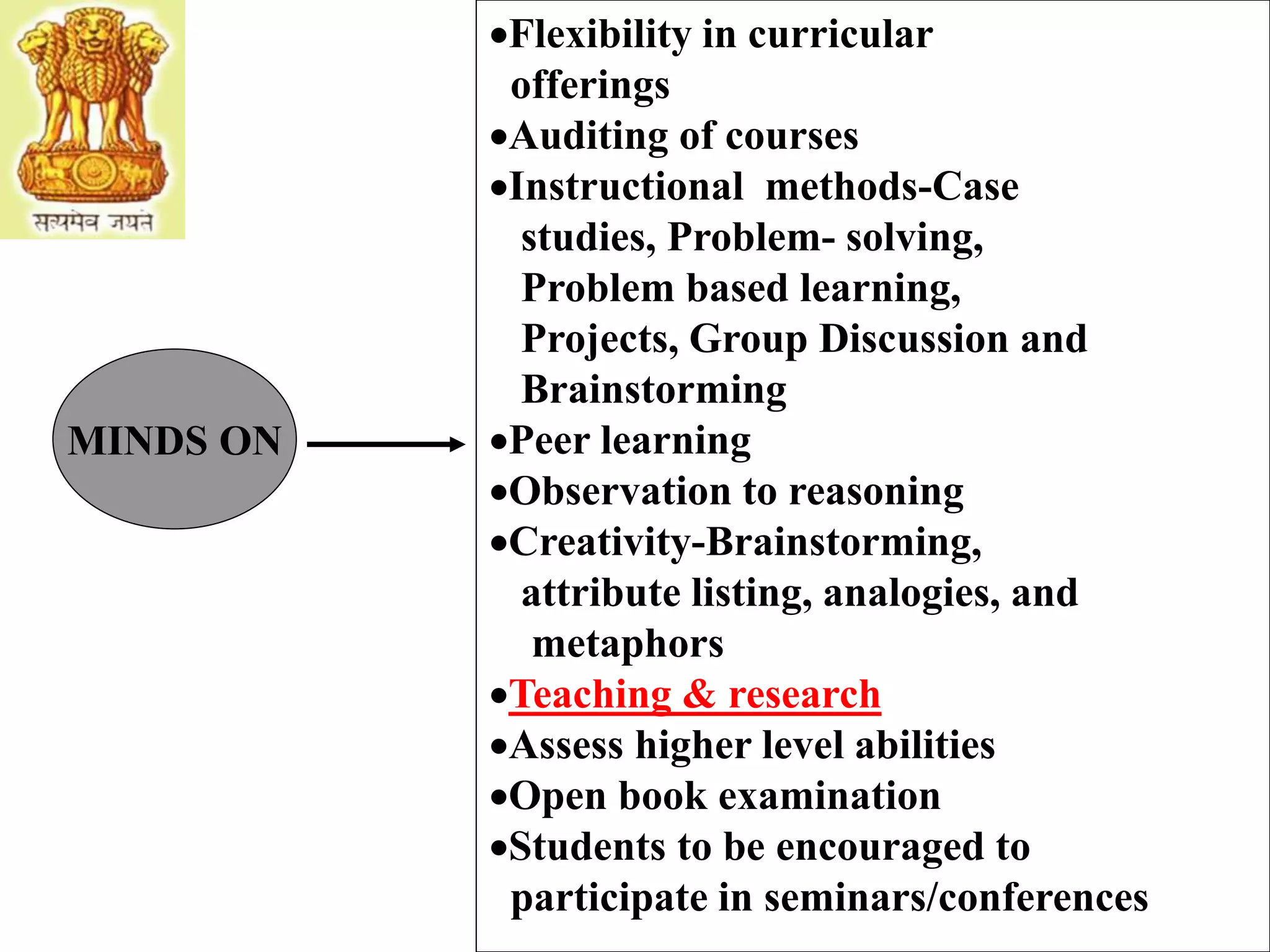
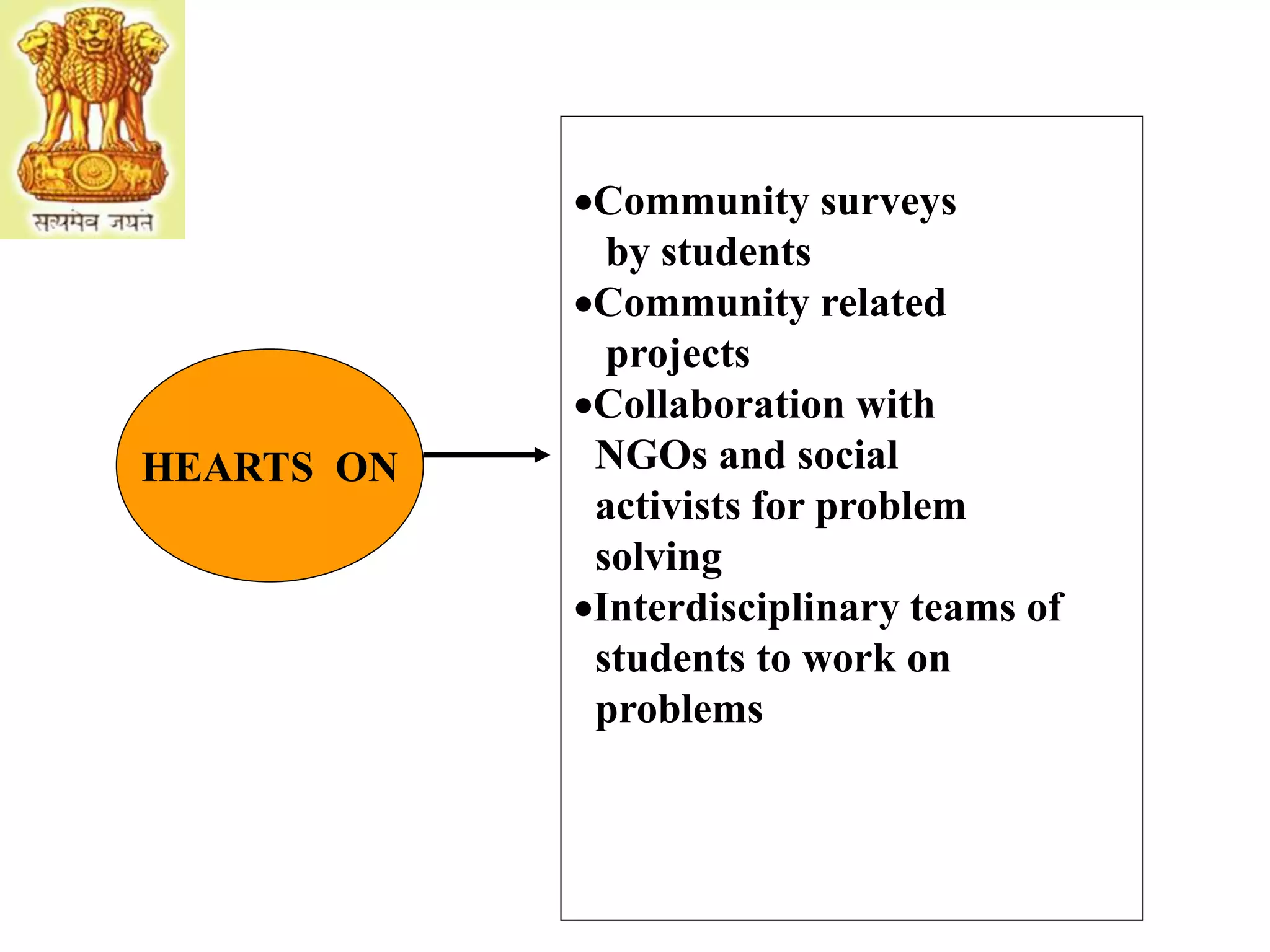
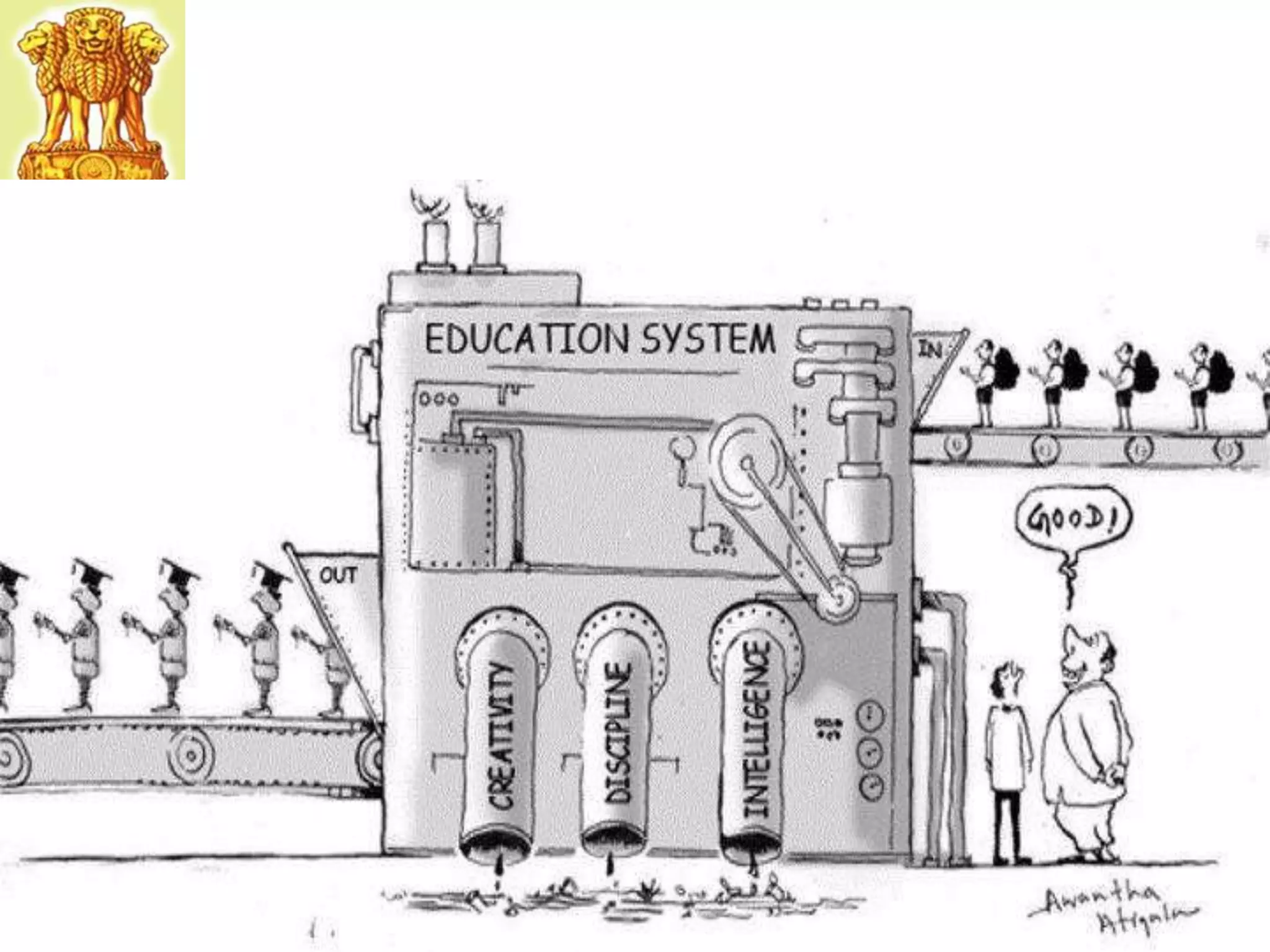
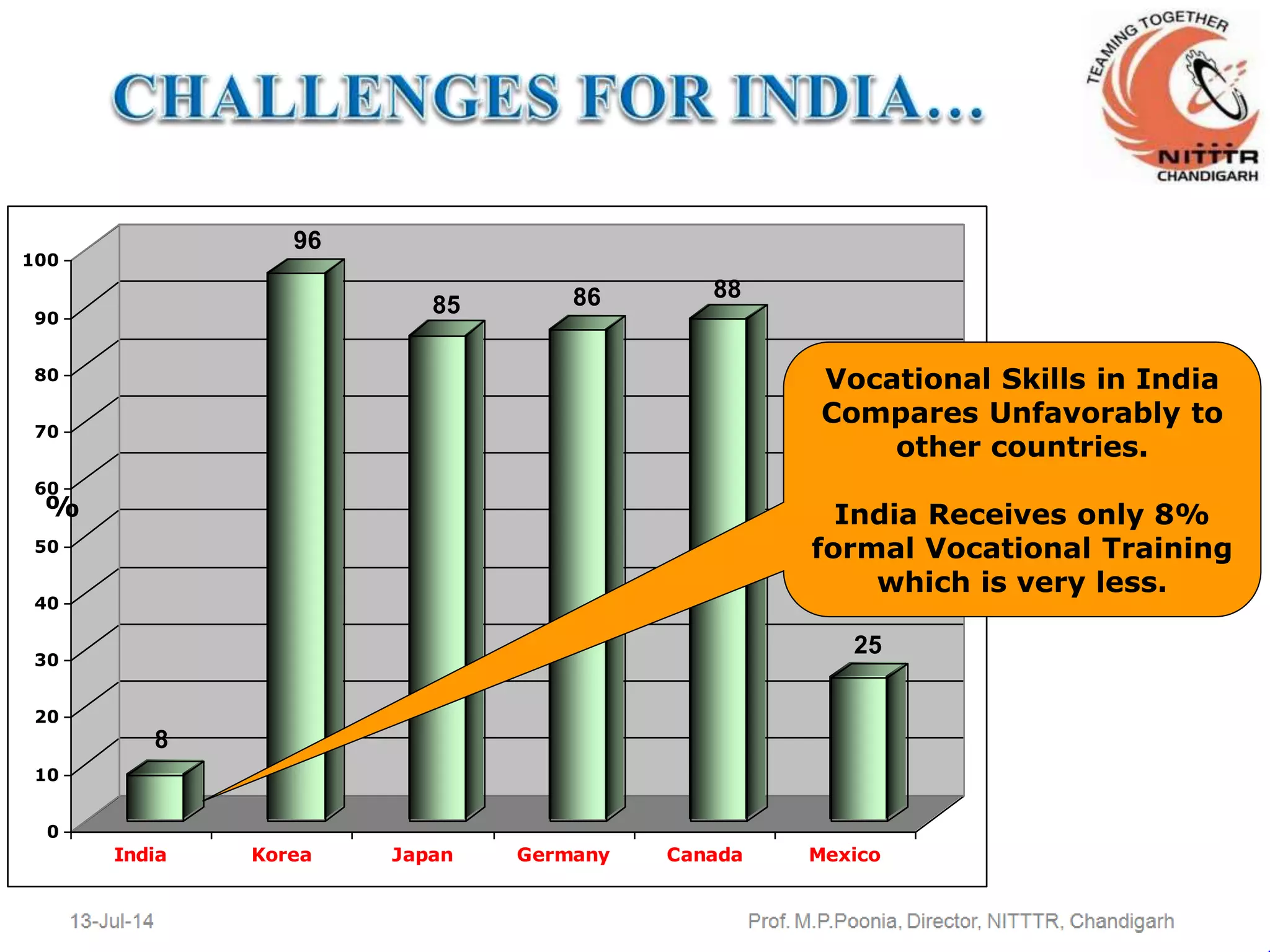
The document discusses the expectations of the industry from technical graduates, highlighting significant gaps in vocational skills and practical knowledge among Indian graduates compared to other countries. It outlines necessary curriculum changes, the importance of industry involvement, and the development of soft skills through collaborative and practical learning experiences. The ultimate goal is to align educational outcomes with industry needs, emphasizing ethics, innovation, and hands-on training.











![Hands
on
Plan-Explore-Practice -Perform
Practical work leading to useful
product
Writing Lab reports in the form
of research papersPankaj_Jindal_Report-
2[1].docx
Laboratories and workshops open for
experimentation
Project work-live problems
Industrial exposure and structured training
Involvement of students in
research and consultancy services
undertaken by faculty
Competitions
Strengthening of Laboratories
Setting up of Labs with assistance
from industry
Industry-academia exchange](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paneldiscussion-150123104357-conversion-gate01/75/expectation-of-industries-from-technical-graduates-17-2048.jpg)