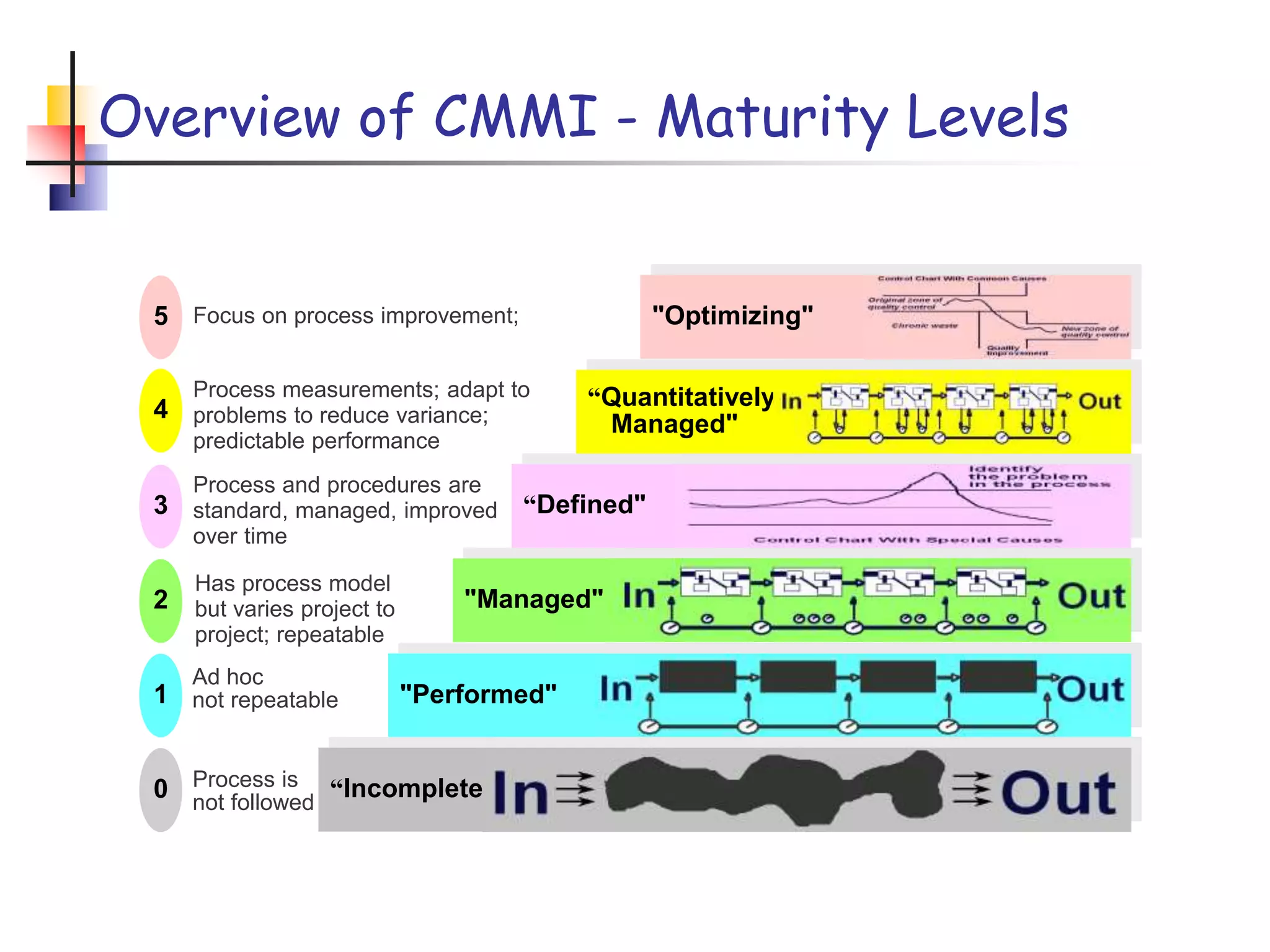
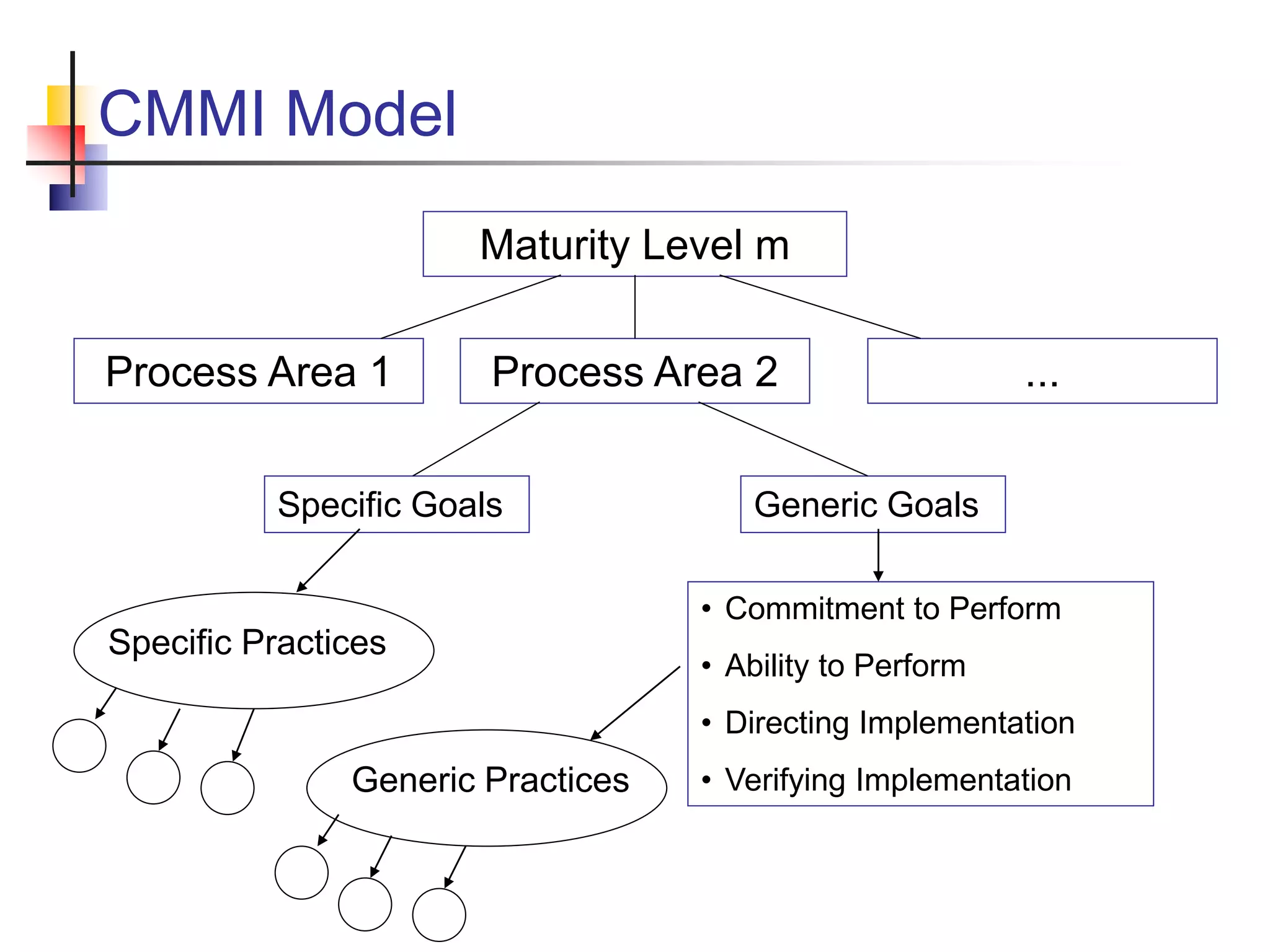
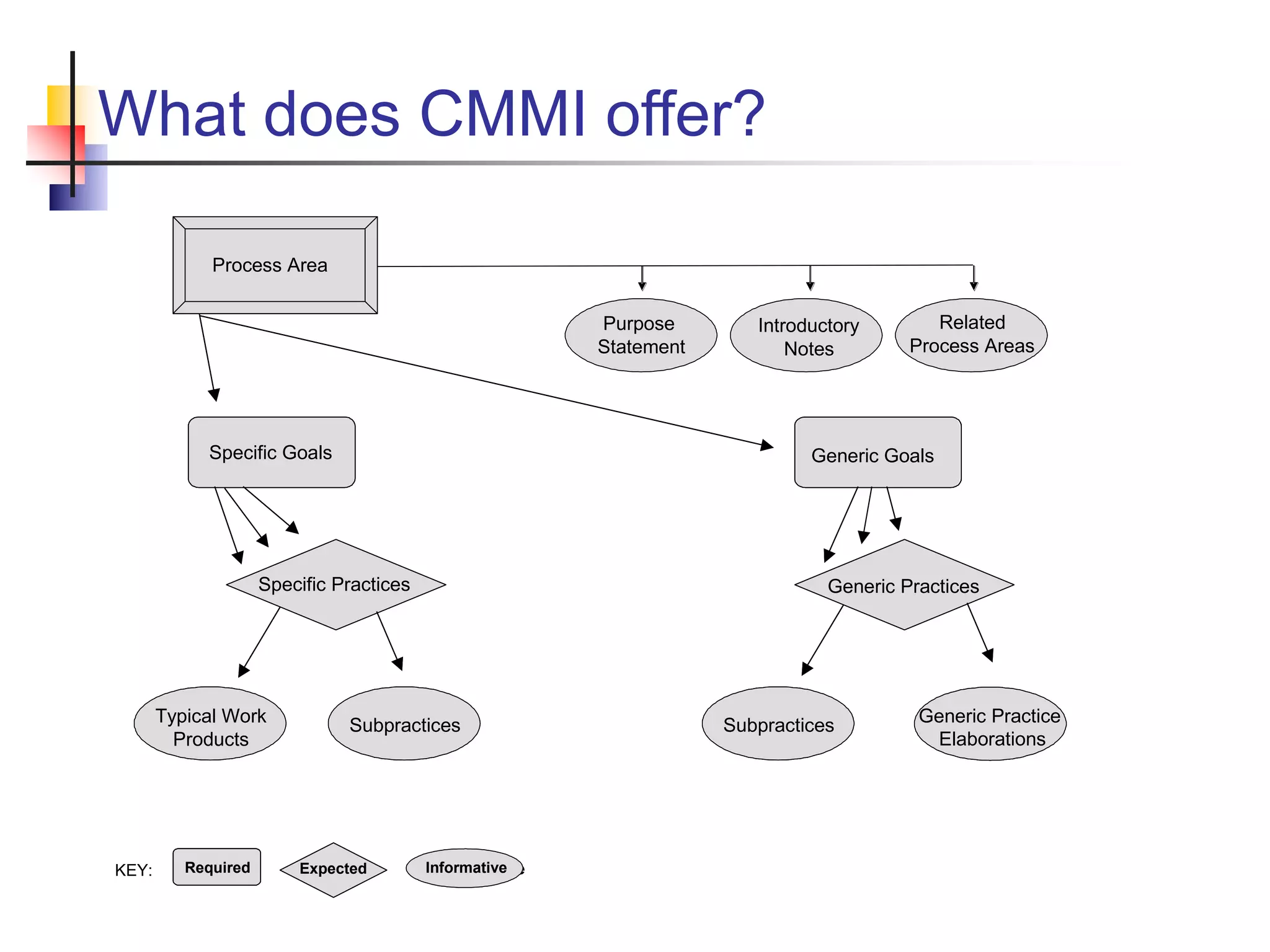
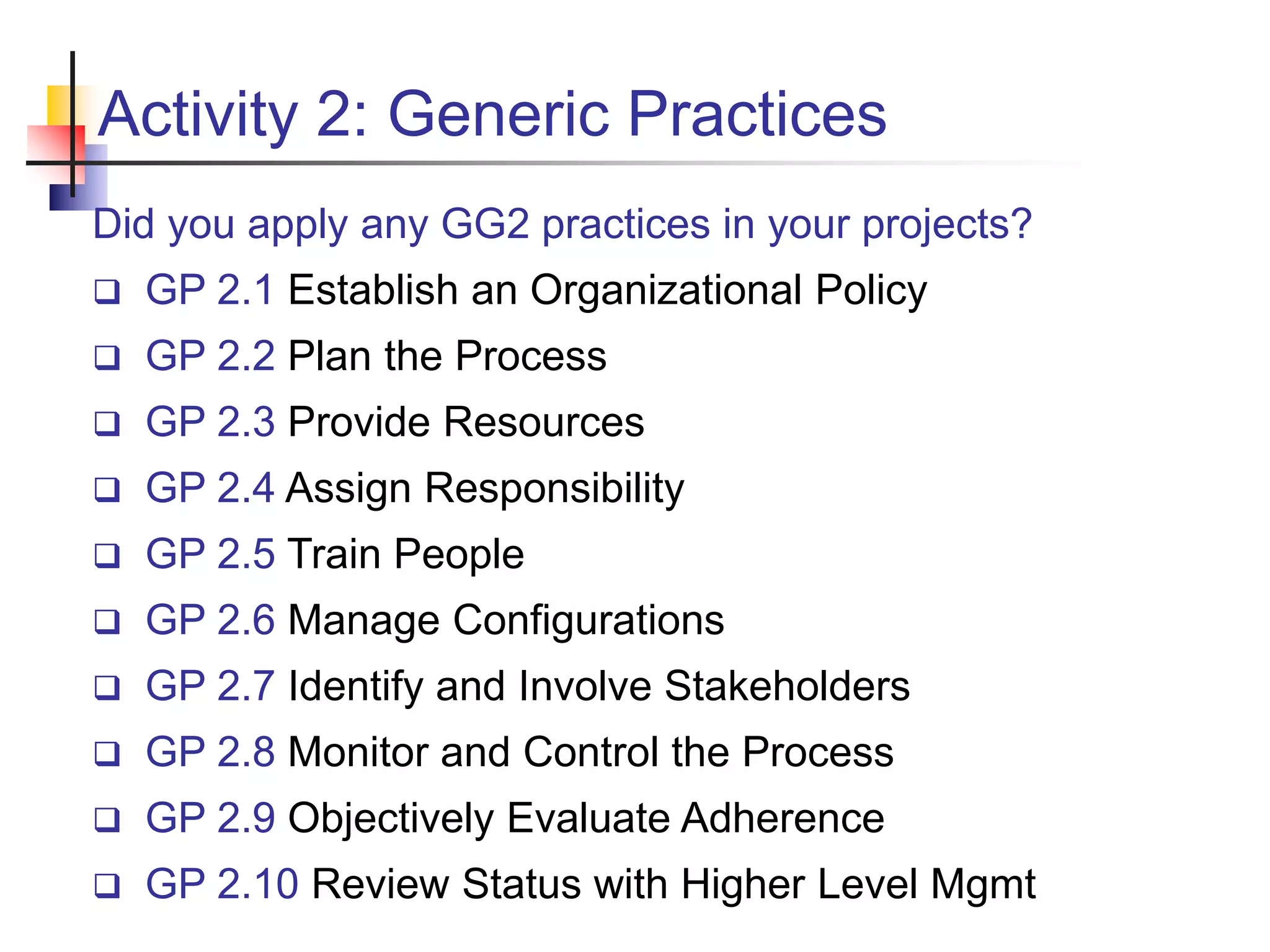
This document discusses the Capability Maturity Model Integrated (CMMI) framework. It provides an overview of CMMI maturity levels and key process areas. A software company president's priorities are discussed, including operating efficiency, predictability, repeatability, and cost/effort control. Obstacles to achieving these goals and how CMMI can help improve a company's ability to achieve its goals are also summarized. Specific CMMI process areas, goals, and practices for project management, engineering, support, and process management are then outlined.