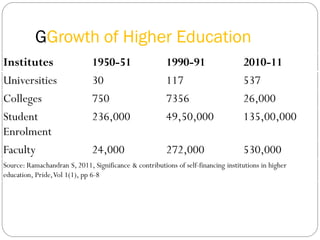
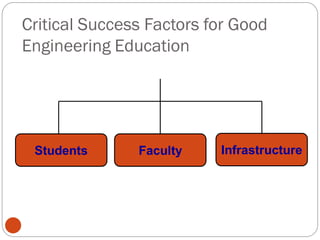
The document discusses the challenges and imperatives in engineering education, emphasizing the need for quality improvements driven by globalization, student and industry expectations. It highlights the weaknesses of current graduates and the essential skills they must possess, such as technical capability, communication, and teamwork. Key issues include faculty development, laboratory enhancements, industry linkages, and preparing students for employability in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.