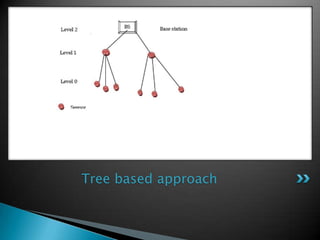
The document discusses data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. It explains that sensor networks aim to gather and aggregate data in an energy efficient manner to extend network lifetime. It describes various data aggregation approaches like centralized, LEACH, and TAG. It also discusses cluster-based and tree-based aggregation where nodes aggregate and transmit data to parent nodes or cluster heads. The document outlines types of queries for sensor networks and benefits of data aggregation in reducing traffic and energy consumption while improving data accuracy.