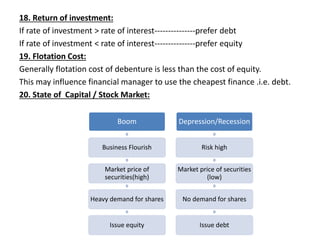
The document discusses various determinants of capital structure, emphasizing factors such as tax benefits of debt, flexibility, control, seasonal variation, competition, and agency costs. It highlights how firms can optimize their capital structure based on their specific needs, industry characteristics, credit ratings, and investor requirements. Additionally, it notes the implications of financial metrics like interest coverage and debt service coverage ratios on financing decisions.