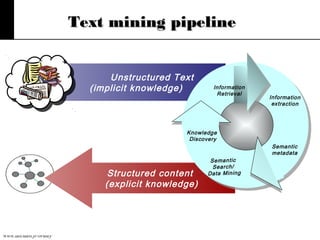
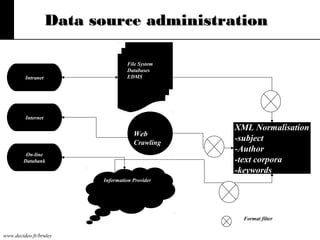
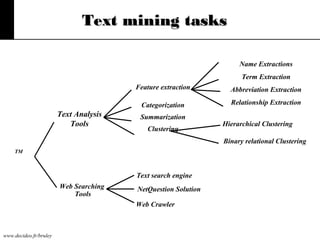
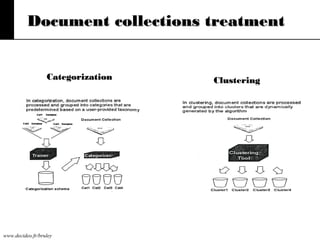
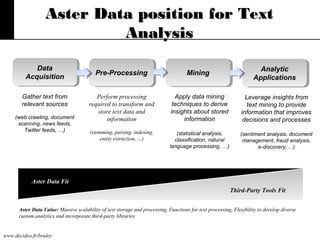
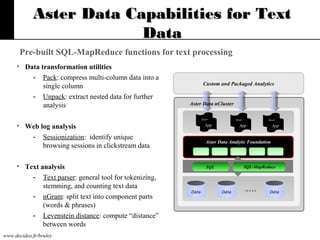
The document discusses text mining, emphasizing the need for automated tools to analyze large textual datasets due to the vast amount of unstructured data available. It outlines the text mining process, including key tasks such as categorization, extraction, and clustering, as well as the challenges faced in processing unstructured information. Moreover, it highlights Aster Data's capabilities for handling massive volumes of text data and providing analytics solutions through SQL-MapReduce frameworks.