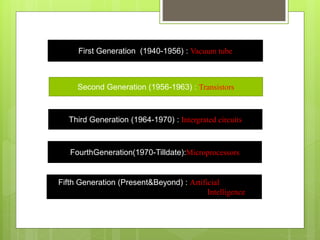
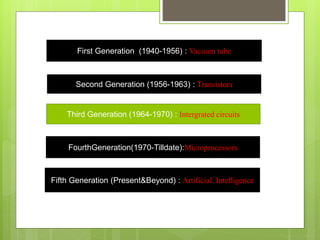
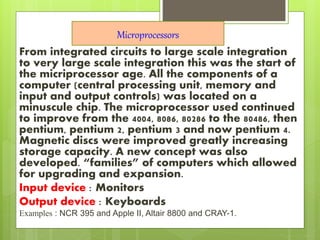
The document summarizes the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. The first generation used vacuum tubes. The second generation used transistors, which were smaller and faster. The third generation used integrated circuits, allowing for more applications. The fourth generation began the microprocessor age where all components were on a single chip. Current and future generations aim to develop artificial intelligence through techniques like expert systems, parallel processing and human behavior simulation.