Topical medications are applied directly to the skin and are designed to achieve high drug concentrations in the skin with minimal systemic exposure. Some key points:
1) The skin is the largest organ of the body and topical absorption depends on the formulation and site of application, with the scrotum and forehead having the highest absorption.
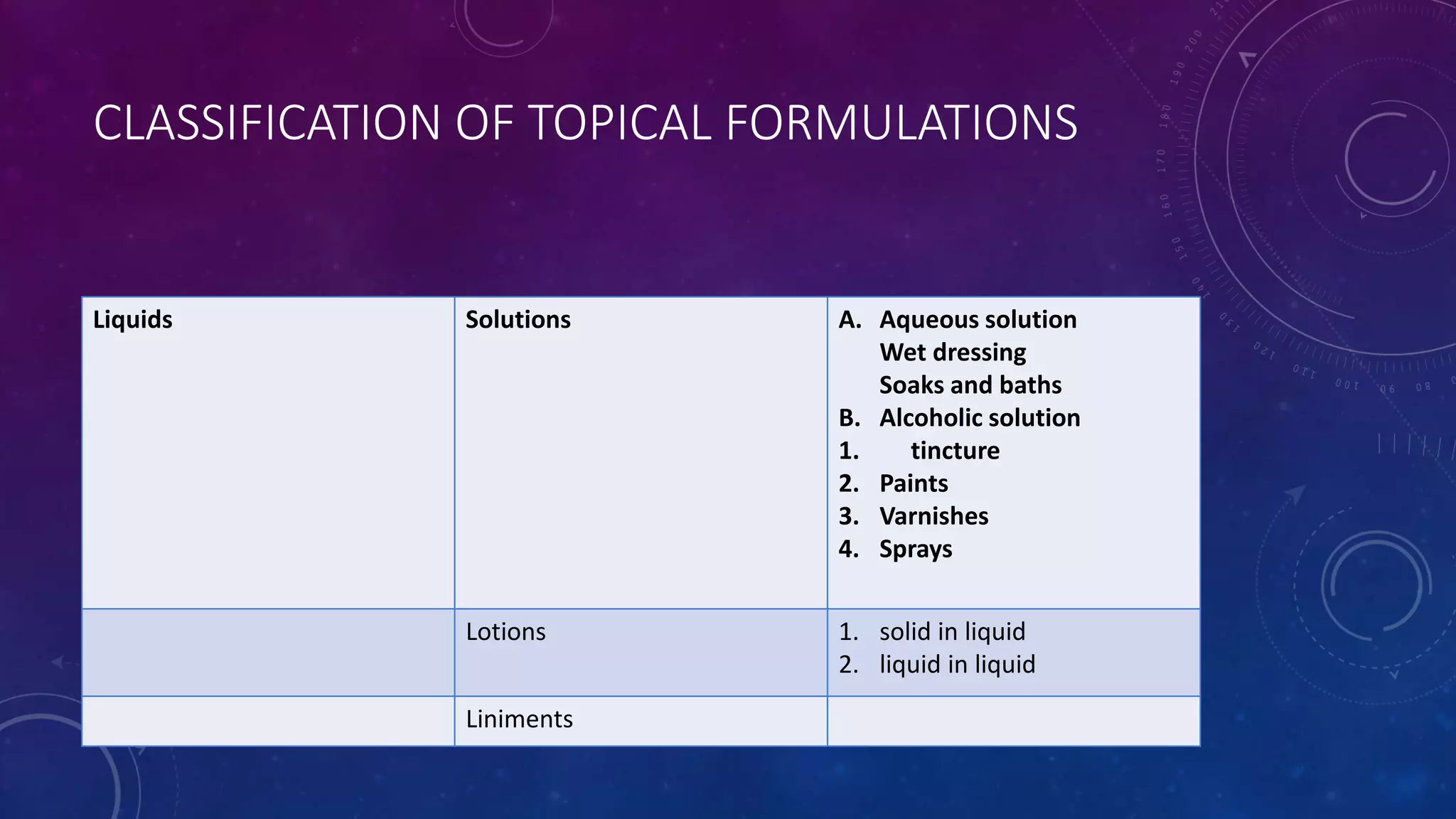
2) Topical formulations include liquids, semisolids, and solids designed for different applications depending on the condition of the skin.
3) When prescribing topical medications, clinicians should specify the concentration, vehicle, application frequency, and quantity to maximize effectiveness and avoid side effects or overuse.