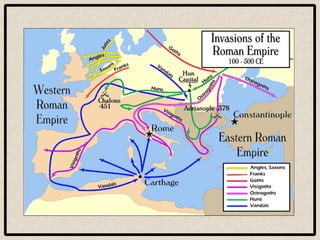
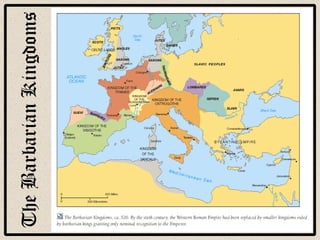
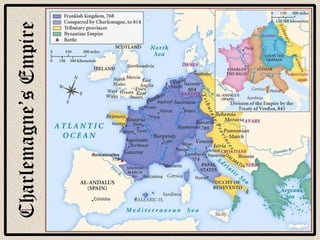
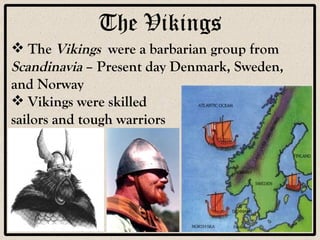
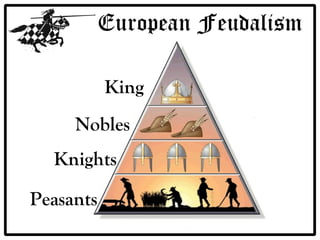
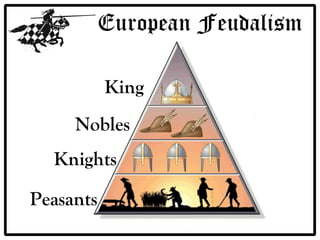
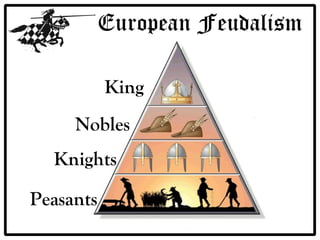
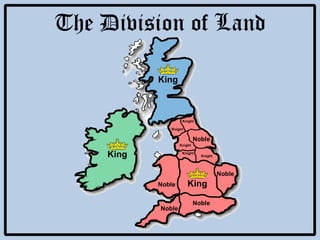
Feudalism developed in Europe following the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Under this system, land was owned by kings or lords but held by vassals in exchange for loyalty and military service. Society was strictly hierarchical, with peasants at the bottom. The manor system formed the economic basis, with self-sufficient manors worked by serfs who were bound to the land and considered the property of the lord. Peasants lived difficult lives, working long hours in poor conditions to sustain their manor.