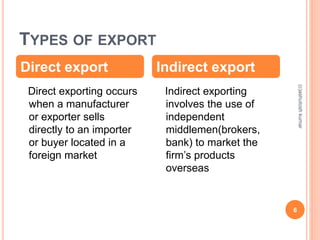
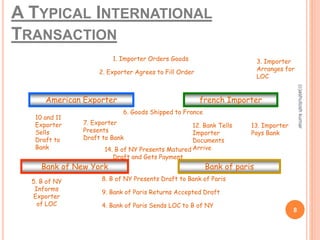
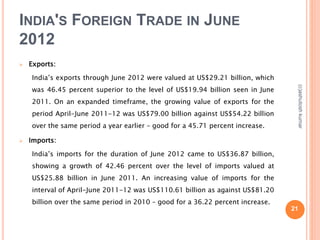
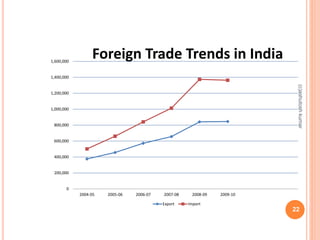
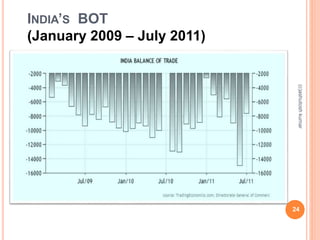
The document discusses India's export and import policies. It provides definitions of key terms like export, import, and trade balance. It outlines the various types of exports and imports, the role of government in promoting trade, and processes involved like market analysis, financing, and regulations. It also summarizes India's export-import policies from 2009-2014, objectives to double exports and trade share, and provides trade statistics.