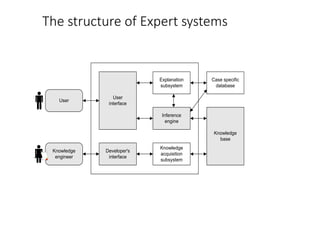
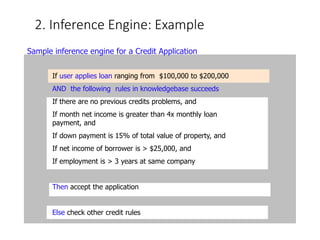
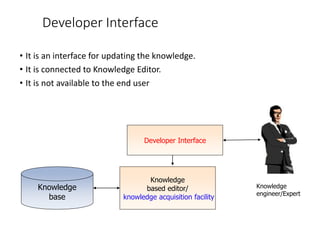
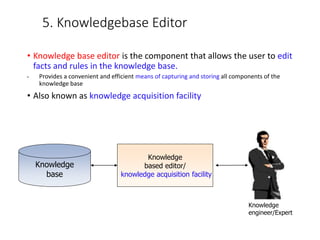
This document discusses expert systems, including definitions, types of knowledge, characteristics, participants in development, structure, and applications. It defines expert systems as attempting to imitate an expert's knowledge and reasoning to solve specific problems. The key components are a knowledge base, inference engine, user interface, and explanation facility. Applications include medical diagnosis, mineral exploration, and natural language interfaces.