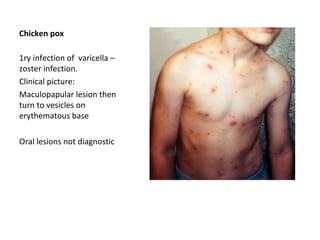
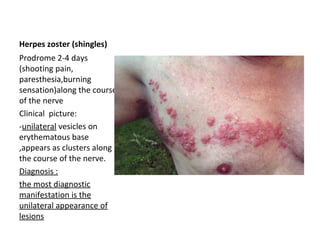
This document discusses several oral ulcer conditions:
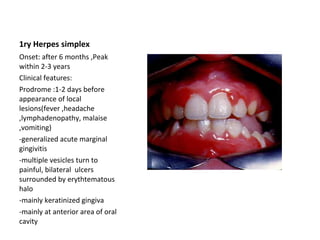
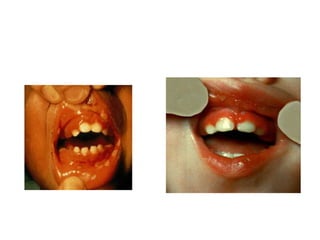
1. Primary herpes simplex causes painful bilateral ulcers surrounded by erythema mainly on the anterior gingiva in children over 6 months.
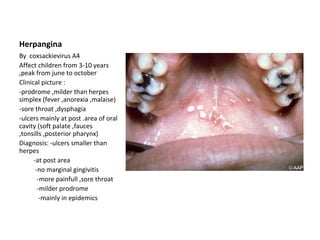
2. Herpangina, caused by coxsackievirus A4, affects children 3-10 years with ulcers mainly on the soft palate and tonsils and a milder prodrome than herpes.
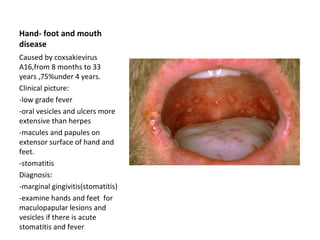
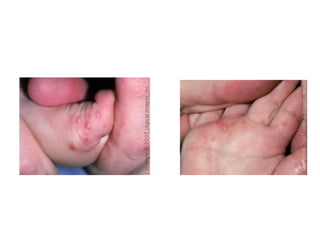
3. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A16 most often affects children under 4 years with oral vesicles/ulcers and maculopapular lesions on the hands and feet along with stomatitis.