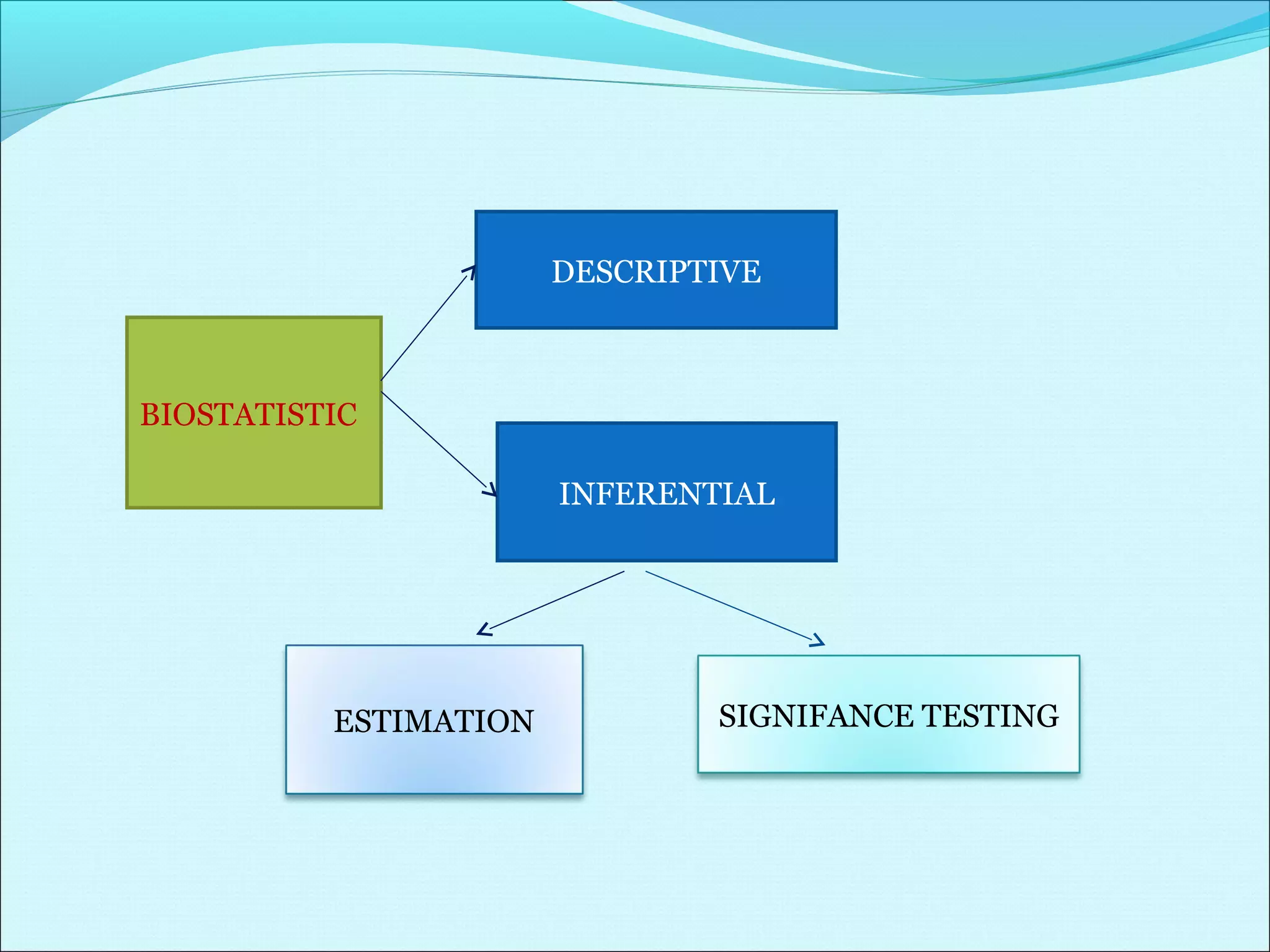
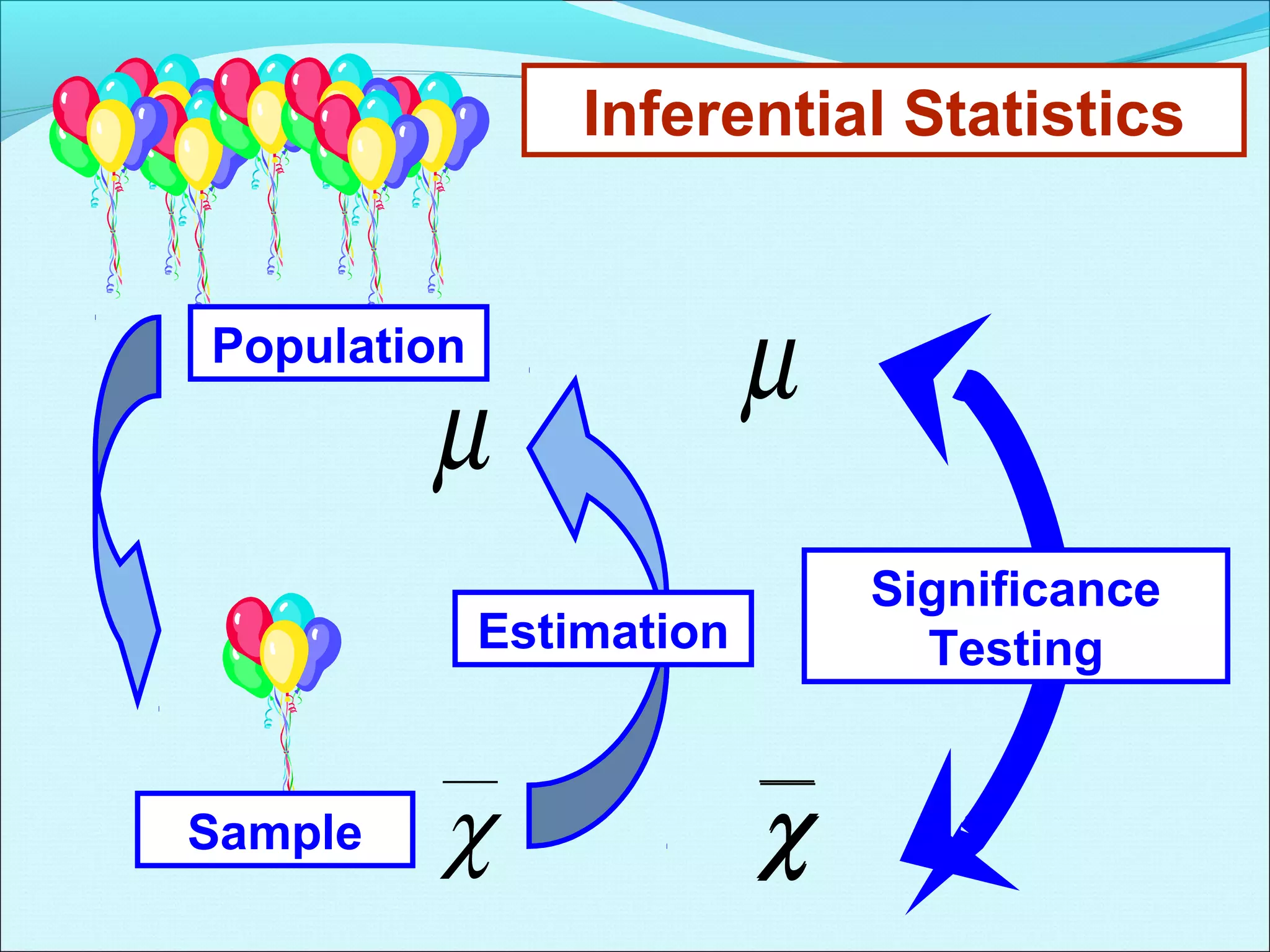
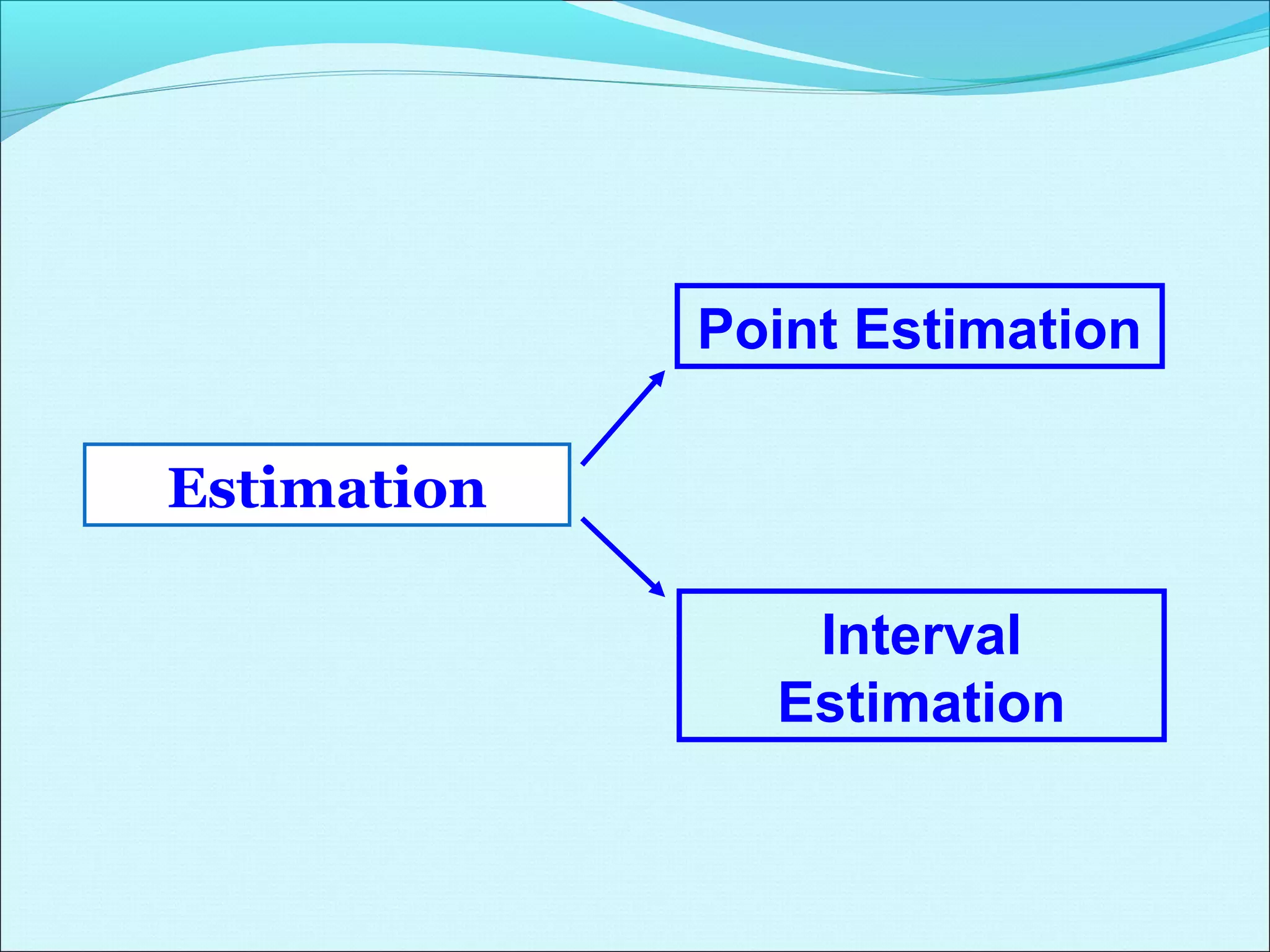
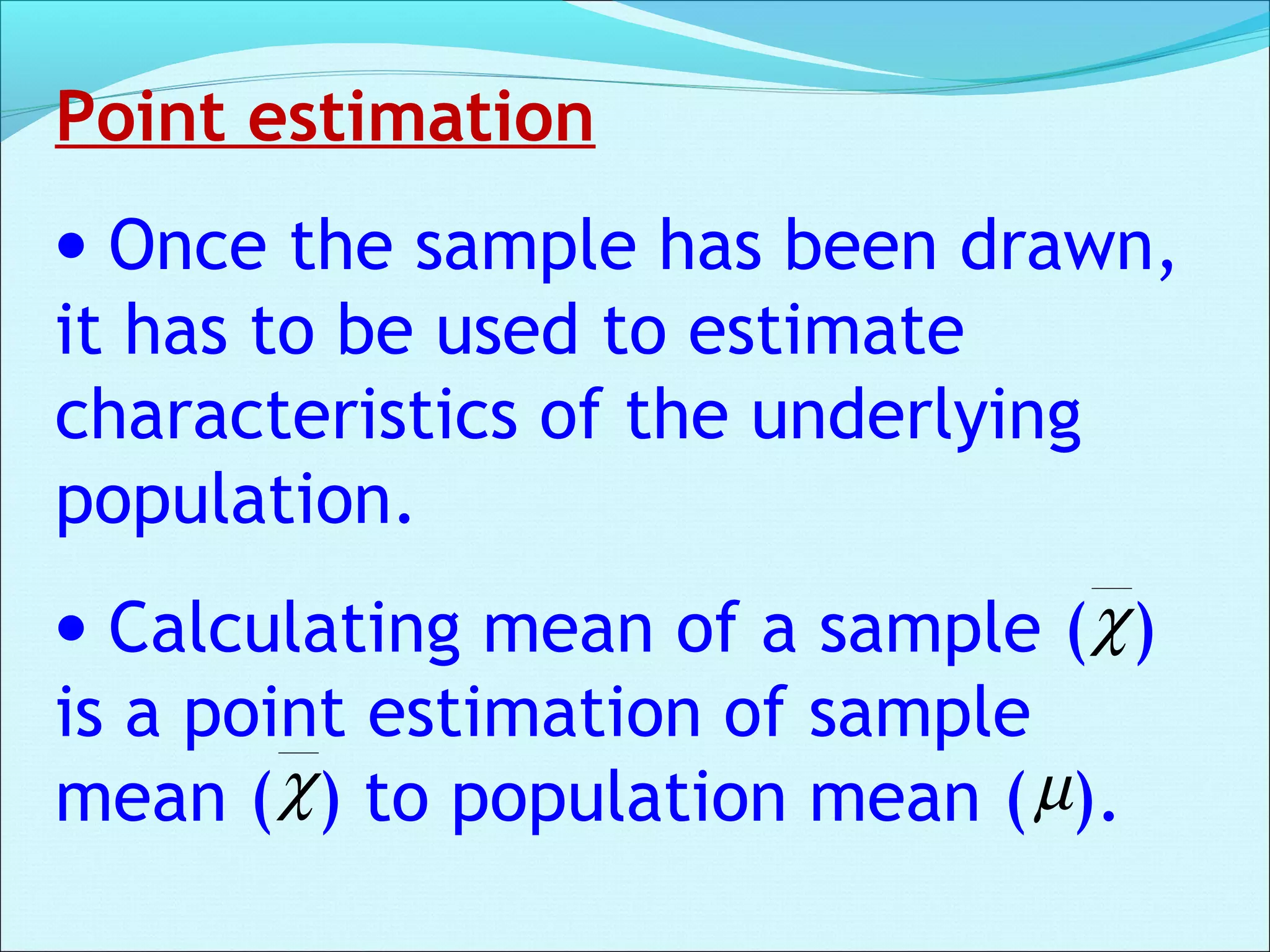
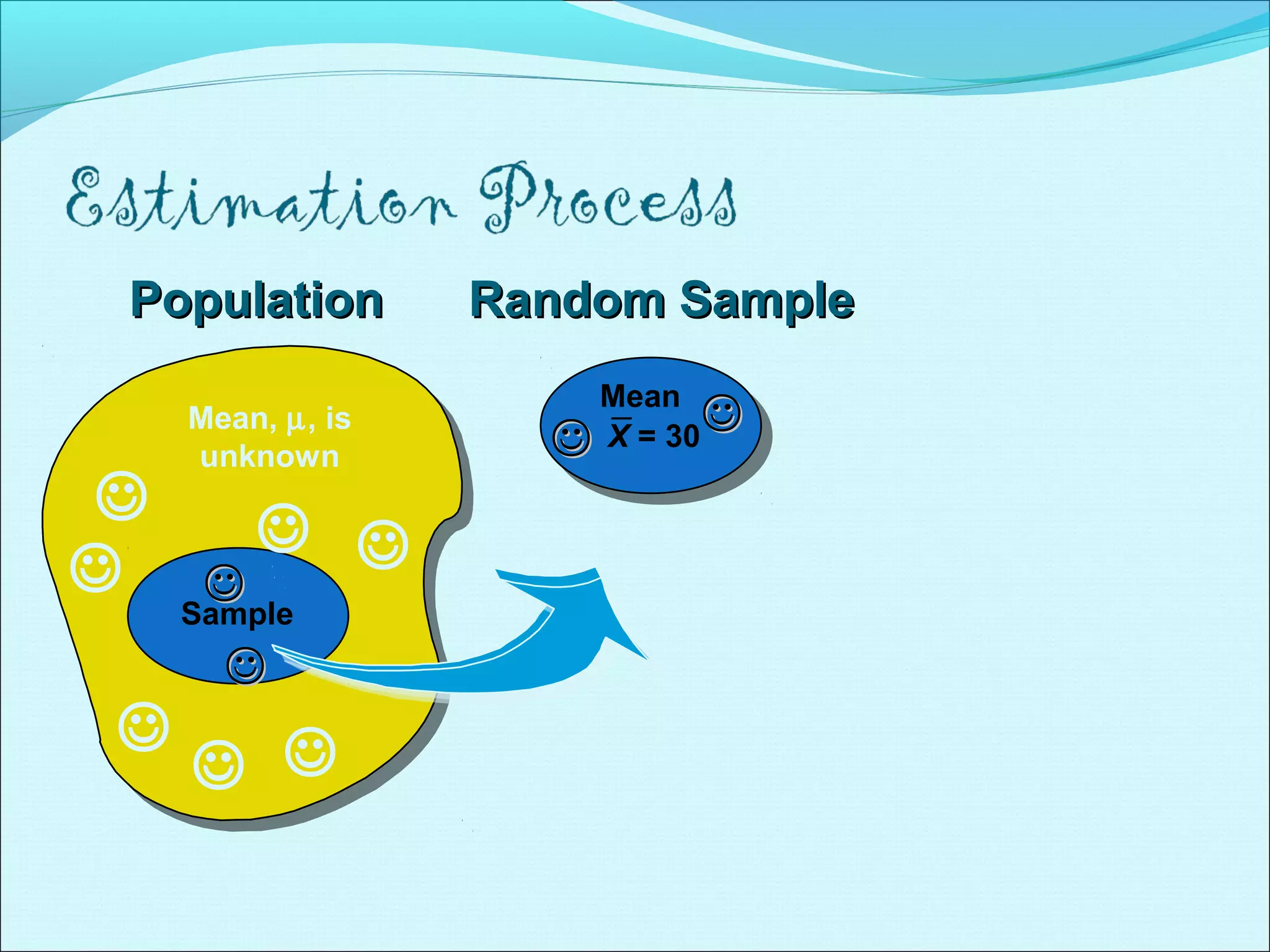
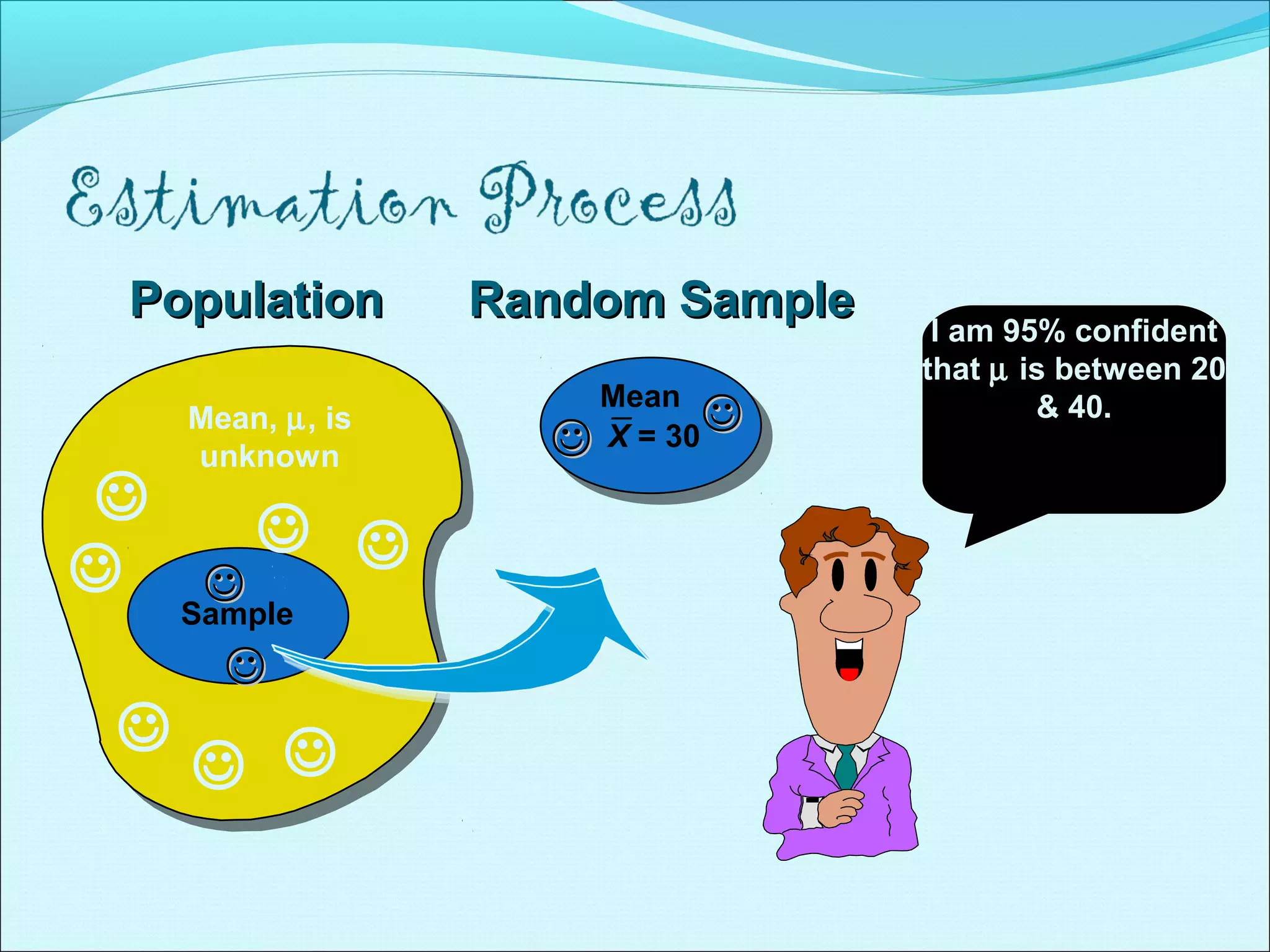
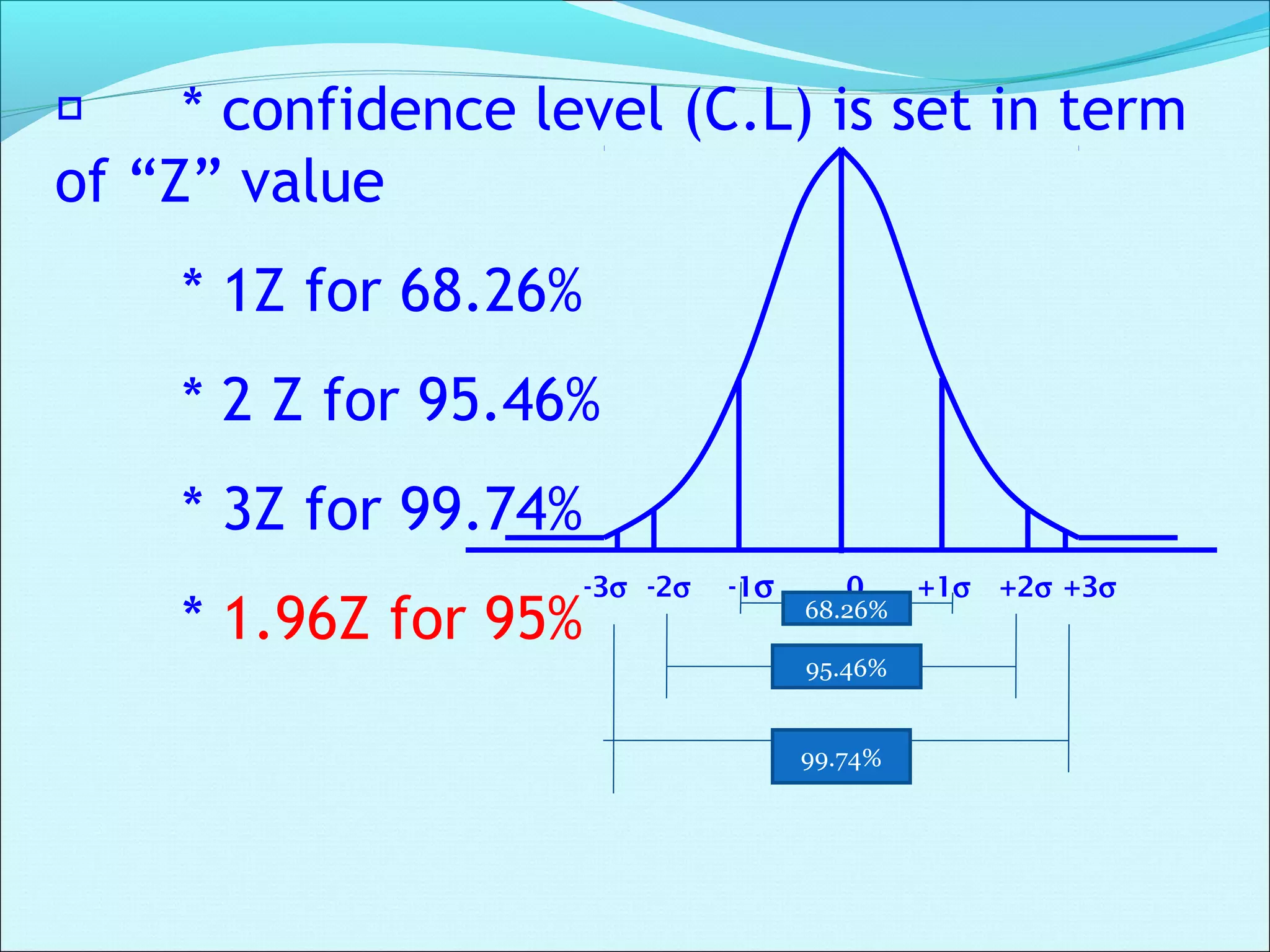
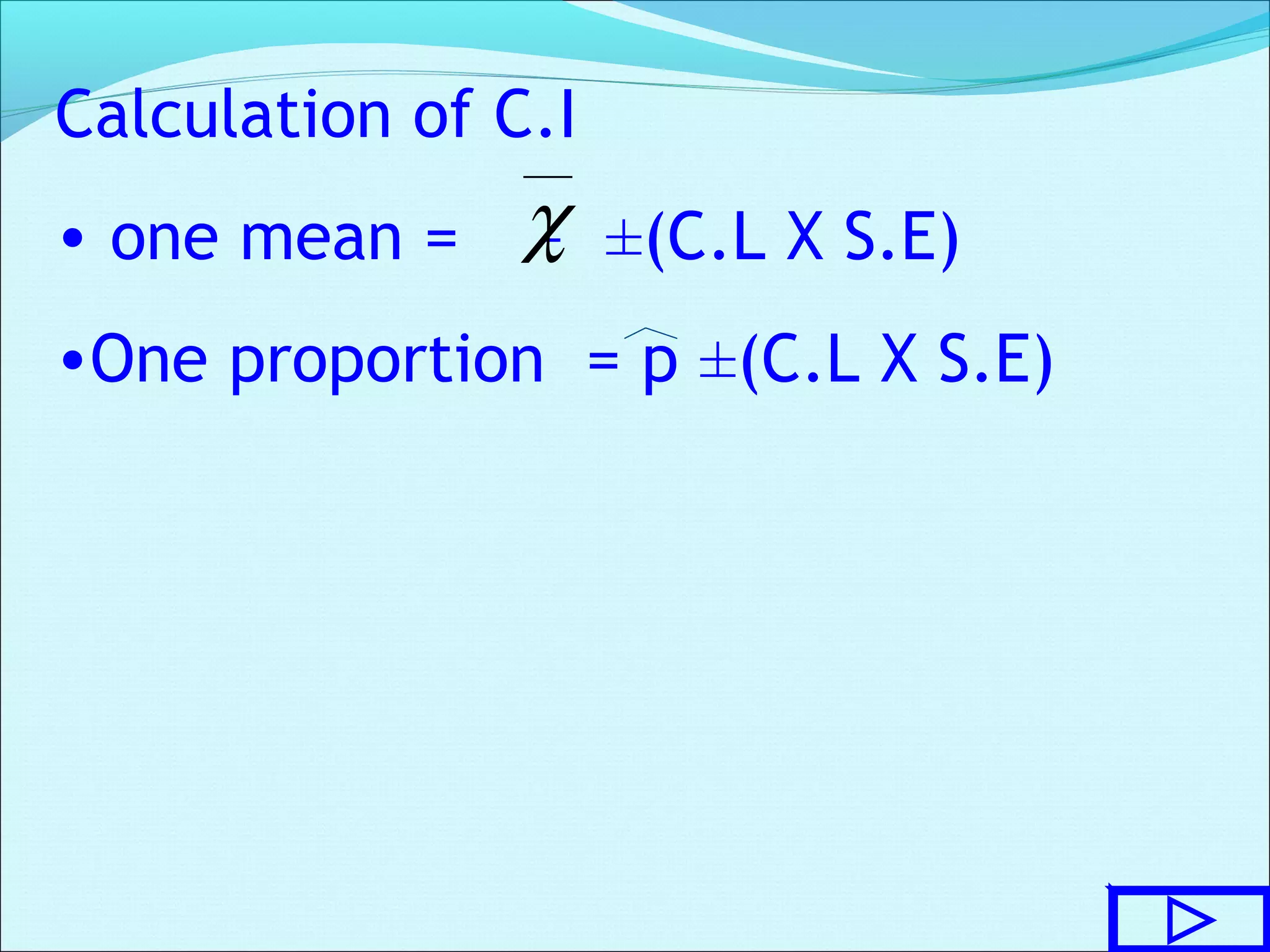
This document discusses statistical concepts related to descriptive and inferential statistics including estimation and significance testing. It explains point estimation and interval estimation. Point estimation provides a single value estimate of a population parameter based on a sample statistic. Interval estimation provides a range of plausible values for the population parameter with a stated probability based on a sample. The document provides examples of calculating confidence intervals and explains how confidence levels and sample sizes impact the width of confidence intervals.