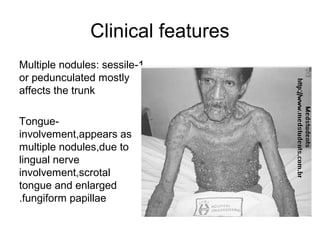
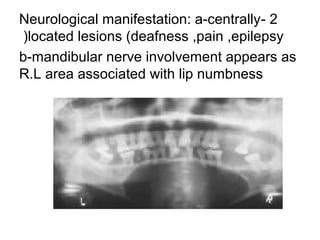
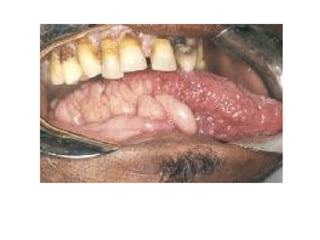
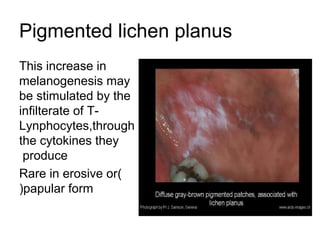
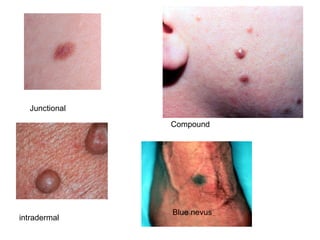
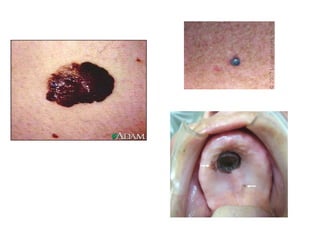
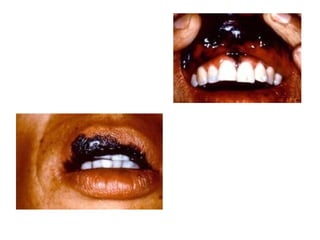
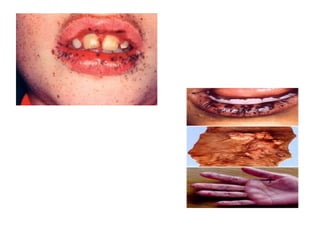
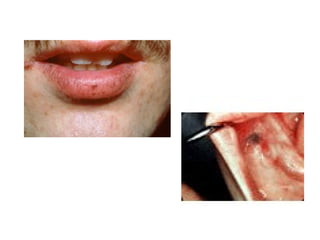
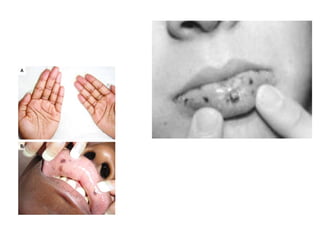
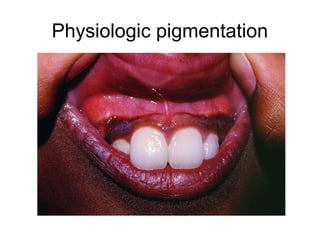
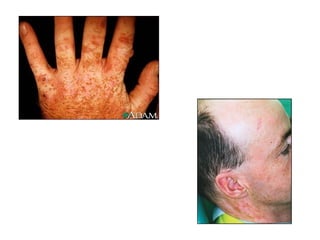
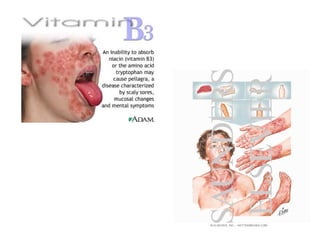
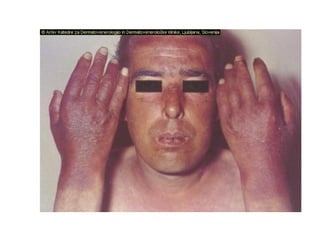
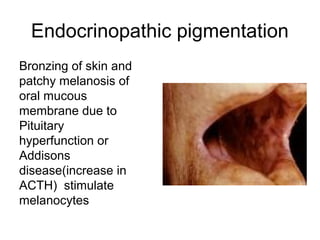
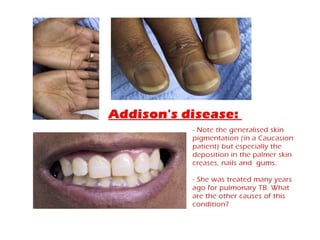
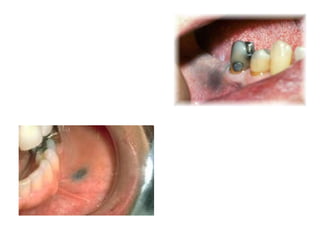
1) The document classifies pigmented lesions as either melanotic or non-melanotic and discusses various localized and diffuse melanotic lesions as well as endogenous and exogenous non-melanotic lesions.
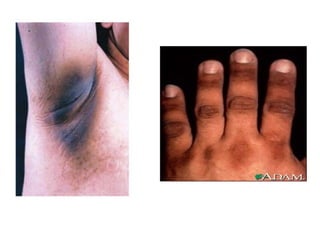
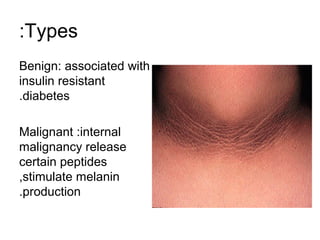
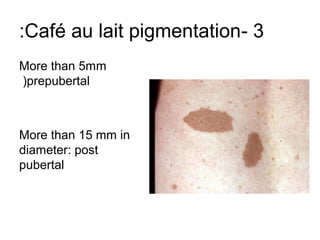
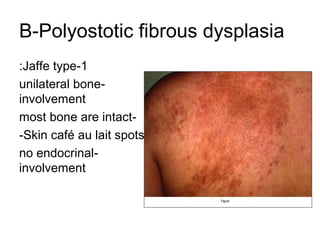
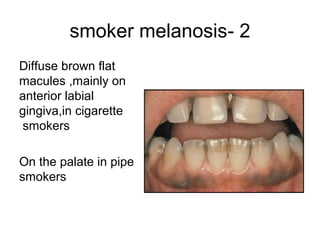
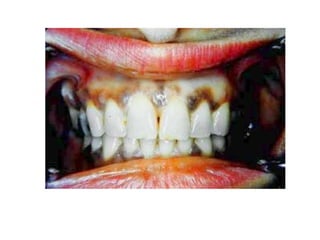
2) Specific melanotic lesions mentioned include acanthosis nigricans, café au lait spots associated with neurofibromatosis or polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, and smoker's melanosis.
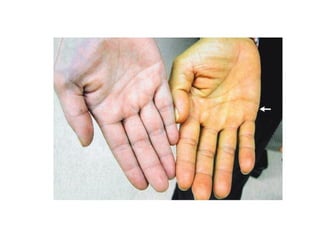
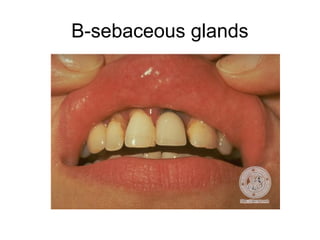
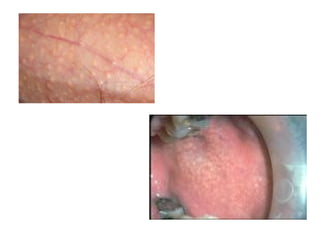
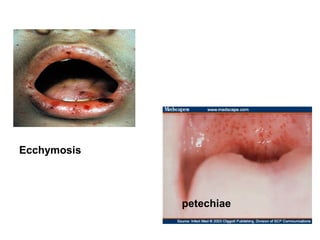
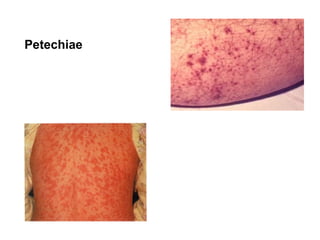
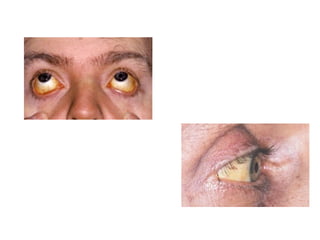
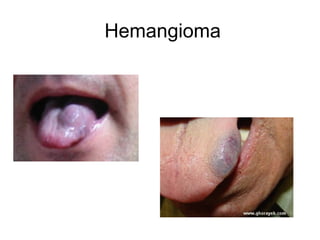
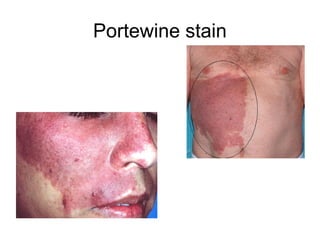
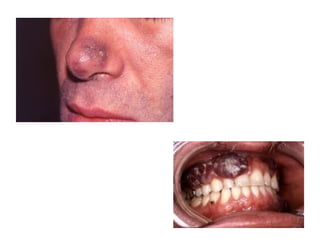
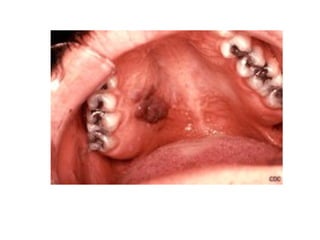
3) Non-melanotic lesions discussed include those caused by lipopigments like carotene, red blood cells, vascular lesions like hemangiomas, port wine stains, Kaposi's sarcoma, and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.