This document discusses sinonasal tumours, including:
1. It classifies sinonasal tumours by tissue of origin such as epithelial, neuroendocrine, soft tissue, bone, etc. and lists examples of benign and malignant lesions within each tissue.
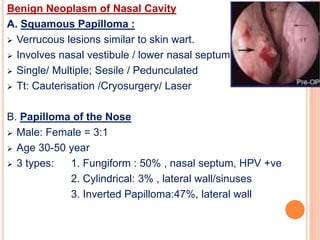
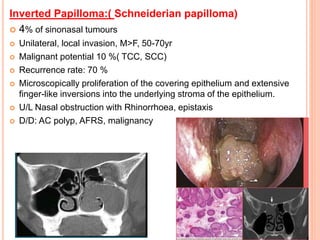
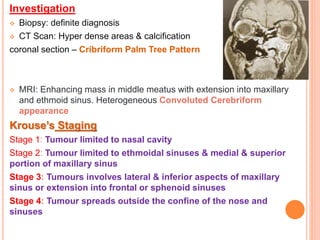
2. It provides details on specific benign tumours such as inverted papilloma, haemangioma, and juvenile angiofibroma.
3. It also discusses malignant tumours of the sinonasal region like squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma and haemangiopericytoma.