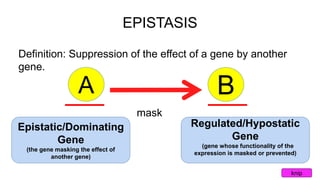
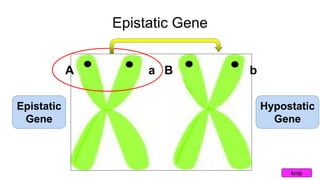
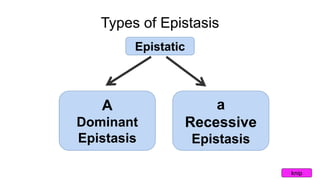
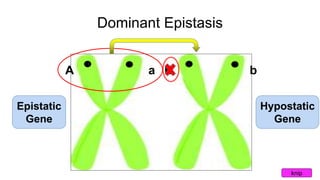
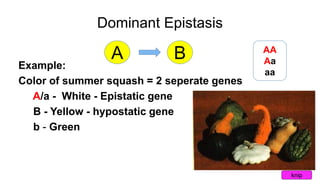
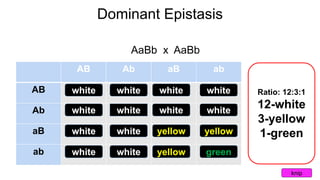
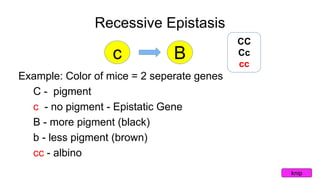
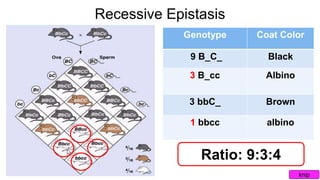
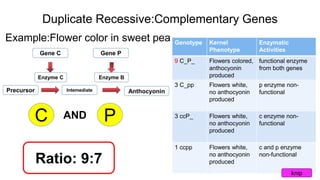
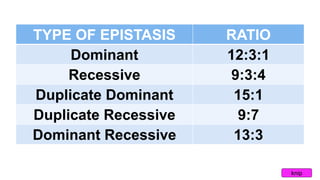
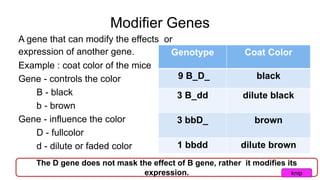
Epistasis occurs when one gene suppresses or masks the expression of another gene. There are different types of epistasis including dominant, recessive, duplicate dominant, and duplicate recessive epistasis. Epistasis ratios in offspring depend on the type of epistasis and can be 12:3:1, 9:3:4, 15:1, or 9:7. Modifier genes modify the effects or expression of another gene without masking it, like genes influencing coat color in mice. Pseudoalleles are two closely linked genes affecting the same trait that can undergo recombination like different eye color mutants in Drosophila.