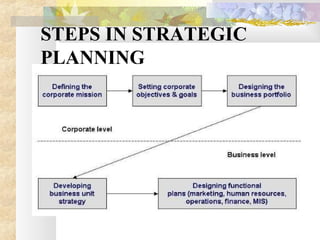
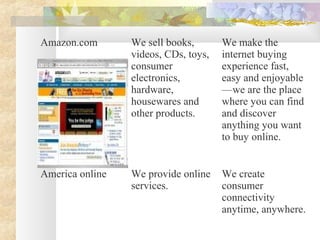
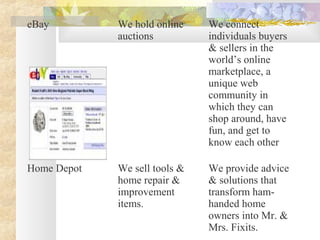
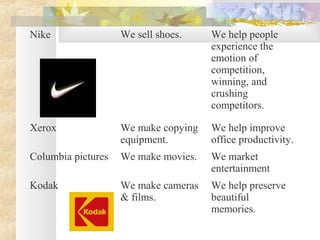
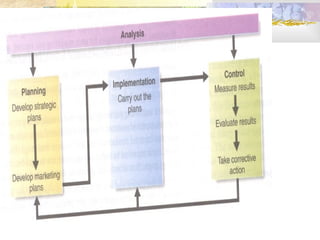
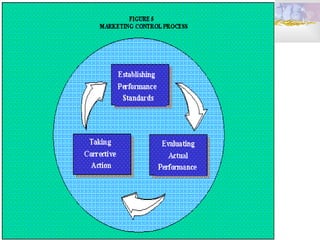
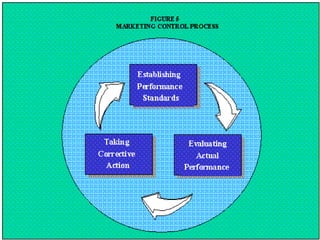
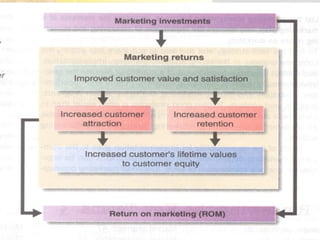
This document discusses strategic planning and marketing strategy. It defines strategic planning as the process of developing a strategic fit between an organization's goals and capabilities and its changing market opportunities. The key steps in strategic planning are defining a market-oriented mission, setting objectives and goals, designing the business portfolio, and coordinating functional strategies. Marketing plays an important role in strategic planning by partnering with other departments and members of the supply chain. The marketing process involves segmentation, targeting, developing the marketing mix, and managing the marketing effort.