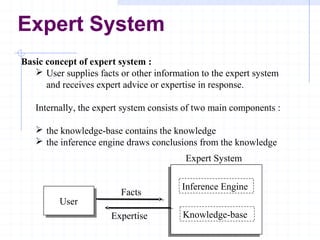
An expert system is an intelligent computer program that uses knowledge and inference procedures to solve problems that require significant human expertise. It consists of a knowledge base containing expertise and an inference engine that draws conclusions. The expert system allows users to input facts to receive expert advice or expertise in response. Expert systems can assist or replace human experts in various fields like accounting, geology, and medicine by making decisions based on stored knowledge. They provide consistent answers but lack common sense and creativity.