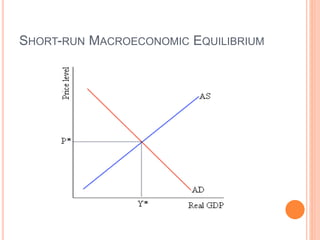
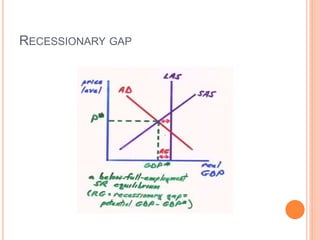
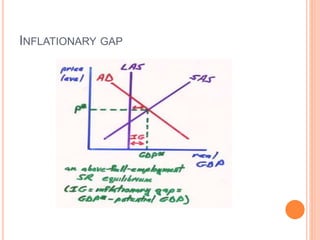
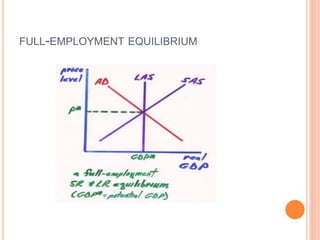
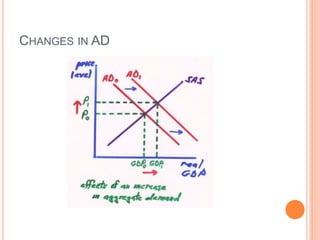
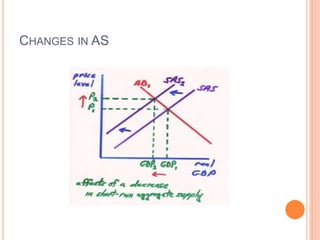
The document discusses macroeconomic equilibrium in the short run and long run. It explains that in the short run, equilibrium occurs at the intersection of aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) curves, determining real GDP and the price level. It then defines and compares short-run situations: a recessionary gap where output is below potential and an inflationary gap where output exceeds potential. The long run equilibrium exists where output is at potential GDP and unemployment is at the natural rate. It also discusses how changes in AD or AS can shift short-run equilibrium.