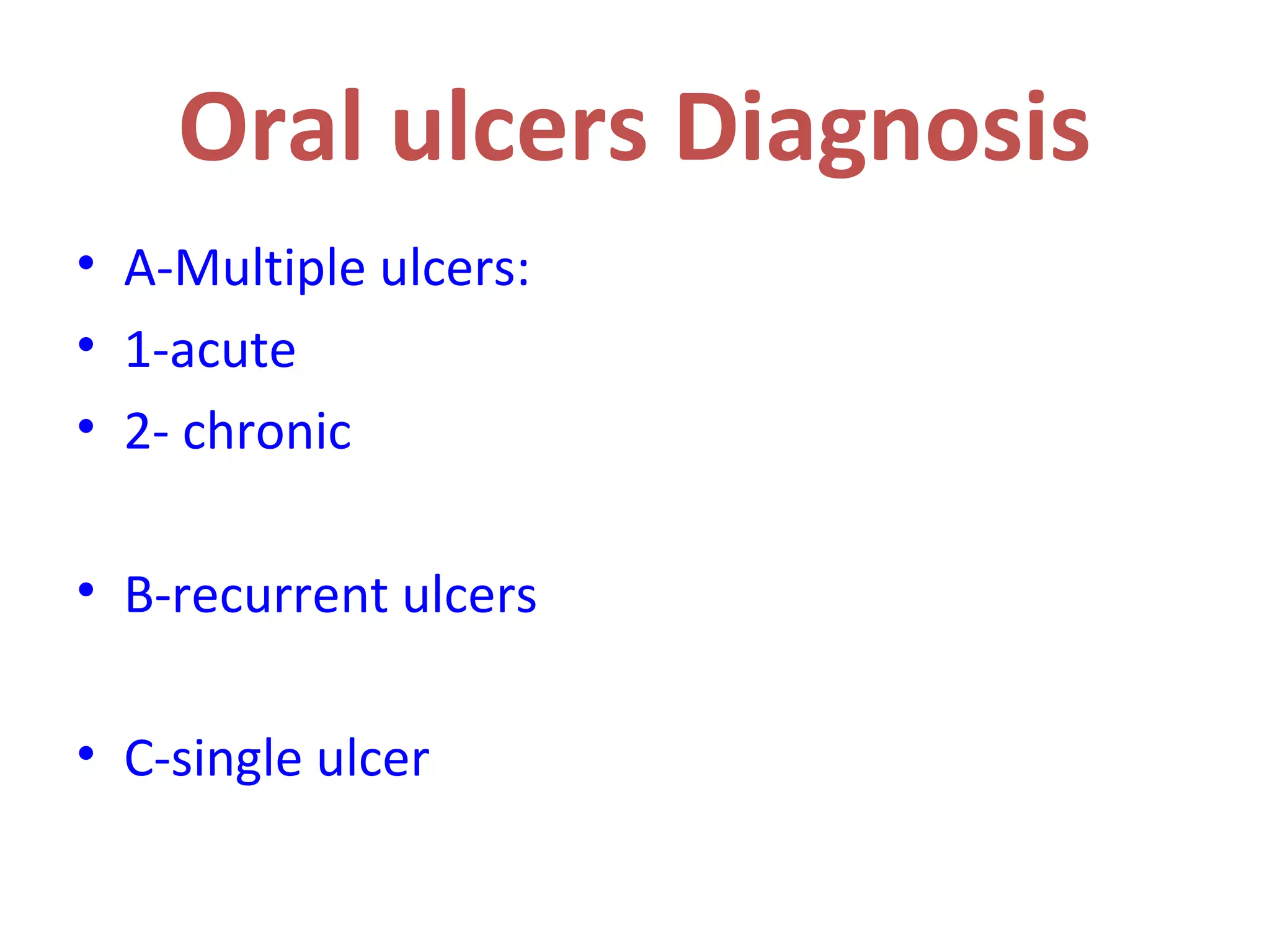
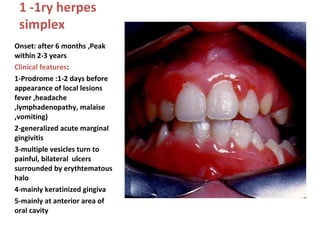
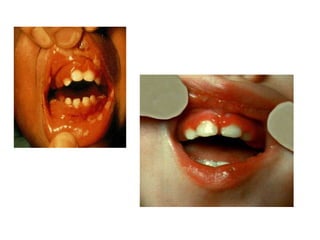
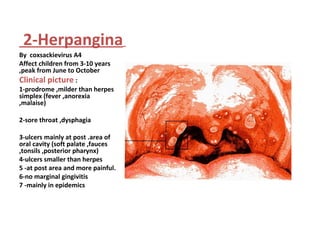
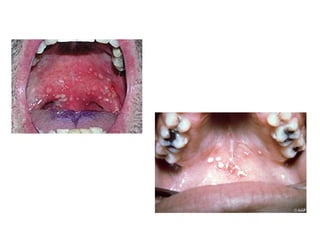
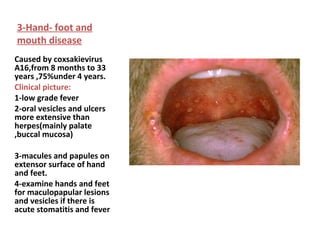
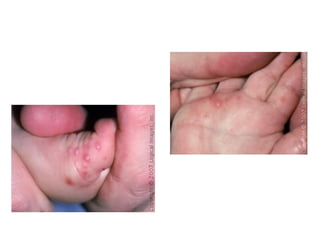
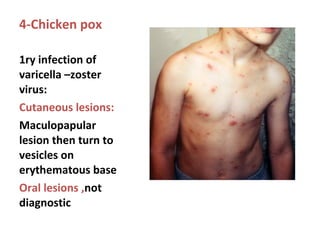
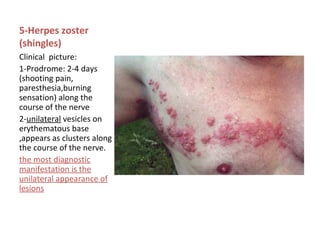
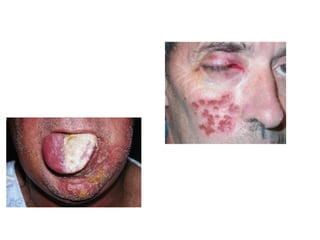
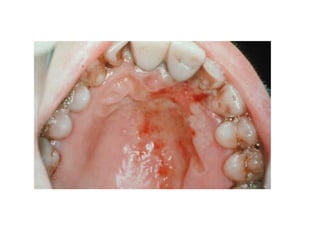
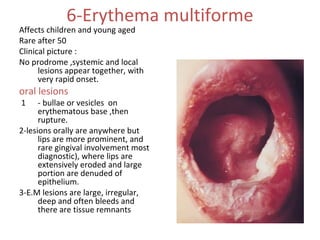
1. Acute multiple oral ulcers can be caused by primary herpes simplex infection, herpangina caused by coxsackievirus A4, hand-foot-and-mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A16, chickenpox caused by varicella zoster virus, or herpes zoster infection.
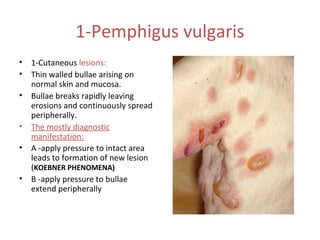
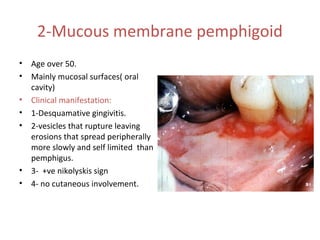
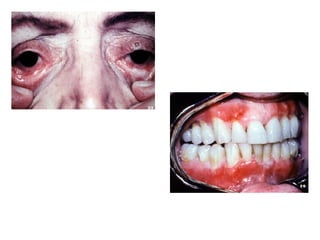
2. Chronic multiple ulcers can be caused by pemphigus vulgaris, characterized by thin-walled bullae and erosions that extend peripherally, or mucous membrane pemphigoid, presenting mainly with desquamative gingivitis and erosions.
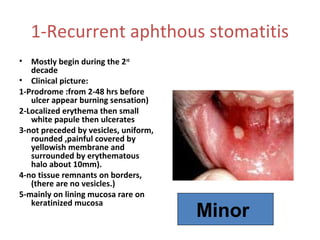
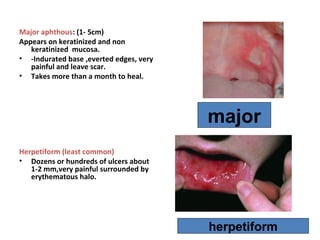
3. Recurrent oral ulcers include recurrent aphthous stomat