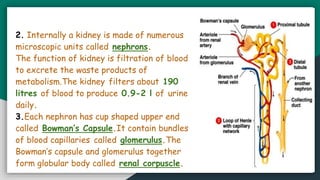
Excretion is the removal of waste products resulting from metabolic activities, essential for all organisms, utilizing specialized organs in multicellular species. In humans, the excretory system comprises kidneys, ureters, the urinary bladder, and urethra, and processes around 190 liters of blood to produce 0.9-2 liters of urine daily through filtration and reabsorption in nephrons. Different organisms exhibit various excretion modes, such as ammonotelism, ureotelism, and uricotelism, adapting their processes based on environmental conditions.