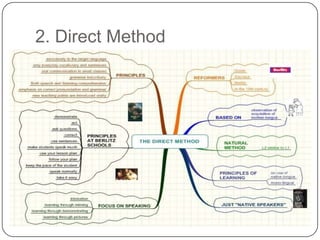
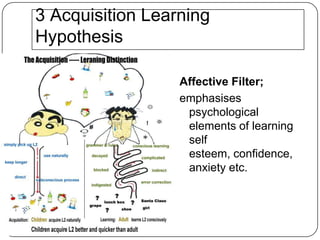
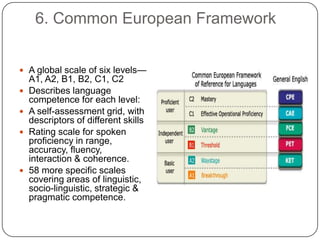
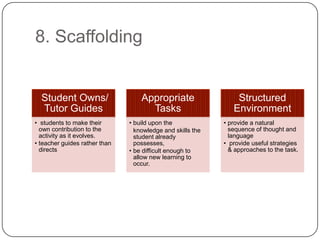
The document discusses several new approaches to teaching English, including Universal Grammar, the Direct Method, the Acquisition Learning Hypothesis, learner strategies, pragmatics, the Common European Framework, feedback, scaffolding, lingua franca, extensive reading, register/genre, and projects/webquests. The Common European Framework describes language competence through six levels and provides self-assessment tools. Extensive reading is recommended as the more someone reads, the more fluent they become. Register/genre looks at the type of language used defined by factors like context and participants.