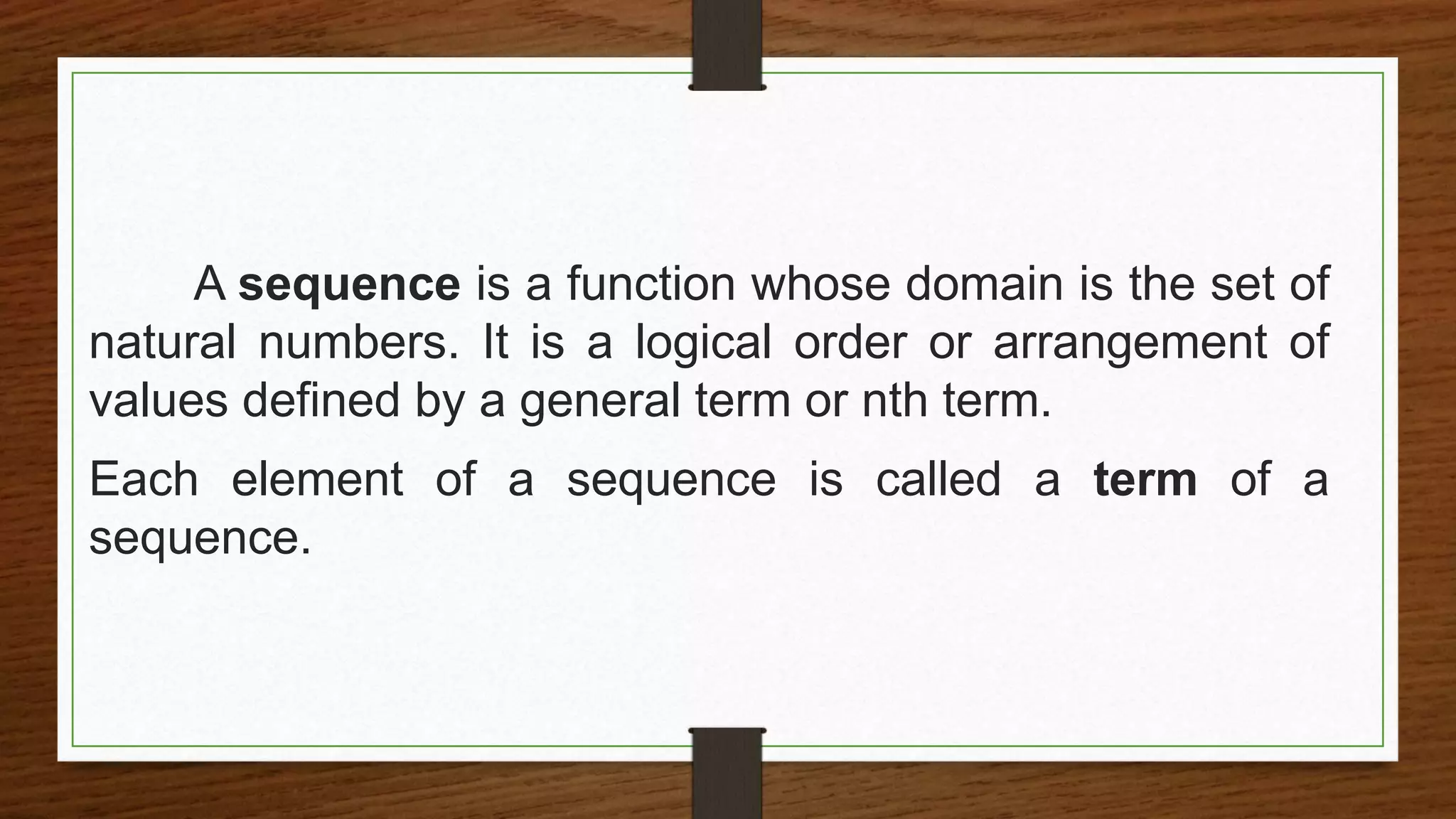
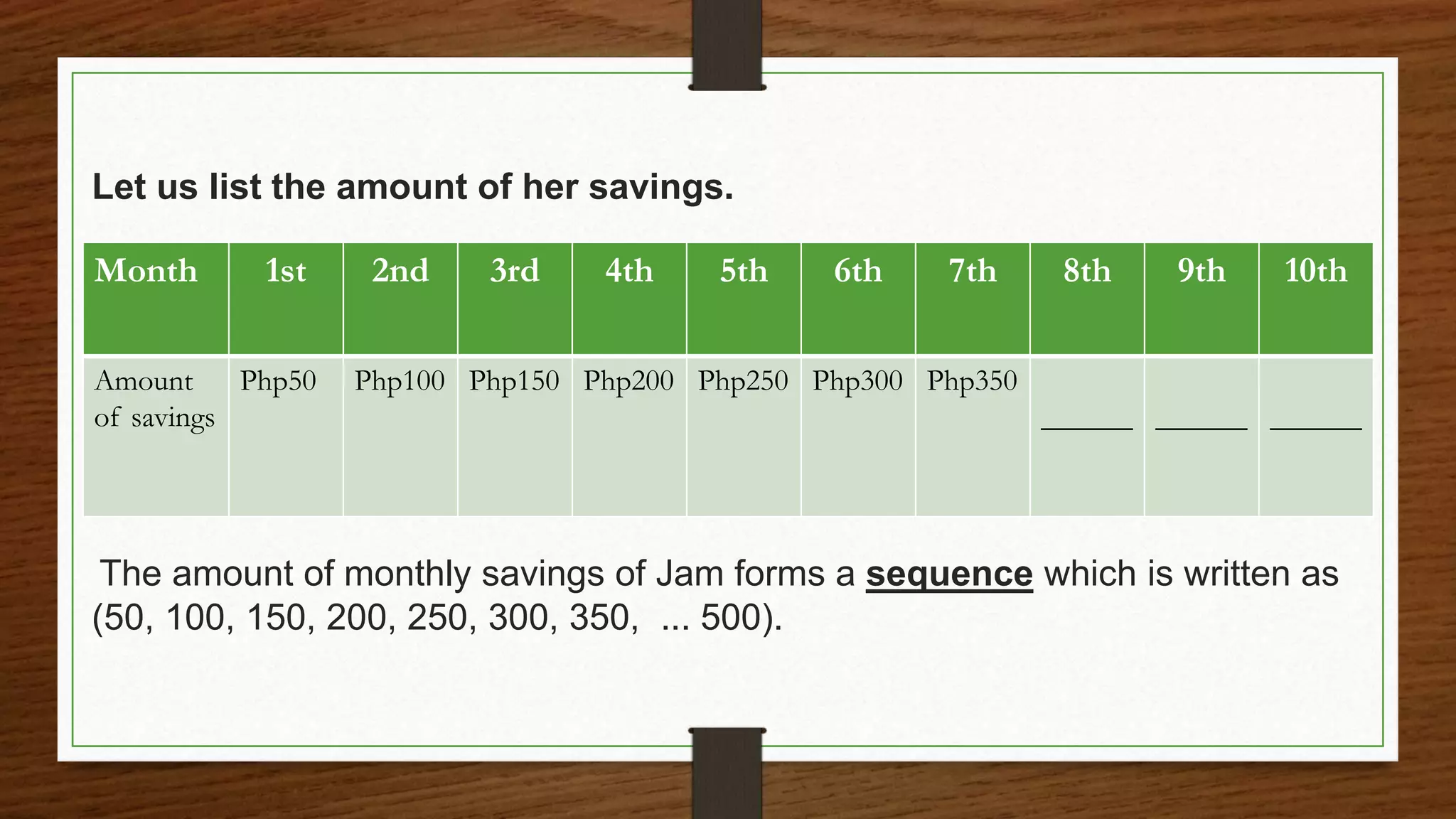
Jam saves increasing amounts of money each month from her allowance. She saves PHP50 the first month, PHP100 the second month, PHP150 the third month, and PHP200 the fourth month. This pattern of increasing savings by PHP50 each month forms a sequence. The question asks how much Jam will save in the tenth month if she continues this pattern of savings.