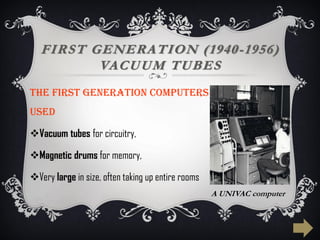
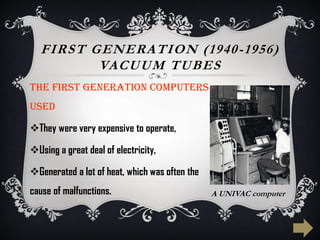
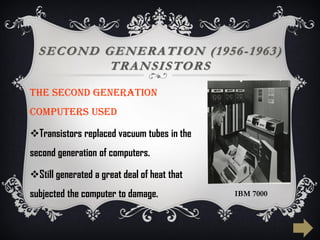
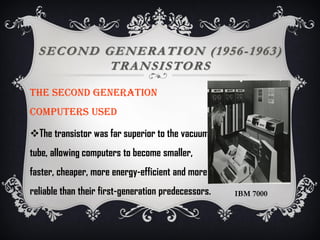
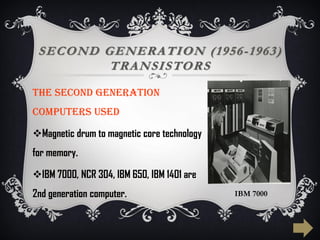
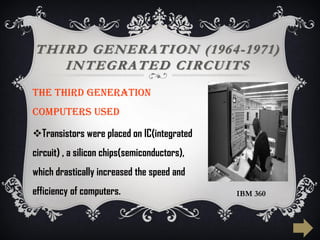
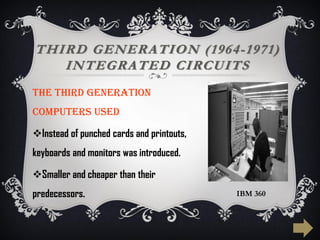
The document summarizes the five generations of computer evolution from 1940 to present day. The first generation used vacuum tubes, were room-sized, and relied on punched cards. The second generation used transistors, were smaller but still generated heat. The third generation used integrated circuits, were smaller and cheaper with keyboards/monitors. The fourth generation used microprocessors on a single chip, could be networked, and developed many programming languages. The fifth generation aims to develop artificial intelligence with natural language and learning capabilities.