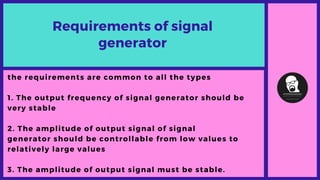
A signal generator is a test equipment that produces electrical signals in waveforms, used in the design, testing, and servicing of electronic devices. The document discusses the purpose, requirements, types, and applications of signal generators, highlighting their stability in output frequency and amplitude control. Types include function generators, RF and microwave generators, and arbitrary waveform generators.