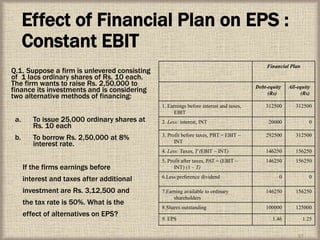
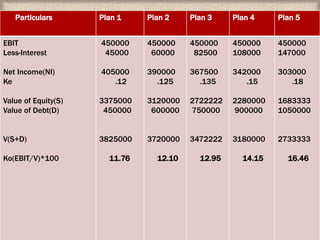
The document defines capital structure as the permanent long-term financing of a company, including long-term debt, common stock, preferred stock, and retained earnings. It discusses the concept of optimal capital structure, which minimizes a firm's cost of capital. The document also outlines various approaches to establishing capital structure, including EBIT-EPS analysis and cash flow analysis. It evaluates capital structure based on factors like flexibility, risk, return, and control.