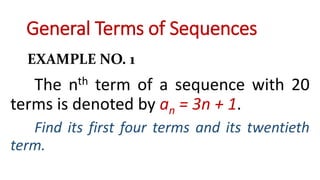
The document defines a sequence as a function whose domain consists of consecutive positive integers starting from 1. Each term is denoted by a(n) where n is the position in the sequence. Sequences can be finite, ending at a set number of terms, or infinite, continuing indefinitely. Examples show common sequences and their terms. The rest of the document provides examples of finding terms of sequences given their general nth term rules and prompts activities to practice finding early terms using stated rules.