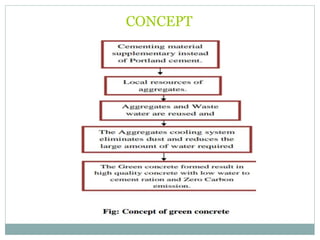
This document provides an overview of green concrete, which is a more sustainable type of concrete made with recycled and waste materials. It discusses how green concrete uses materials like recycled demolition waste, fly ash, and quarry dust as partial substitutes for cement, making production more eco-friendly while remaining comparable in cost. The document outlines the objectives, advantages, disadvantages and applications of green concrete, and provides examples of previous literature on the topic. It concludes that green concrete has significant potential to reduce environmental impacts compared to traditional concrete, while remaining economically viable.










![REFERENCE
[1]CHIRAG GARG & AAKASH JAIN 2014 ''green concrete: efficient &
eco-friendly construction materials."international journal of
research in engineering & technology (impact: ijret) issn(e): 2321-
8843;issn(p): 2347-4599vol. 2, issue 2, feb 2014, 259-264
[2]MS. MONICA C. DHOKA 2013"green concrete: using industrial
waste of marble powder, quarry dust and paper pulp”international
journal of engineering science inventionissn (online): 2319 – 6734,
issn (print): 2319 – 6726www.ijesi.org volume 2 issue 10ǁ october
2013 ǁ pp.67-70](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greenconcrete-200318113056/85/Green-concrete-14-320.jpg)
![[3]PANDEYSHIVAM,ETAL 2017, a review on the study of
green concrete,issn: 2350-0328international journal of advanced
researchinscience,engineeringandtechnologyvol.4,issue7,july201
7
[4]SHWETAMBARA VERMA,2012,green concrete – an
emerging trend in india,eedings of international conference on
advances in architecture and civil engineering (aarcv 2012), 21st
–23rd june 2012 paper id sam101, vol. 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greenconcrete-200318113056/85/Green-concrete-15-320.jpg)
