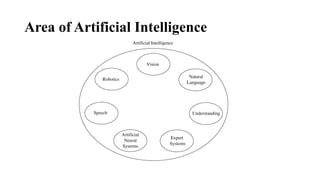
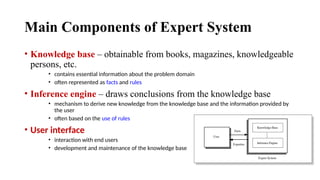
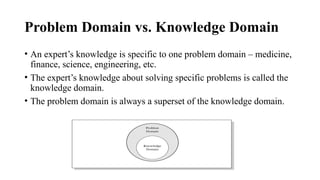
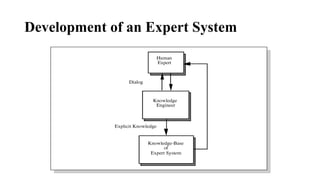
Expert systems are AI programs that replicate human decision-making by using a knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface to solve complex problems through symbolic reasoning. They rely on specific knowledge domains to operate but have advantages like consistent solutions and improved decision-making speed, despite challenges such as high costs and potential errors. Development involves collaboration between domain experts, knowledge engineers, and end-users to build and maintain the system effectively.