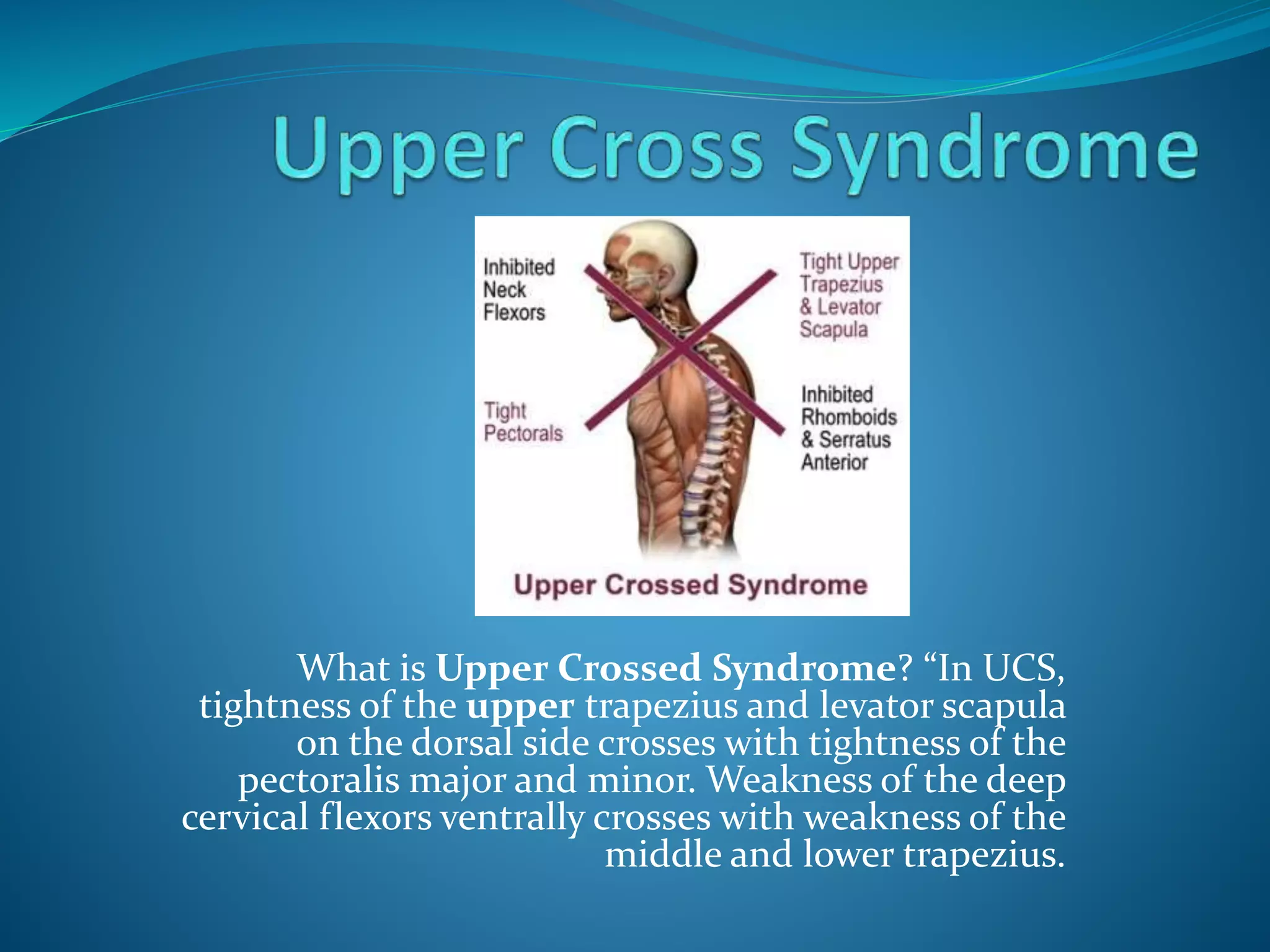
Upper crossed syndrome is a postural condition caused by prolonged forward head positioning from activities like computer use, driving, and phone use. It involves tightness in the upper trapezius and levator scapula muscles crossing with tightness in the pectoralis muscles, and weakness in the deep cervical flexors crossing with weakness in the middle and lower trapezius. Exercises like foam rolling, rows, and chin tucks can help correct muscle imbalances, as can improving posture awareness and taking breaks from aggravating activities.