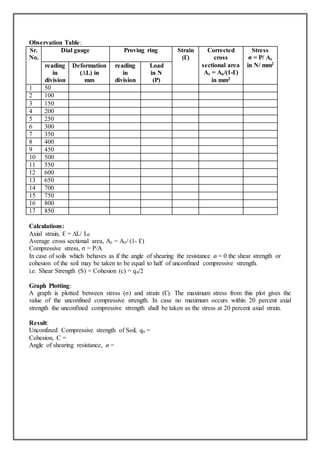
1) The experiment determines the unconfined compressive strength (qu) of soil, which is the maximum load per unit area at which an unconfined cylindrical soil specimen fails during compression testing.
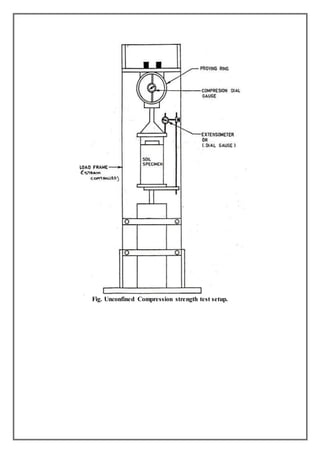
2) A cylindrical soil specimen is prepared at optimum moisture content and maximum dry density, and compressed axially between loading plates at a controlled strain rate while measuring load and deformation.
3) The stress-strain curve is plotted, and qu is taken as either the peak stress or stress at 20% axial strain. Shear strength S of the soil is then calculated as qu/2, assuming the soil's angle of shearing resistance φ is 0.