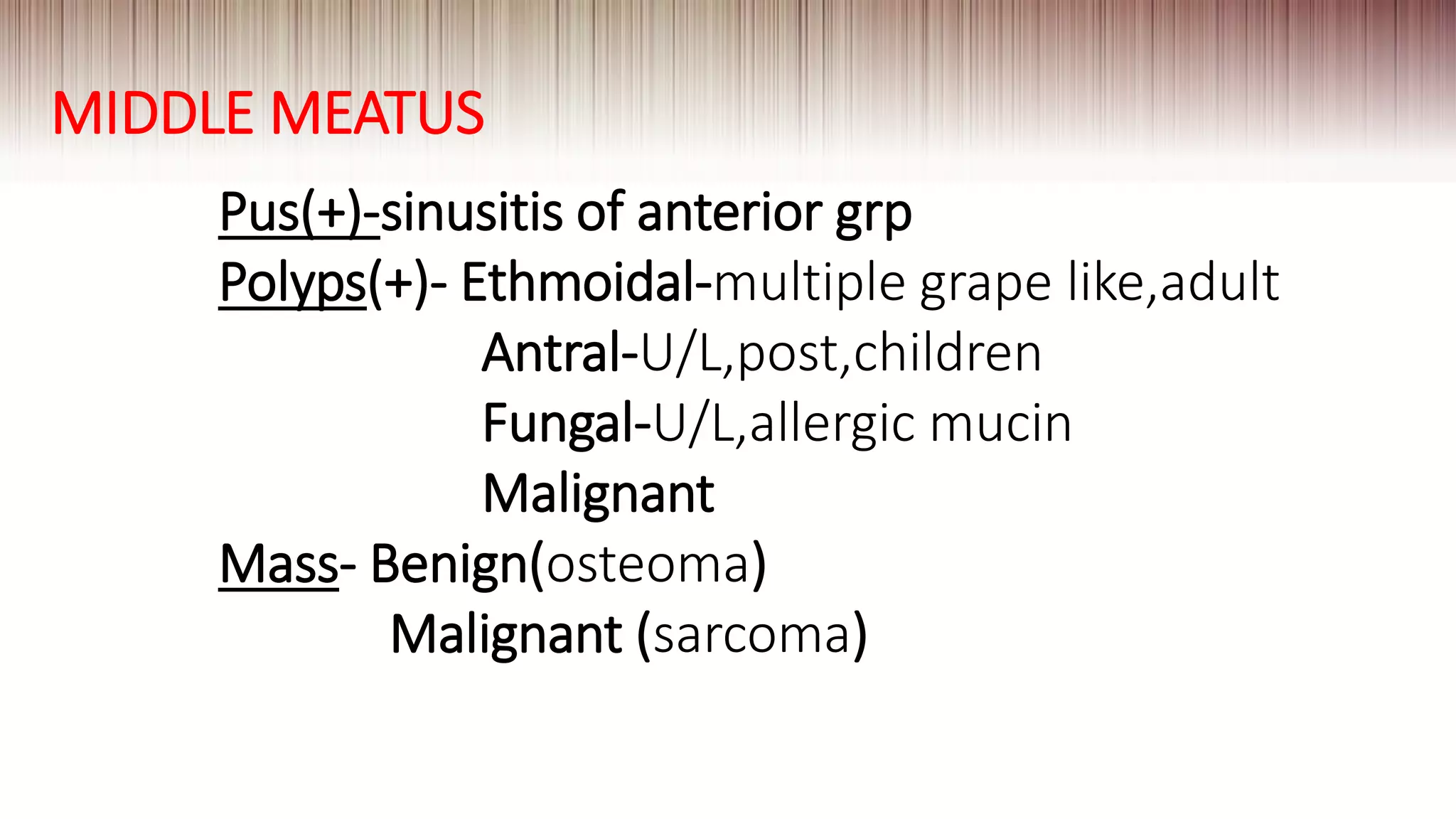
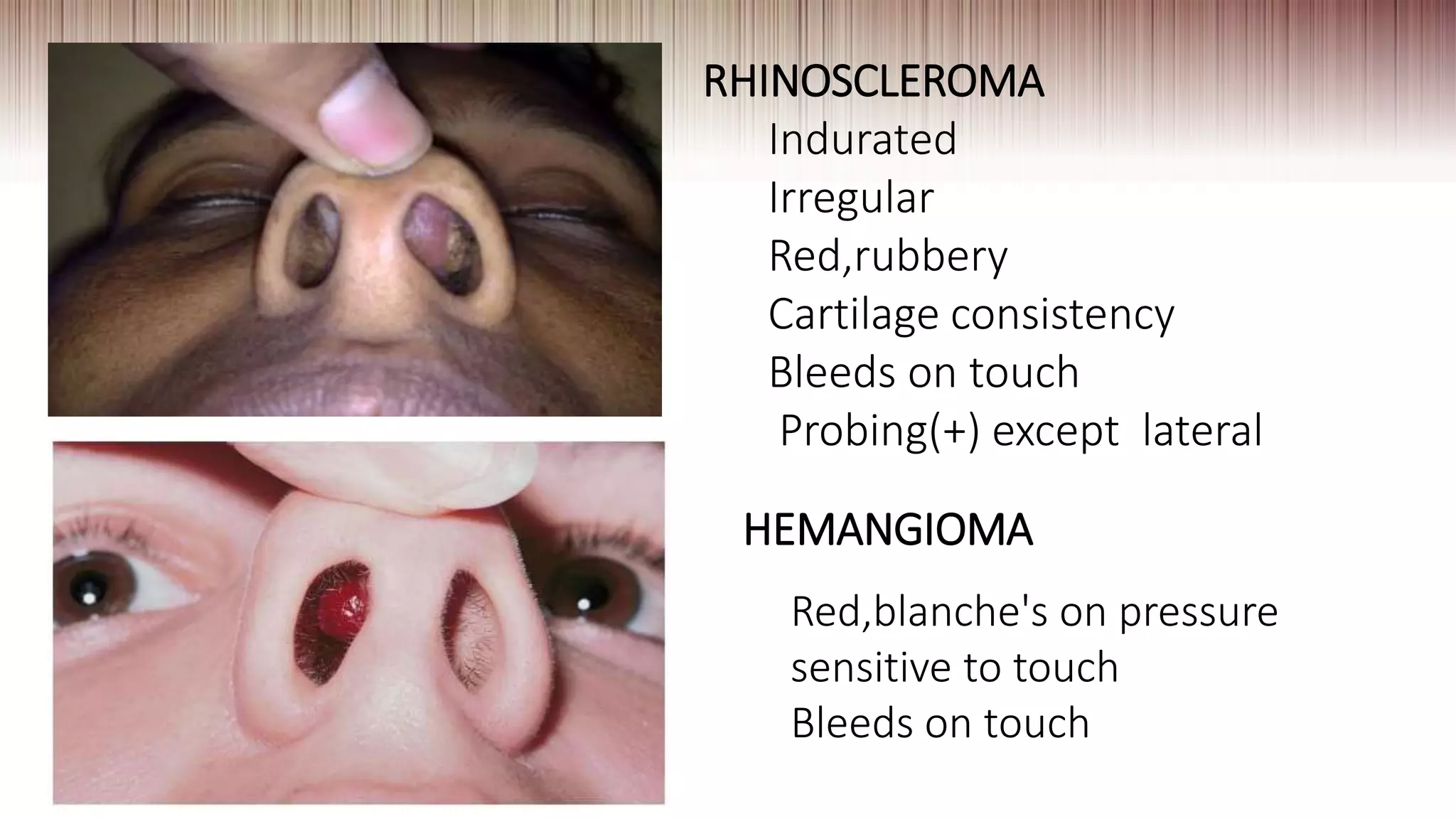
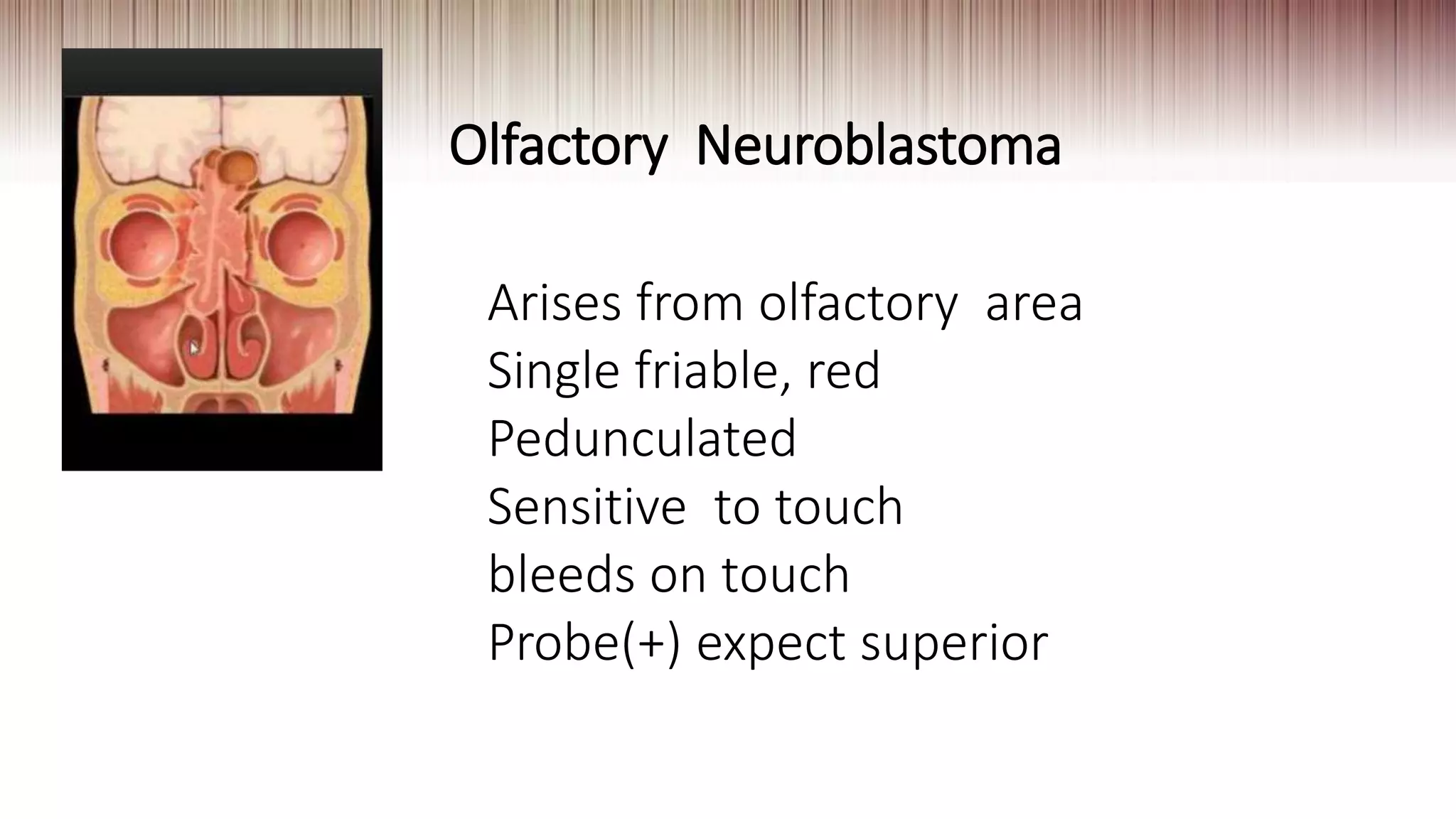
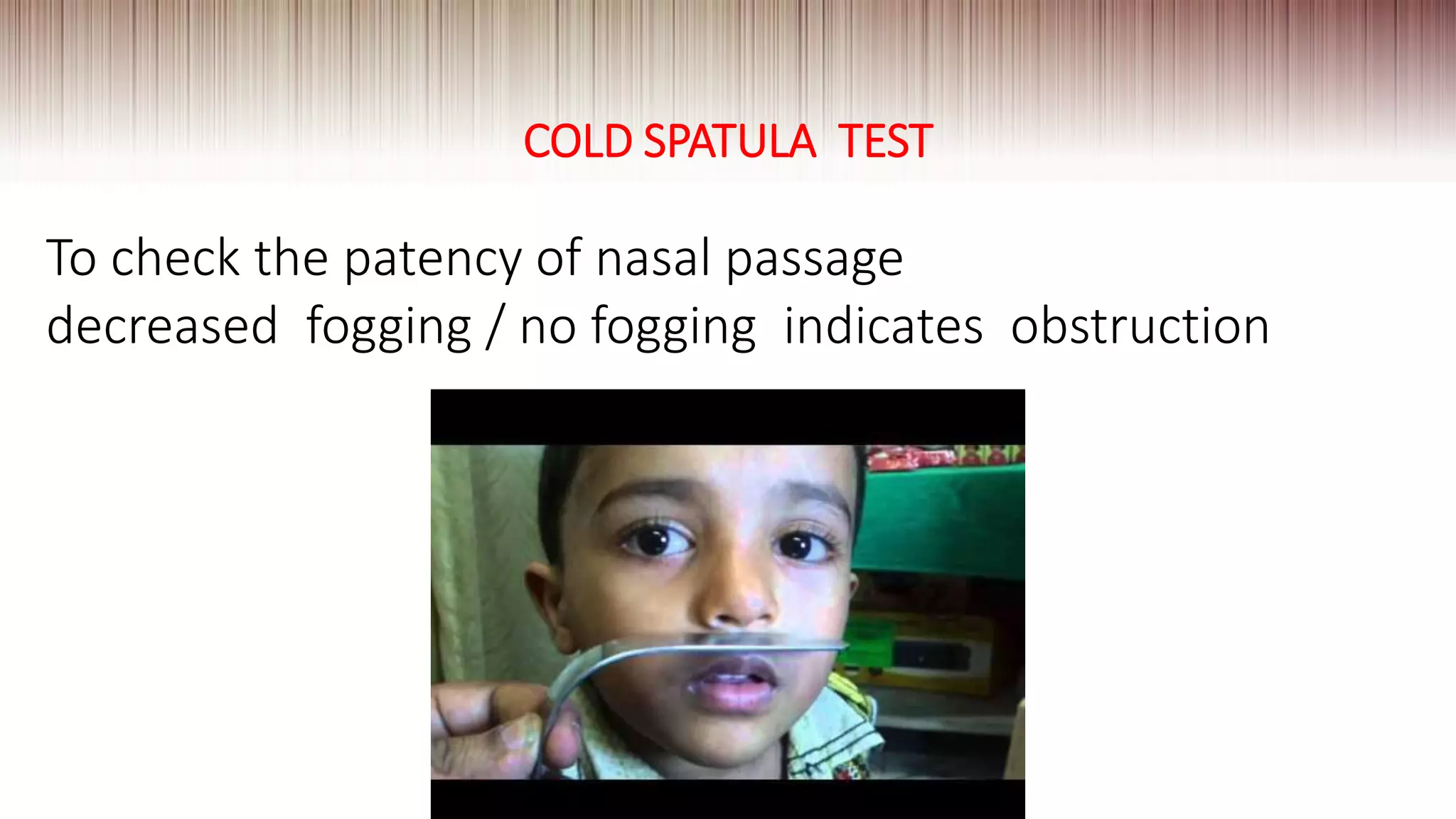
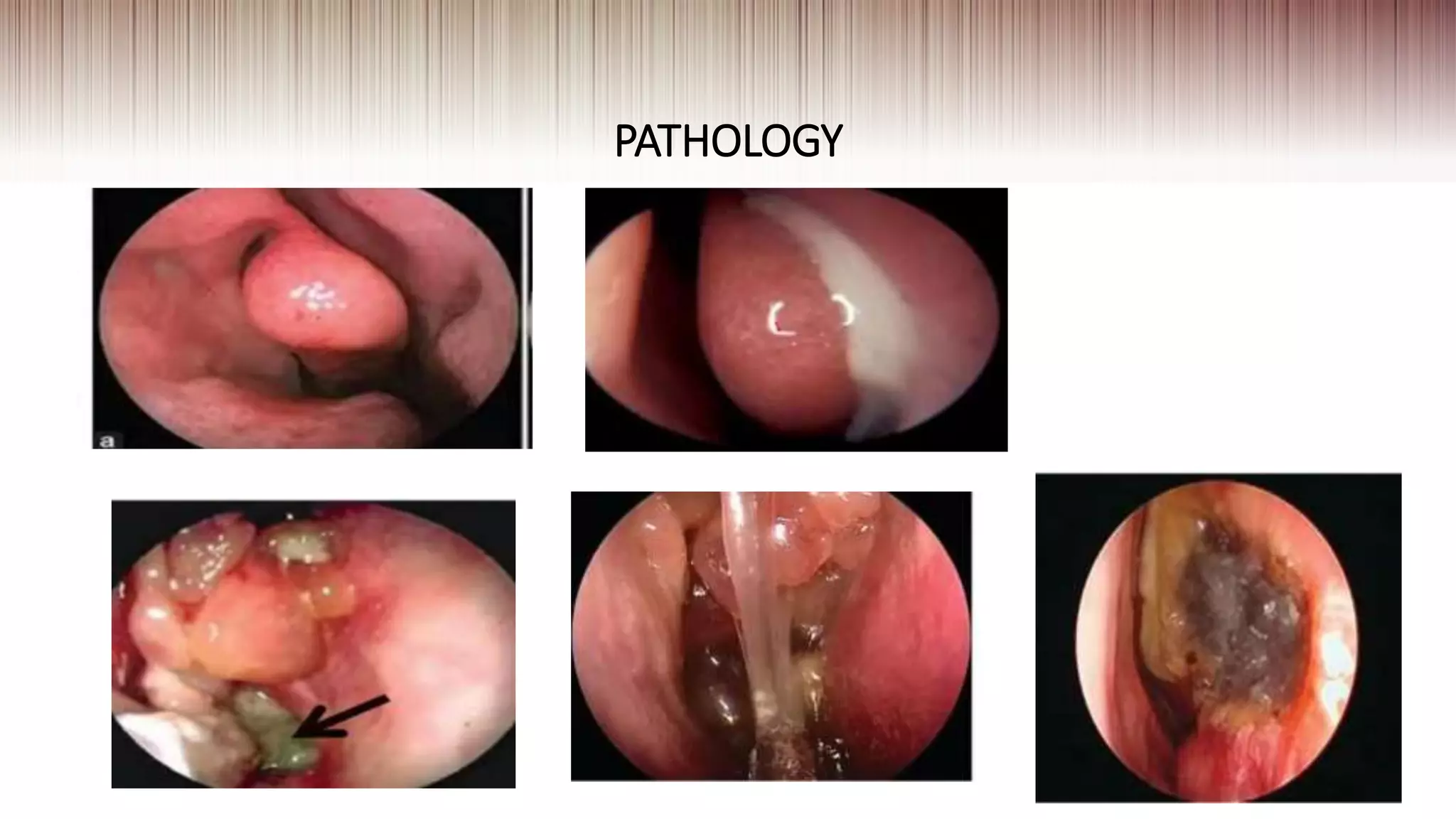
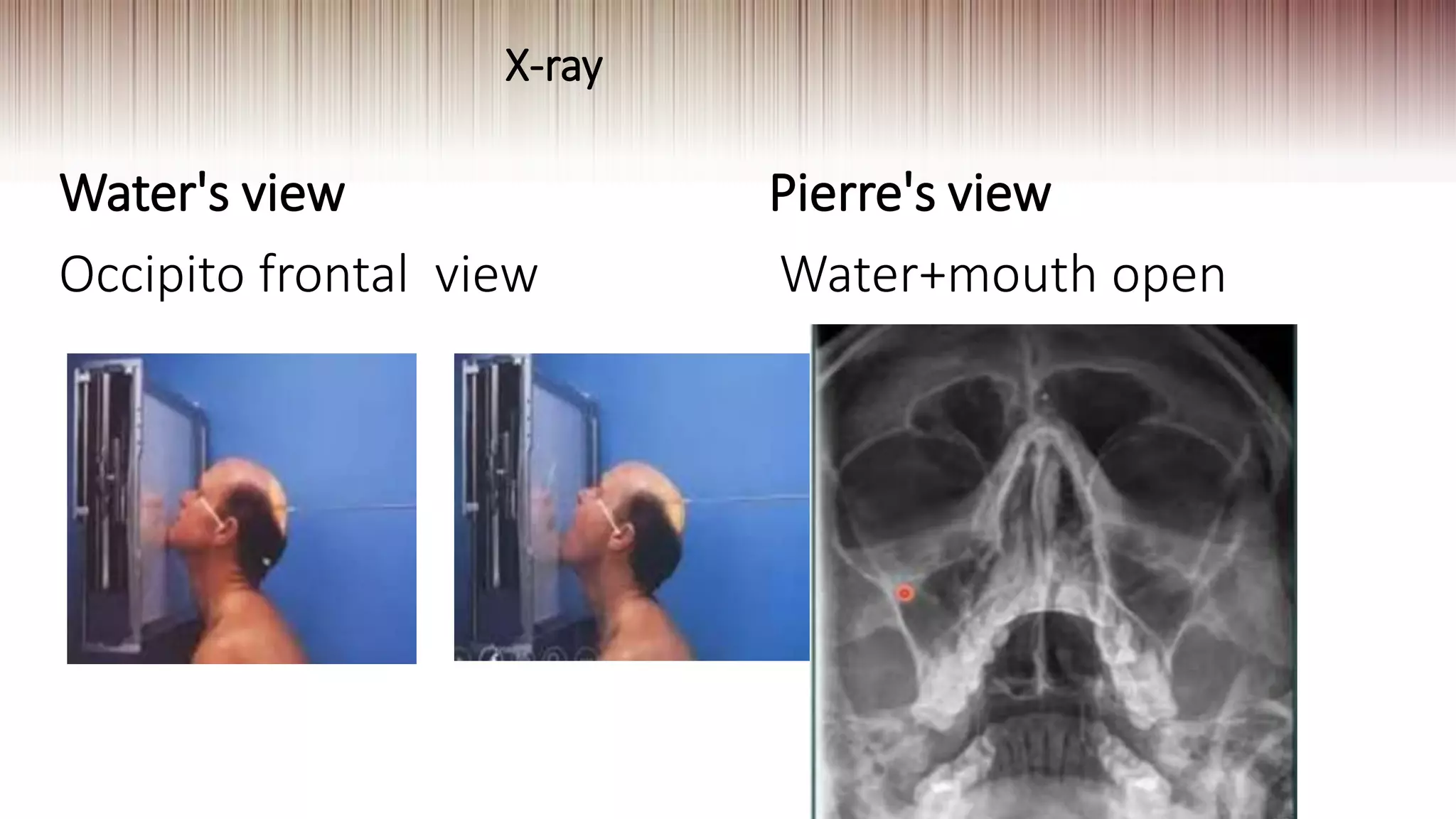
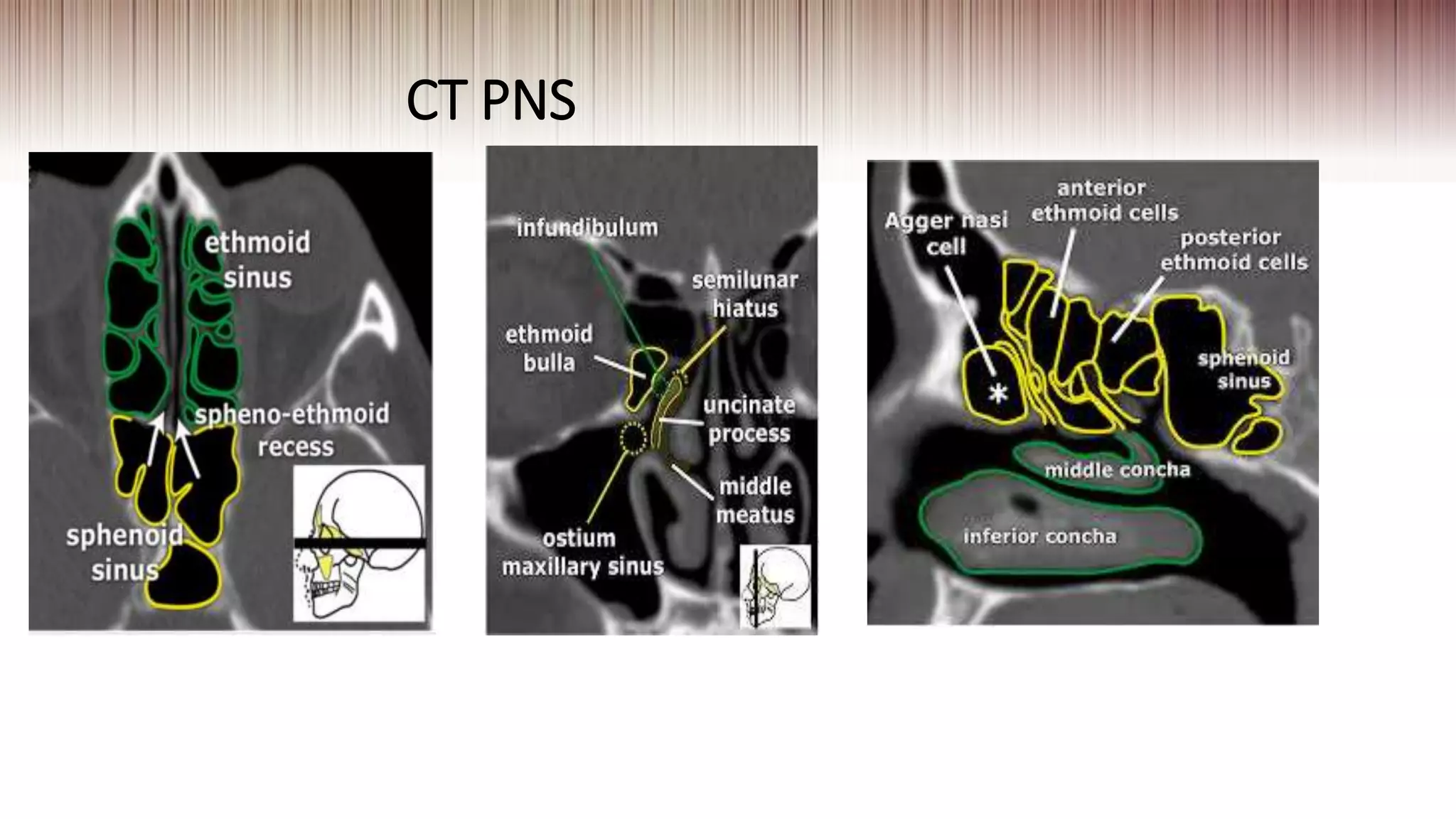
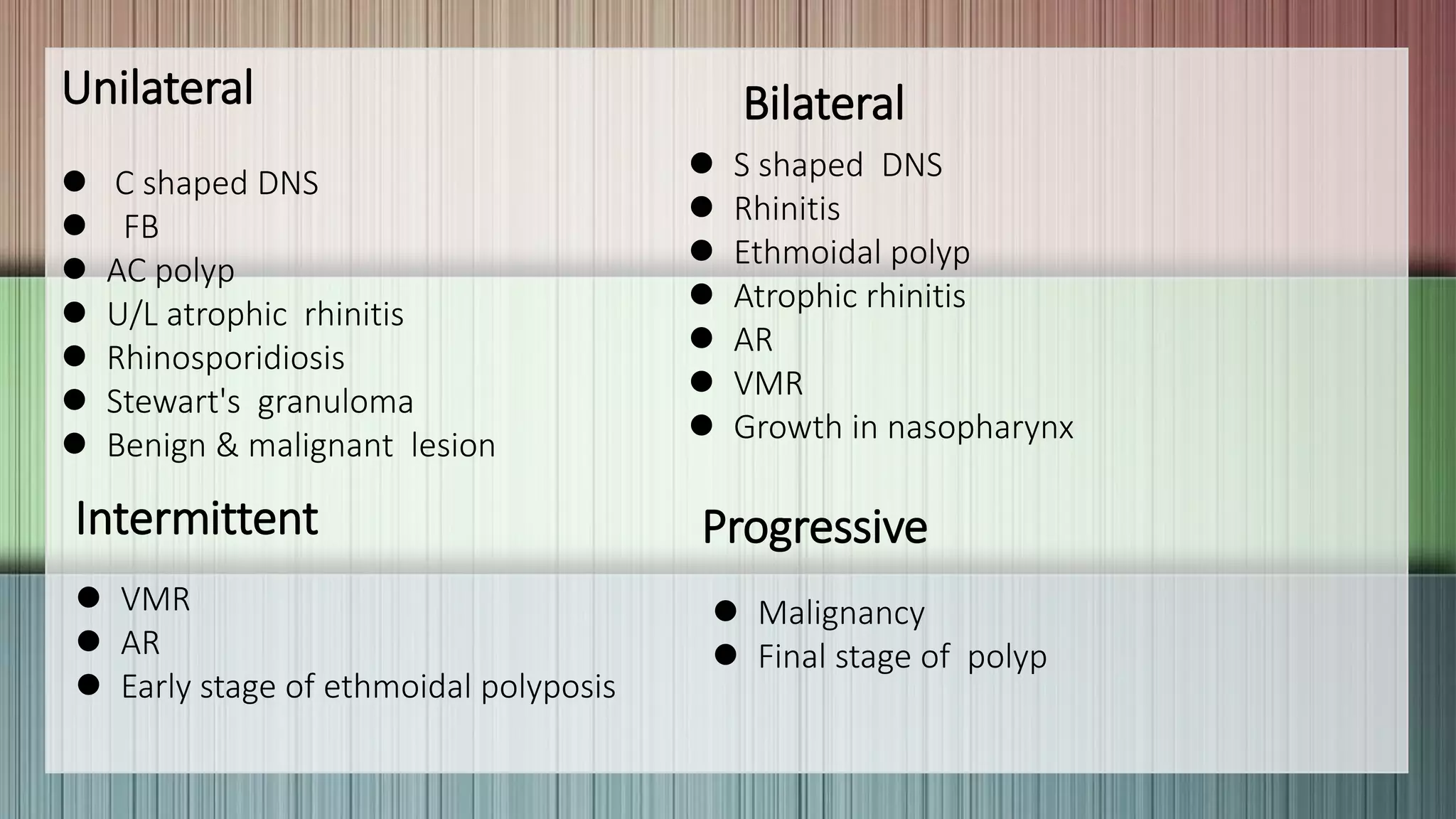
This document provides guidance on clinically evaluating the nose. It outlines the key steps including taking a thorough patient history, performing a general examination, and conducting a local examination of the nose. The local examination involves anterior and posterior rhinoscopy to inspect the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses. Potential abnormalities are described. Recommended blood investigations and radiological imaging include a CBC, sinus CT, and tests for underlying conditions. The goal is to arrive at an accurate diagnosis by combining the clinical findings with investigation results.



































![MIDDLE TURBINATE:
Hypertrophied- concha bullosa
Types1.Inferior[bulbous]
2.superior[lamellar]
3.Extensive type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/examofnosepg-201112183528/75/Exam-of-nose-pg-42-2048.jpg)