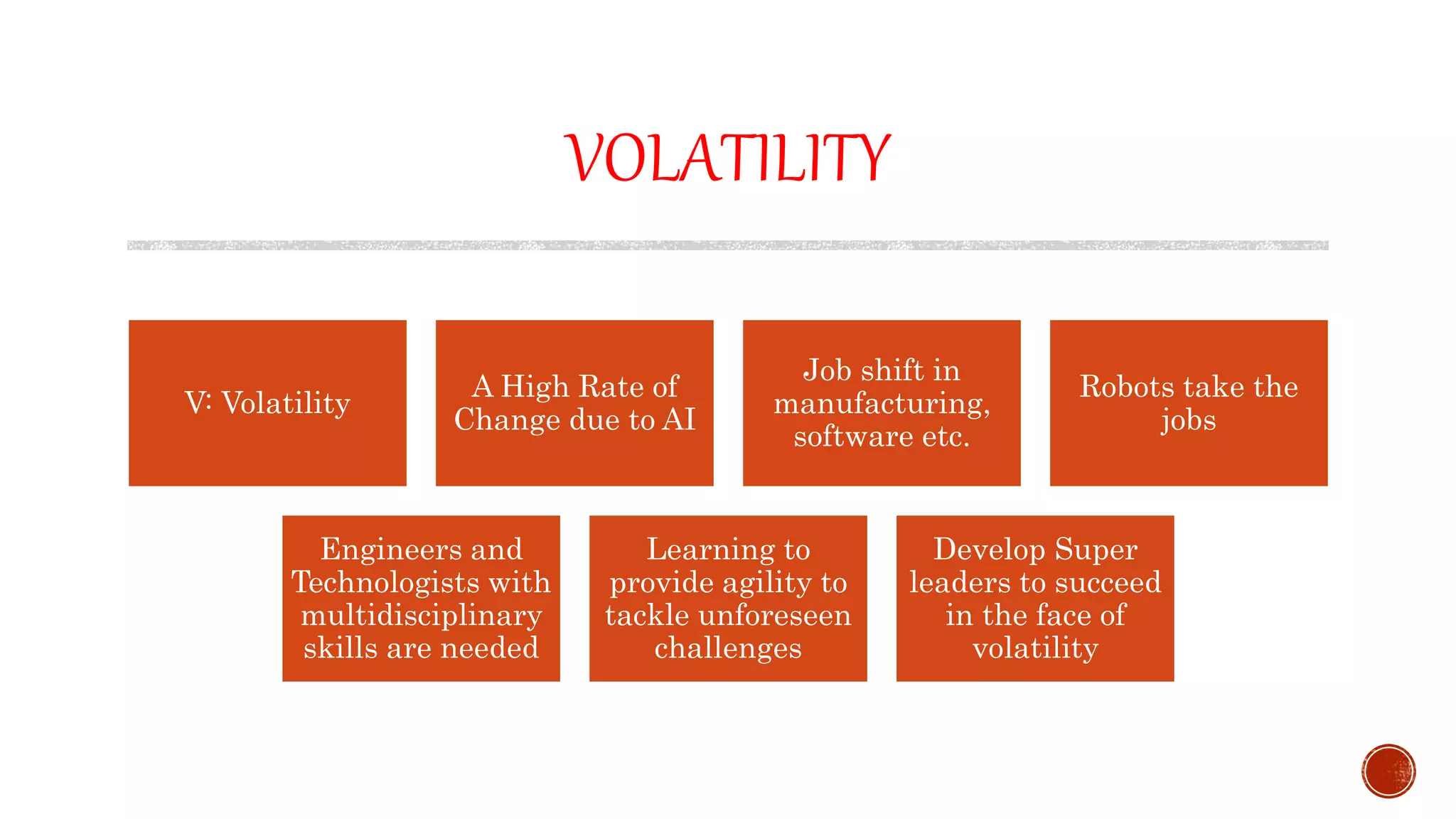
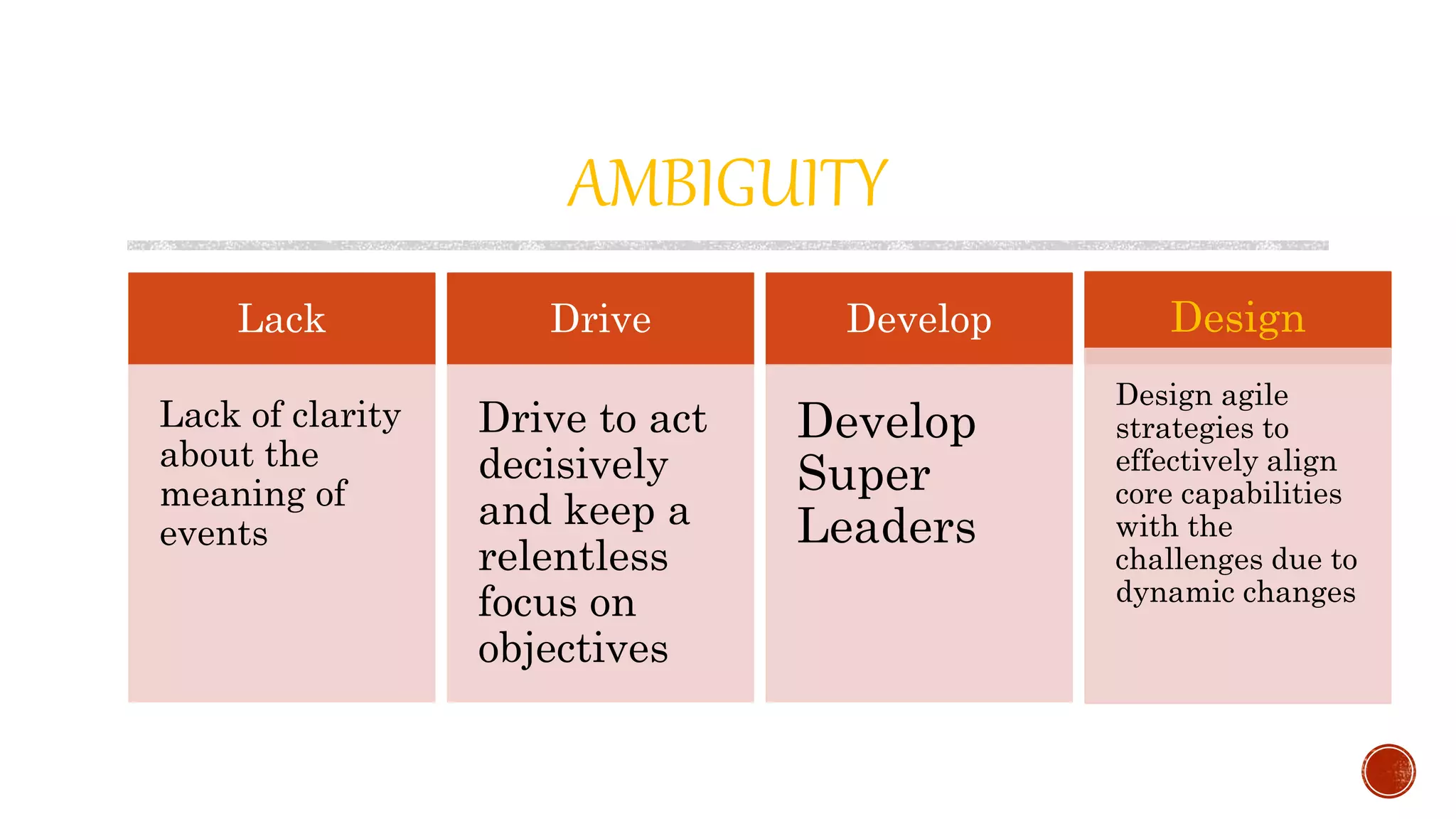
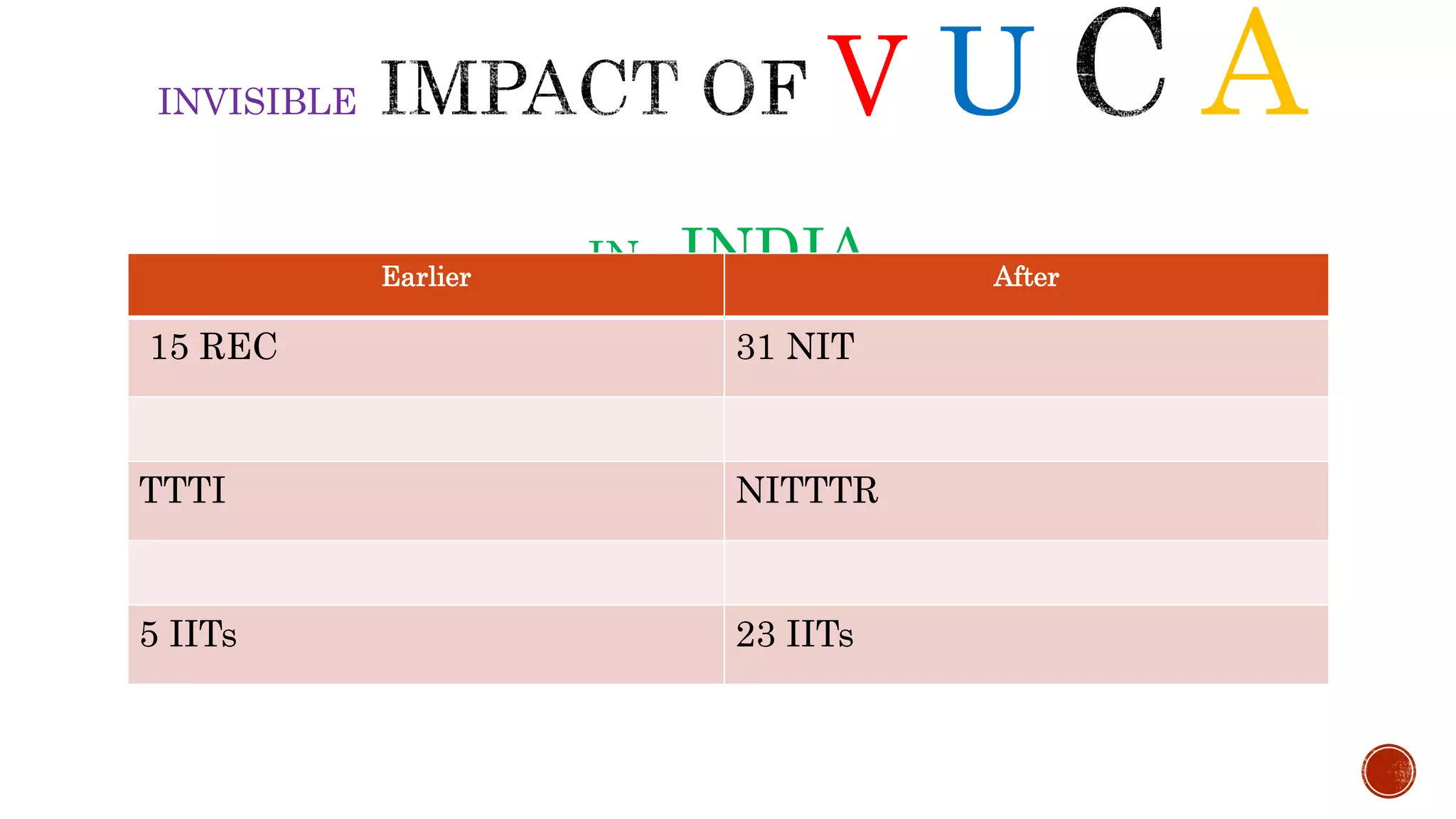
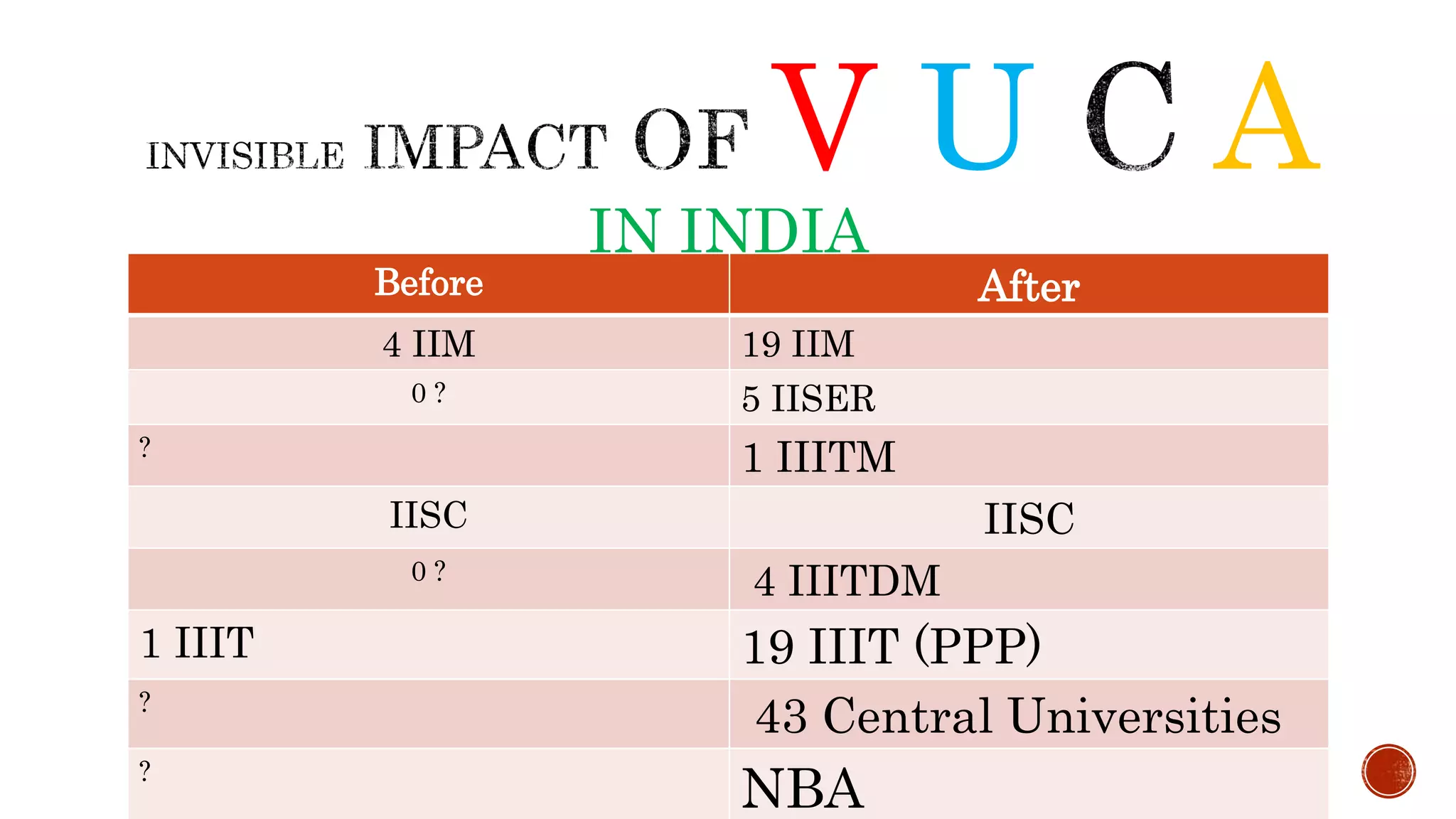
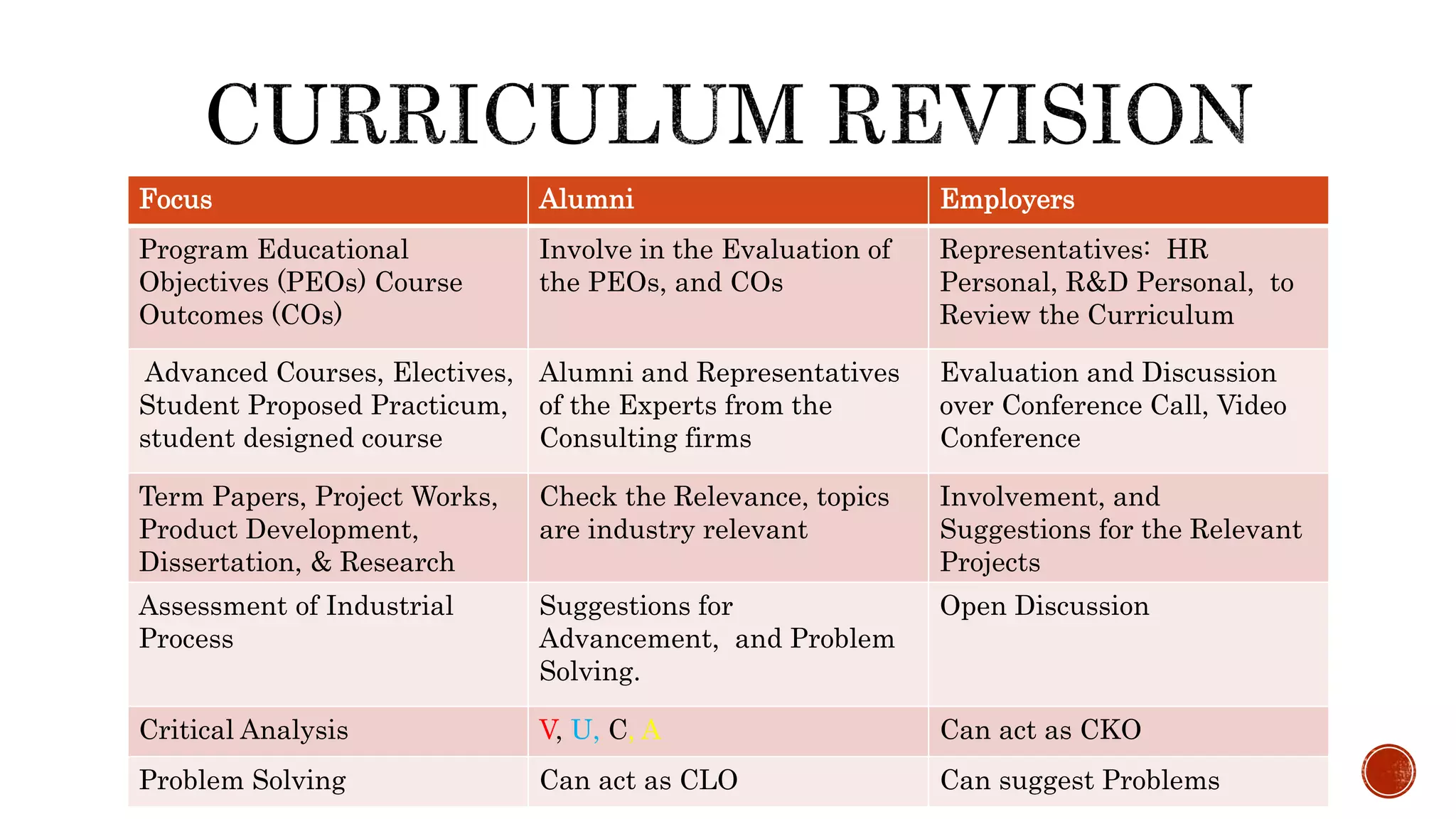
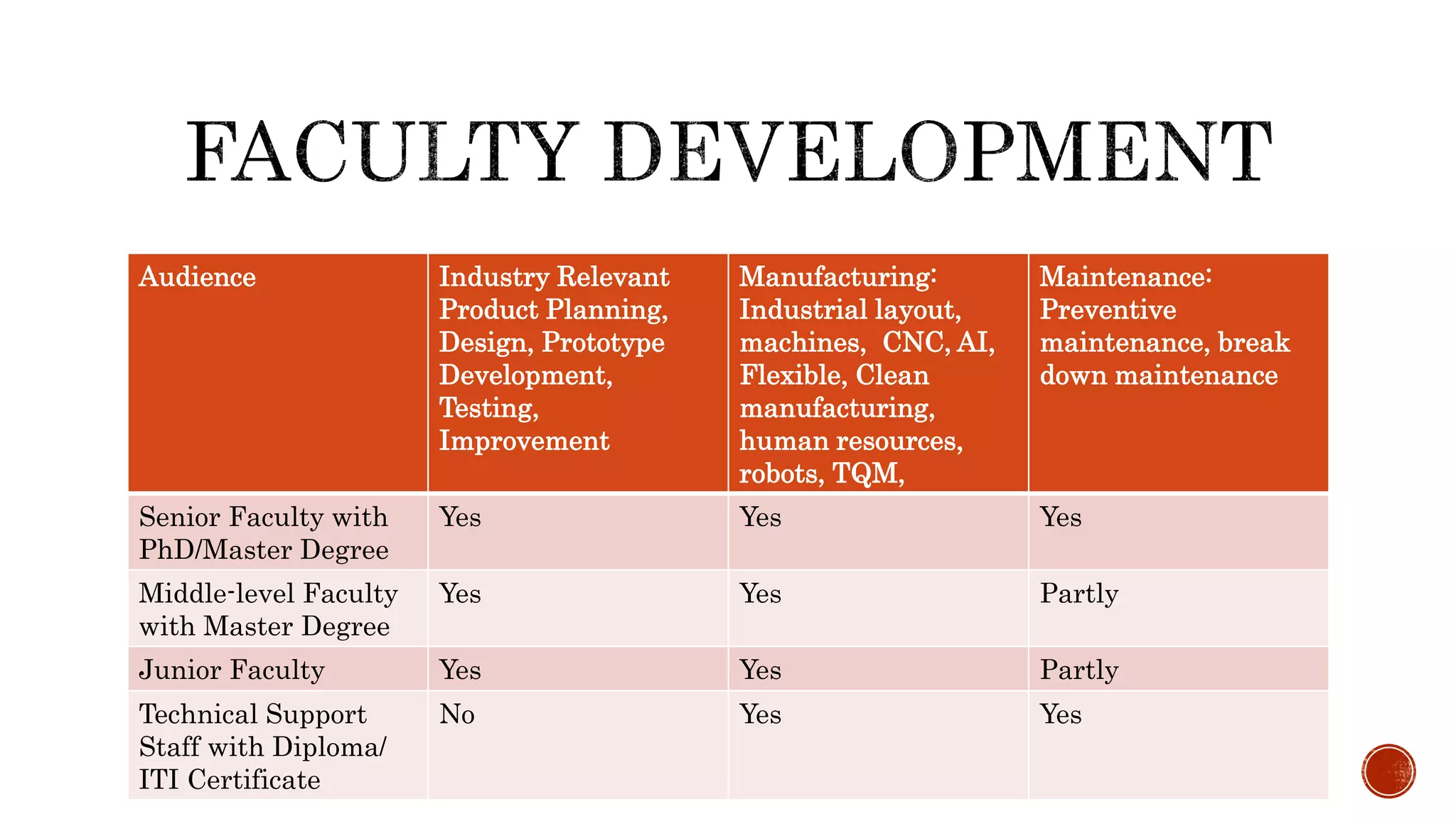
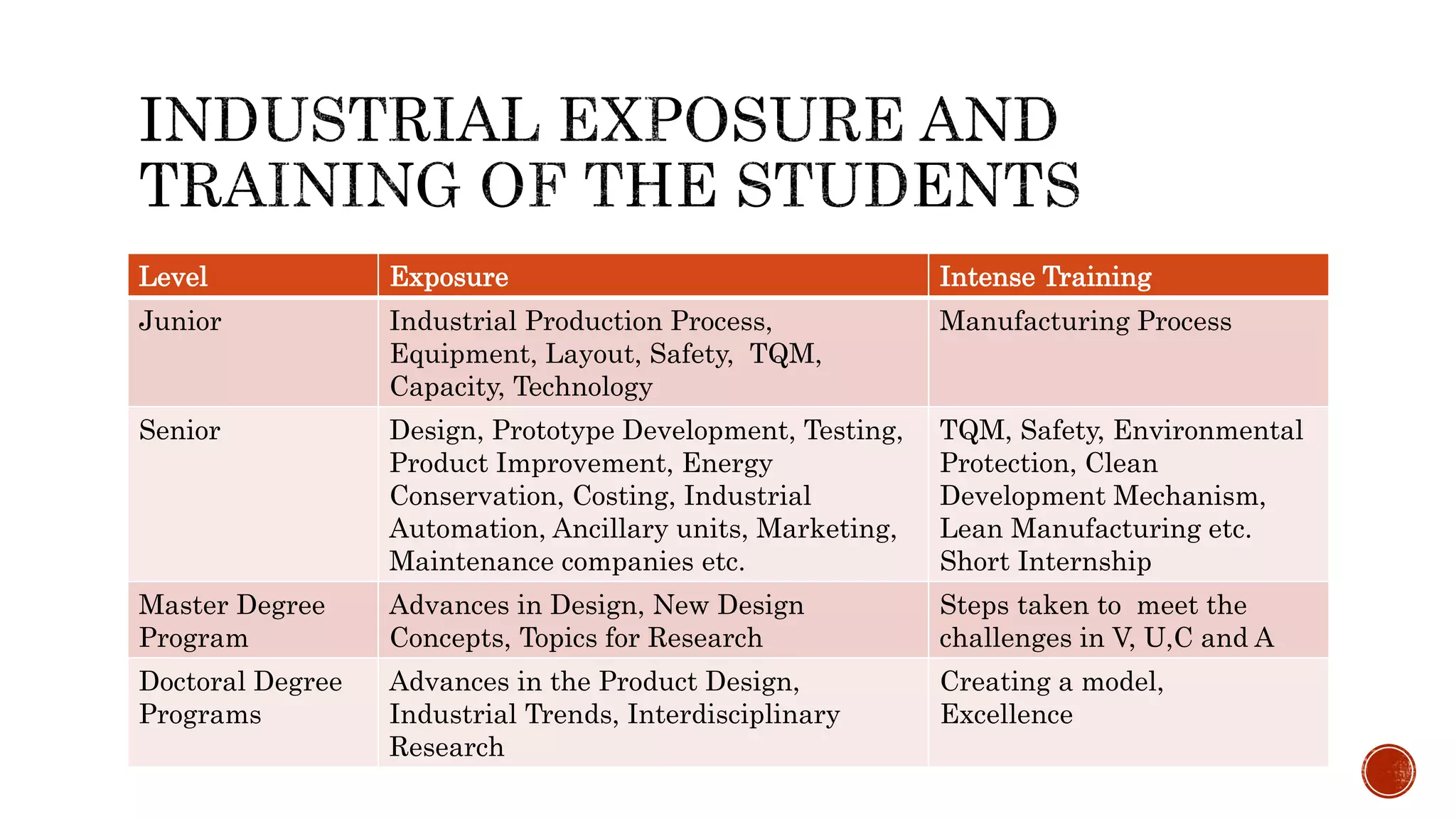
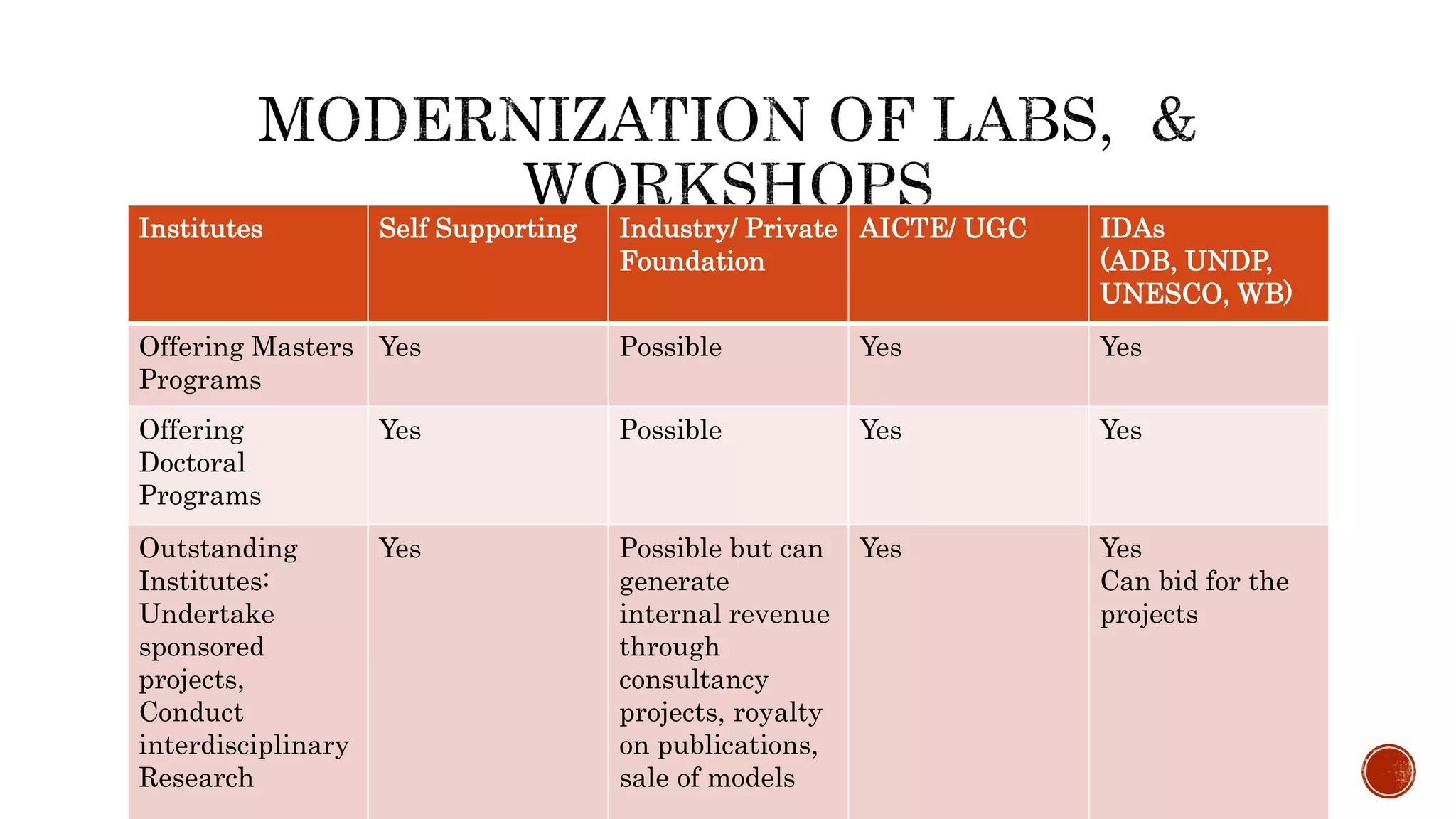
The document discusses the need for transformation in engineering education to address the challenges of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity (VUCA) in the job market, emphasizing the importance of multidisciplinary programs and agile leadership. It outlines strategies for educational leaders to develop competencies, innovate curricula, and align with global trends to better prepare graduates for a dynamic environment. Recommendations include fostering collaboration between educational institutions and industry to create relevant training and skill development opportunities.