, 'A Survey on Fault Management in Wireless Sensor
Networks' School of Computing & Mathematical Science Liverpool John Moores
University, 2007
[3] Farinaz Koushanfar1, Miodrag Potkonjak2, Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli1, ' FAULT
TOLERANCE IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS'1Department of Electrical Engineering
and Computer Science Univeristy of California, Berkeley , CA, US 94720, 2Department of
Computer Science Univeristy of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA, US 90095
[4] Nithya Ramanathan, Kevin Chang, Rahul Kapur, Lewis Girod, Eddie Kohler, and eborah
Estrin,' Sympathy for the Sensor Network Debugger' UCLA Center for Embedded Network
Sensing, ACM 2005
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faulttoleranceinwsn-121004082836-phpapp01/85/Fault-tolerance-in-wsn-29-320.jpg)
![References(cont’d)
[5] Jessica Staddon, Dirk Balfanz, Glenn Durfee' Efficient Tracing of Failed Nodes in
Sensor Networks ', September 28, 2002, Atlanta, Georgia, USA,ACM.
[6] Sapon Tanachaiwiwat1, Pinalkumar Dave1, Rohan Bhindwale2, Ahmed Helmy1,'
Secure Locations: Routing on Trust and Isolating Compromised Sensors in Location-Aware
Sensor Networks ' 1. Department of Electrical Engineering – Systems 2. Department of
Computer Science University of Southern California, ACM 2003
[7] Gaurav Gupta1, Mohamed Younis2, ' Fault-Tolerant Clustering of Wireless Sensor
Networks ', Dept. of Computer Science and Elec. Eng. Dept. of Computer Science and
Elec. Eng. University of Maryland Baltimore County University of Maryland Baltimore
County 2003 IEEE
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faulttoleranceinwsn-121004082836-phpapp01/85/Fault-tolerance-in-wsn-30-320.jpg)
![References(cont’d)
[8] Jinran Chen, Shubha Kher, and Arun Somani,' Distributed Fault Detection of Wireless
Sensor Networks' Dependable Computing and Networking Lab Iowa State University
Ames, Iowa 50010, 2006 IEEE
[9] Sameh Gobriel, Sherif Khattab, Daniel Moss´e, Jos´e Brustoloni and Rami Melhem,’
RideSharing: Fault Tolerant Aggregation in Sensor Networks Using Corrective Actions’,
Computer Science Department, University of Pittsburgh,2006
[10] Weiyi Zhang, Guoliang Xue and Satyajayant Misra,'Fault-Tolerant Relay Node
Placement in Wireless Sensor Networks', Department of Computer Science and
Engineering at Arizona State University, IEEE INFOCOM 2007
[11] S Harte1, A Rahman1, K M Razeeb2 'FAULT TOLERANCE IN SENSOR NETWORKS
USING SELF-DIAGNOSING SENSOR NODES', 1 University of Limerick, Ireland 2 Tyndall
National Institute, Ireland,2005
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faulttoleranceinwsn-121004082836-phpapp01/85/Fault-tolerance-in-wsn-31-320.jpg)