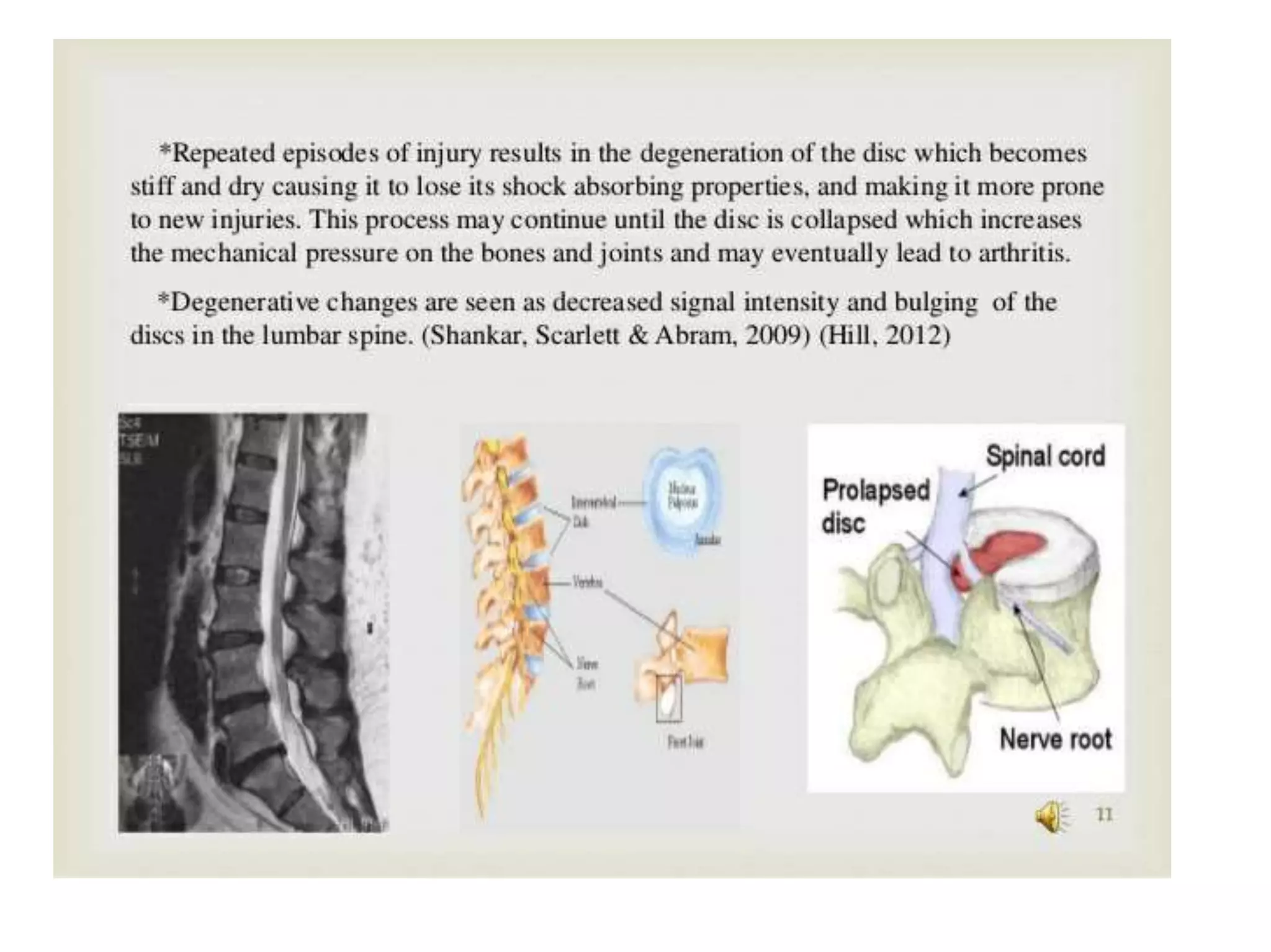
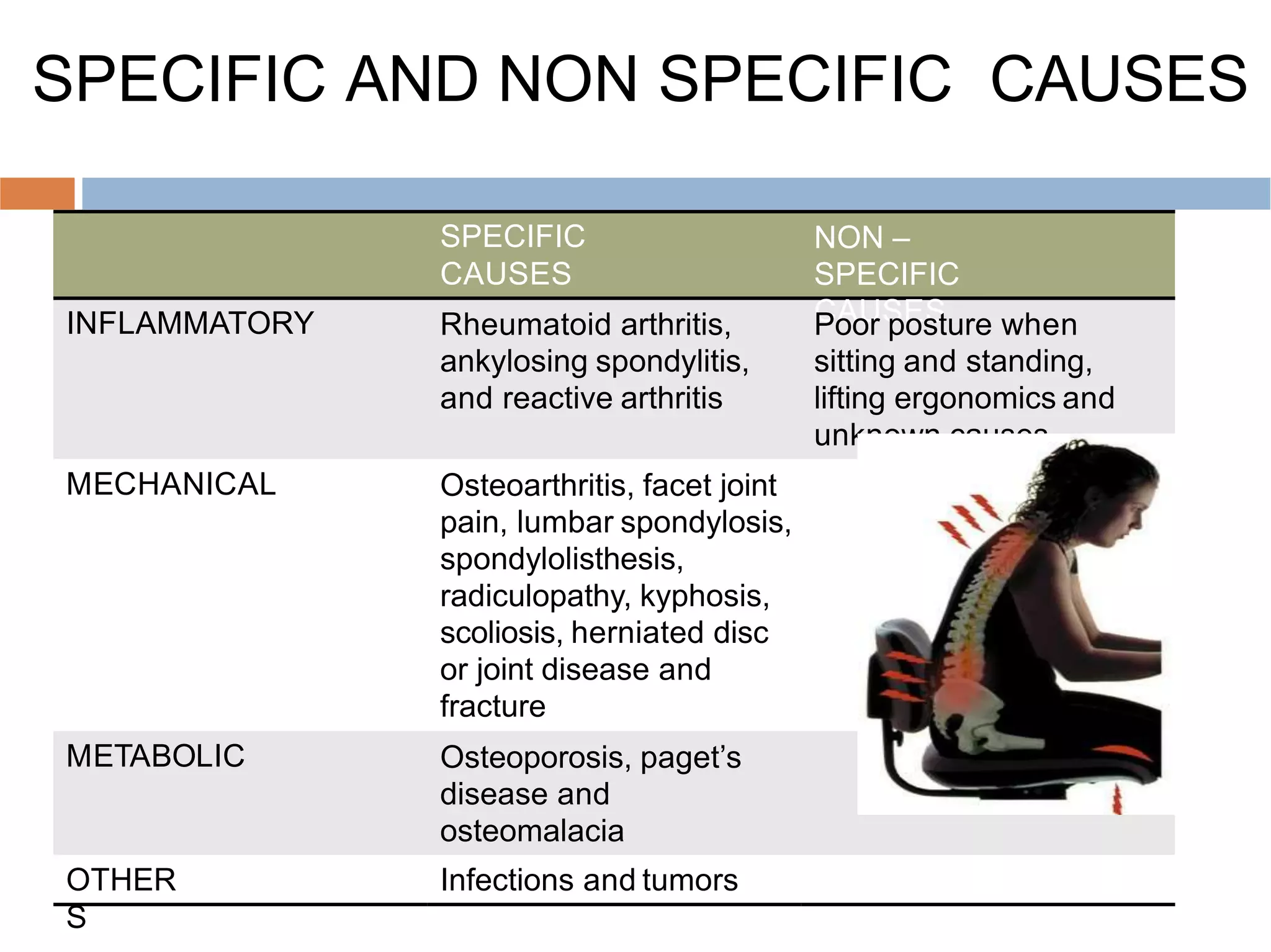
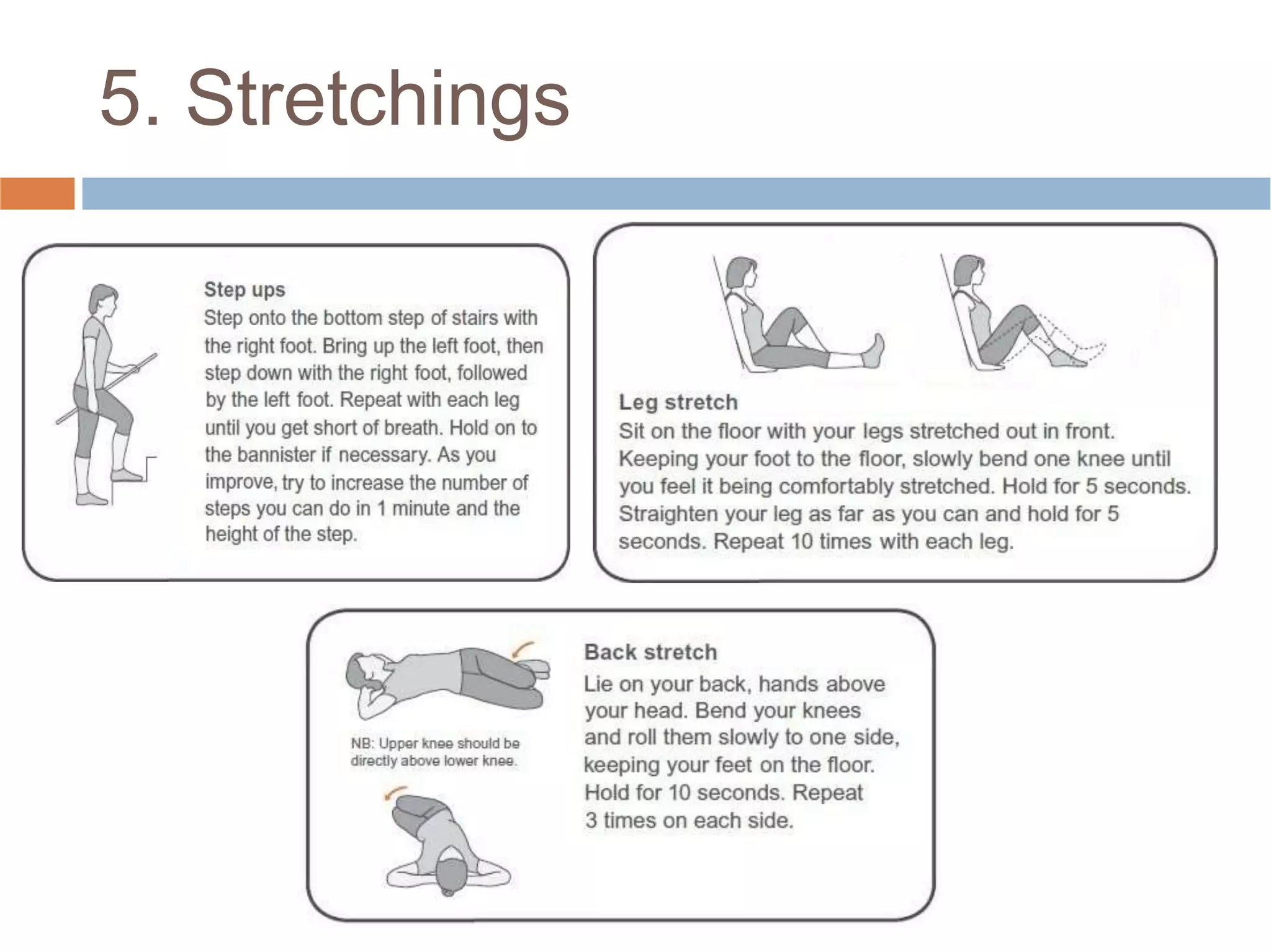
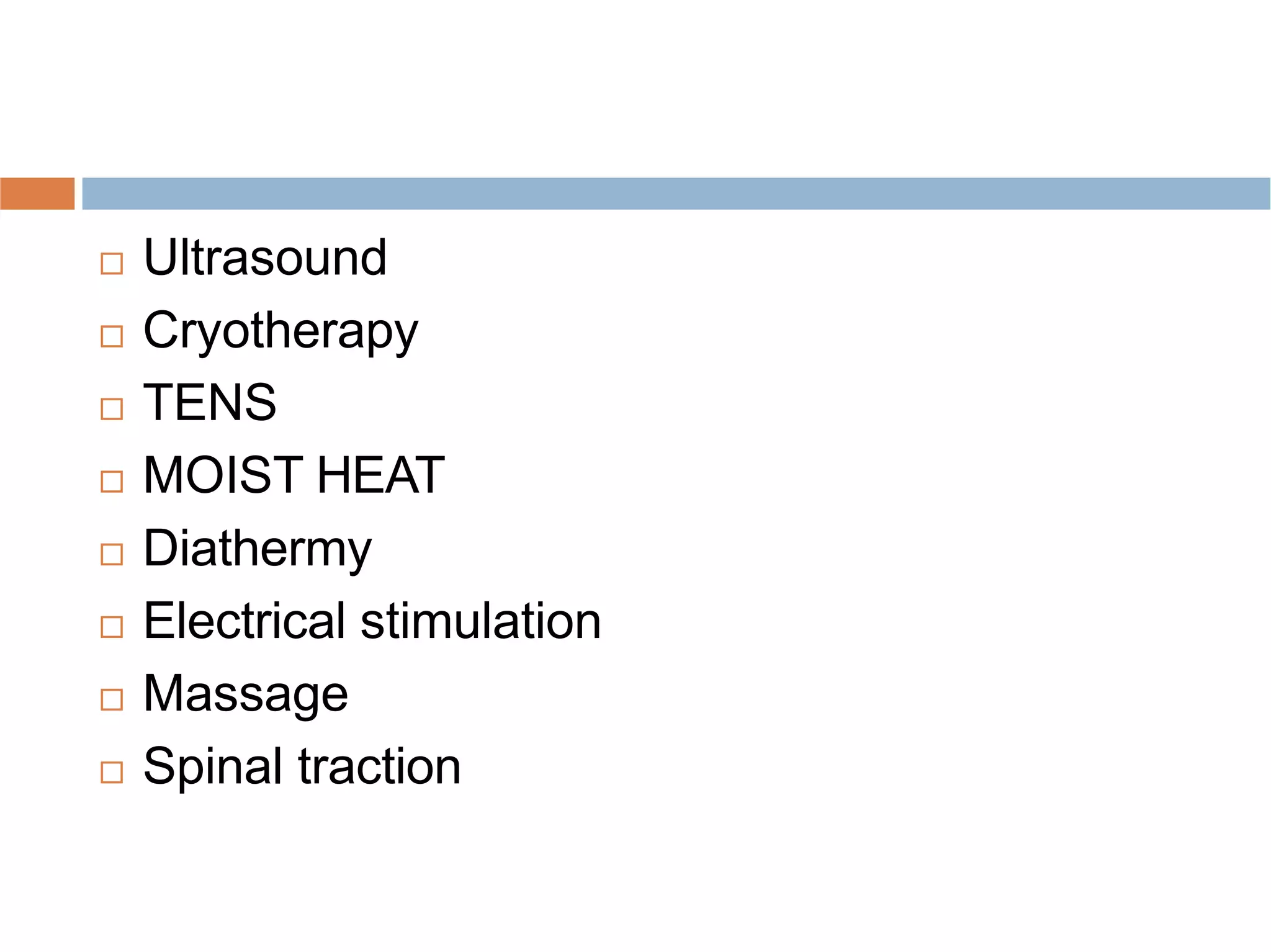
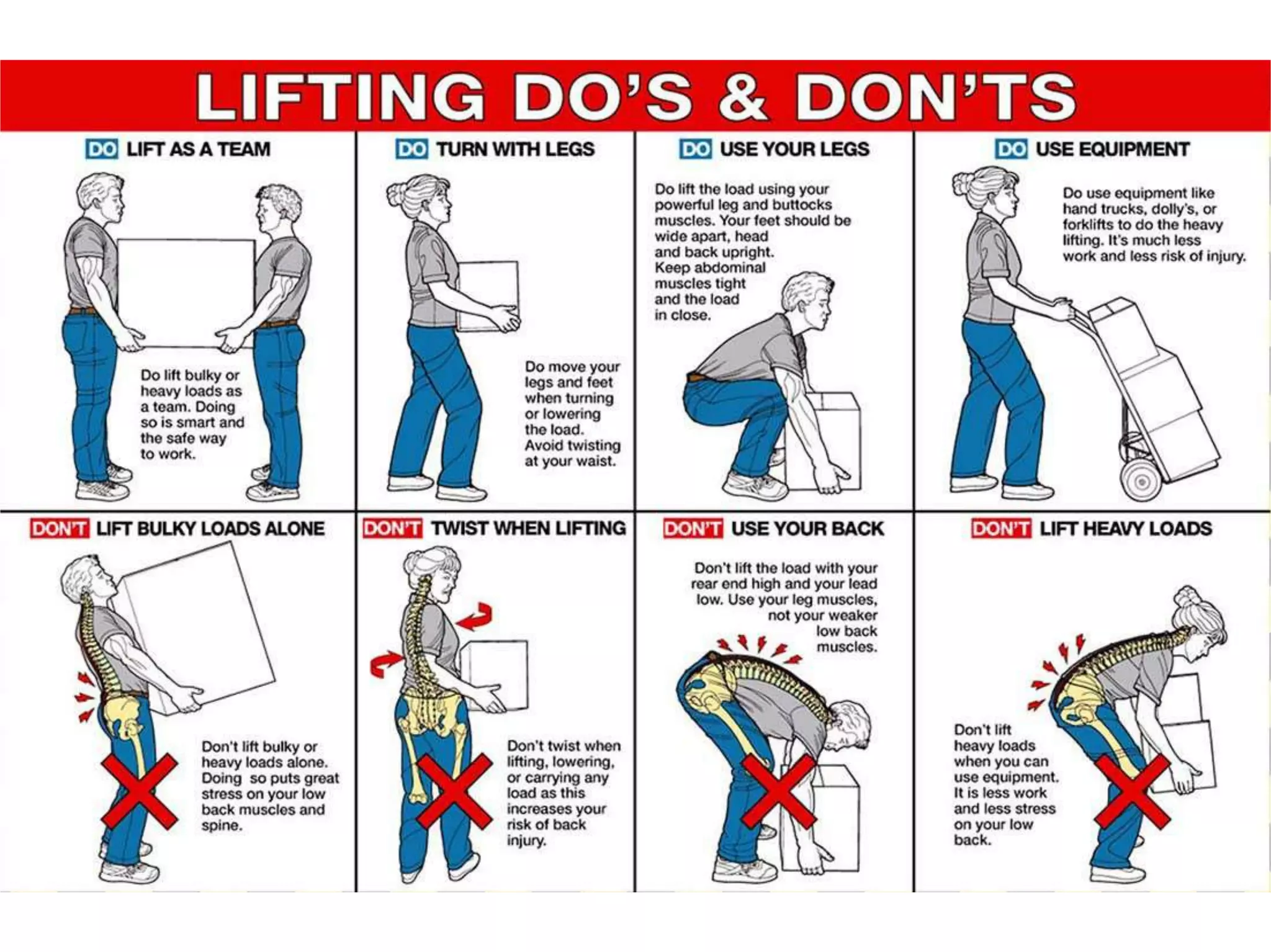
Low back pain is a common cause of disability that affects people of all cultures. It can be acute, lasting less than three months, or chronic, lasting over three months. Common causes include muscle strains, arthritis, herniated discs, and osteoporosis. Physical examination involves assessing range of motion, neurological function, and diagnostic tests like x-rays and MRIs. Physiotherapy management aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve muscle strength and flexibility, and prevent recurrence through exercises and physical agents like ultrasound, TENS, and spinal traction.