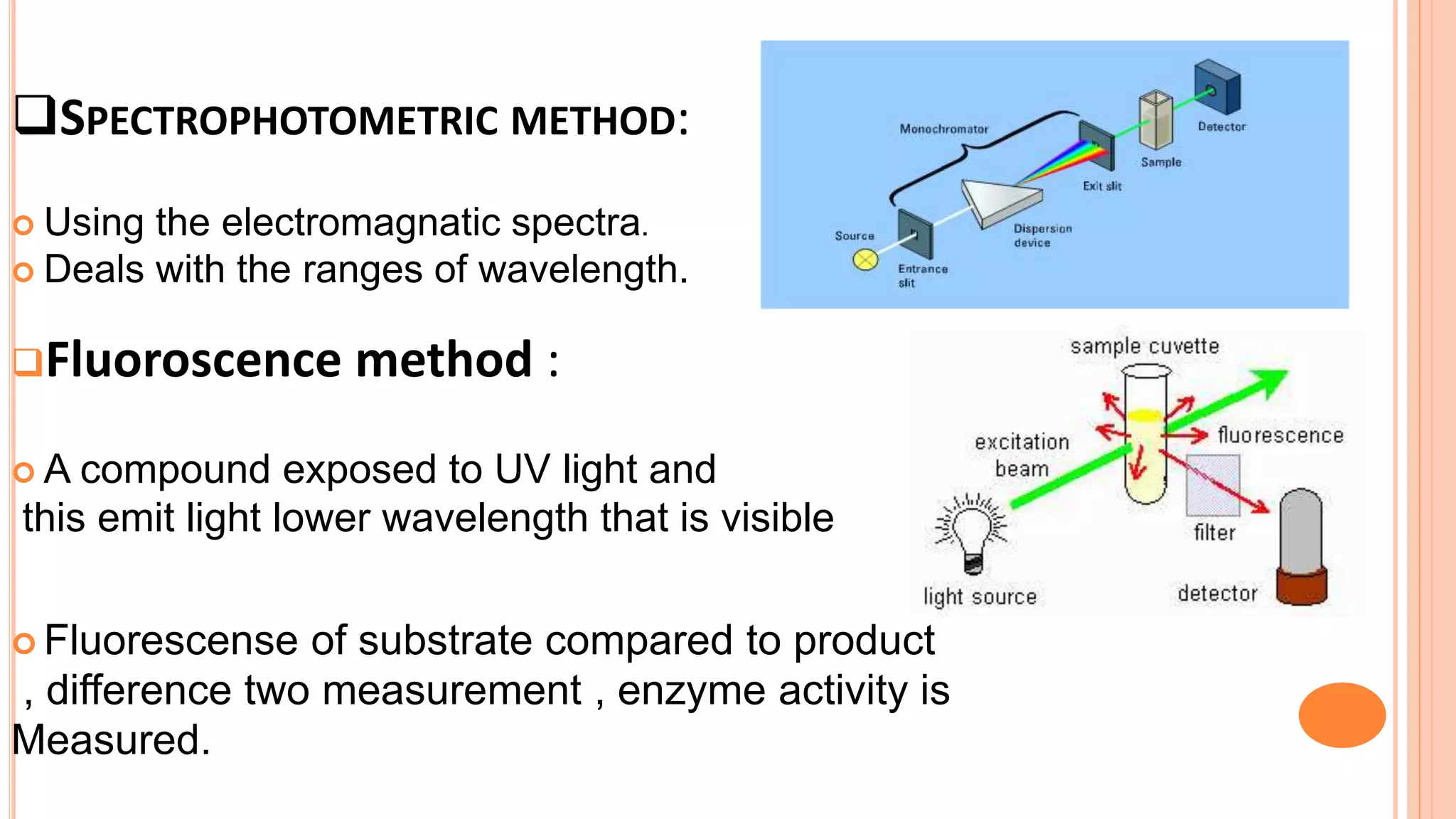
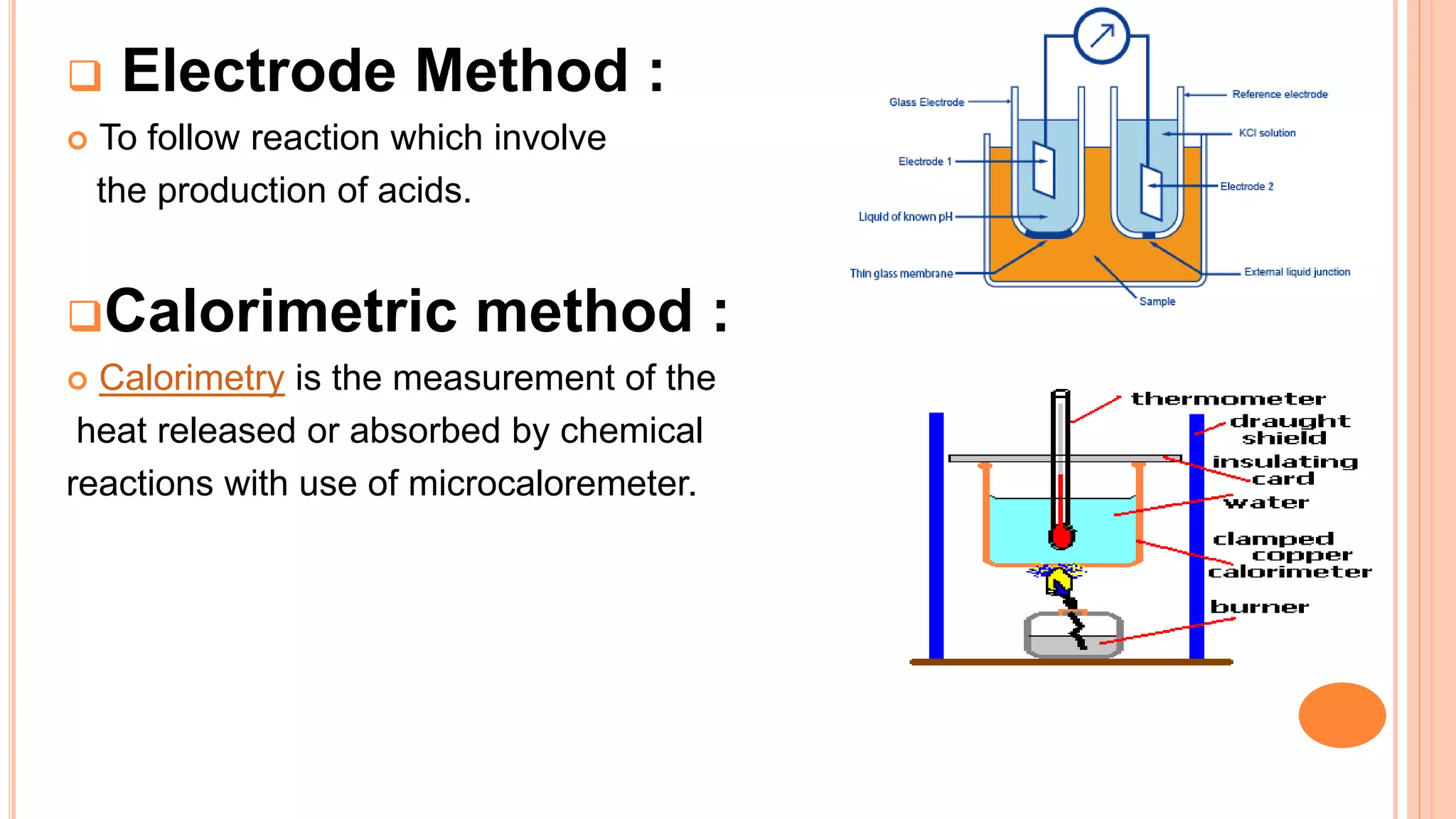
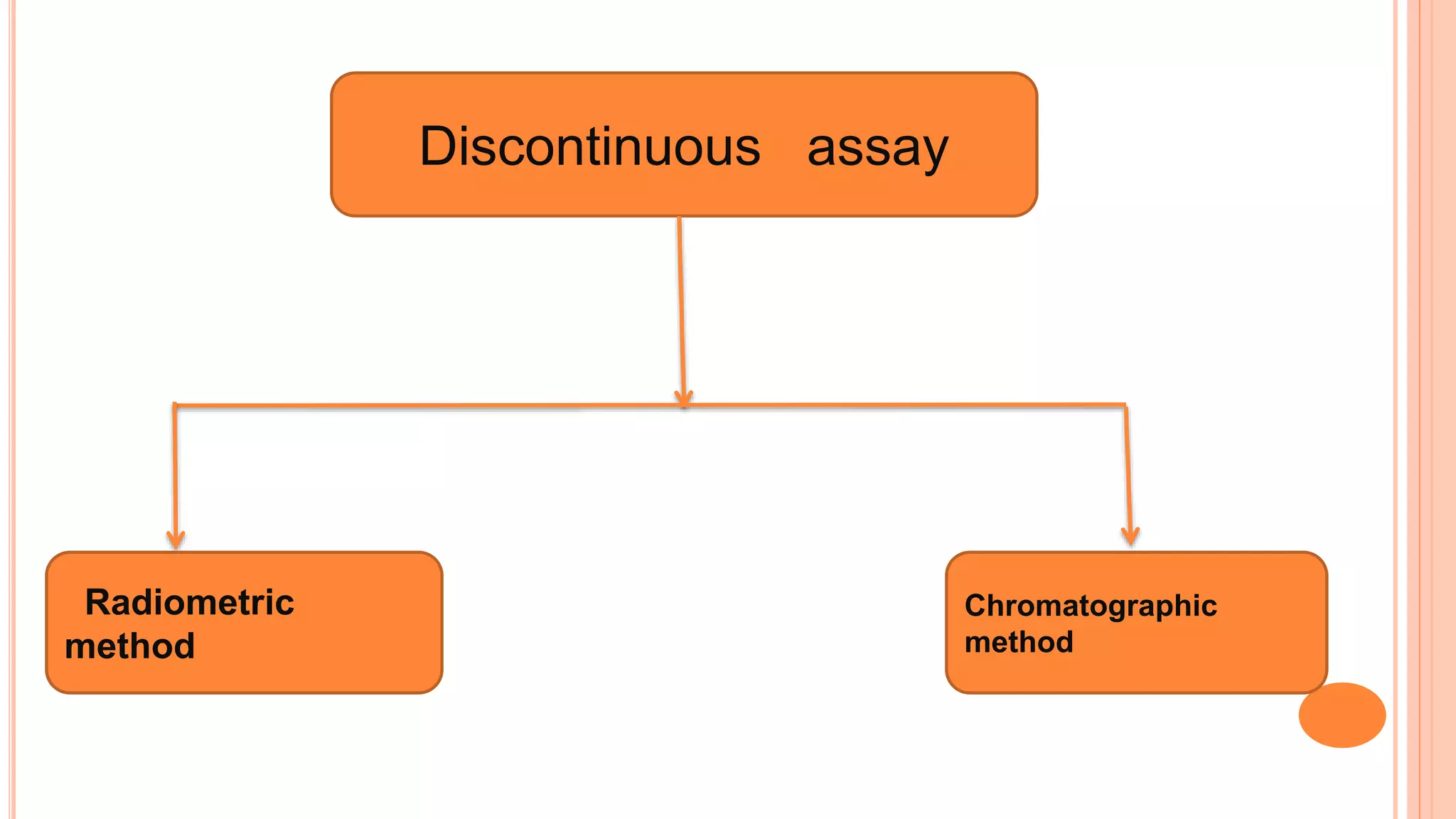
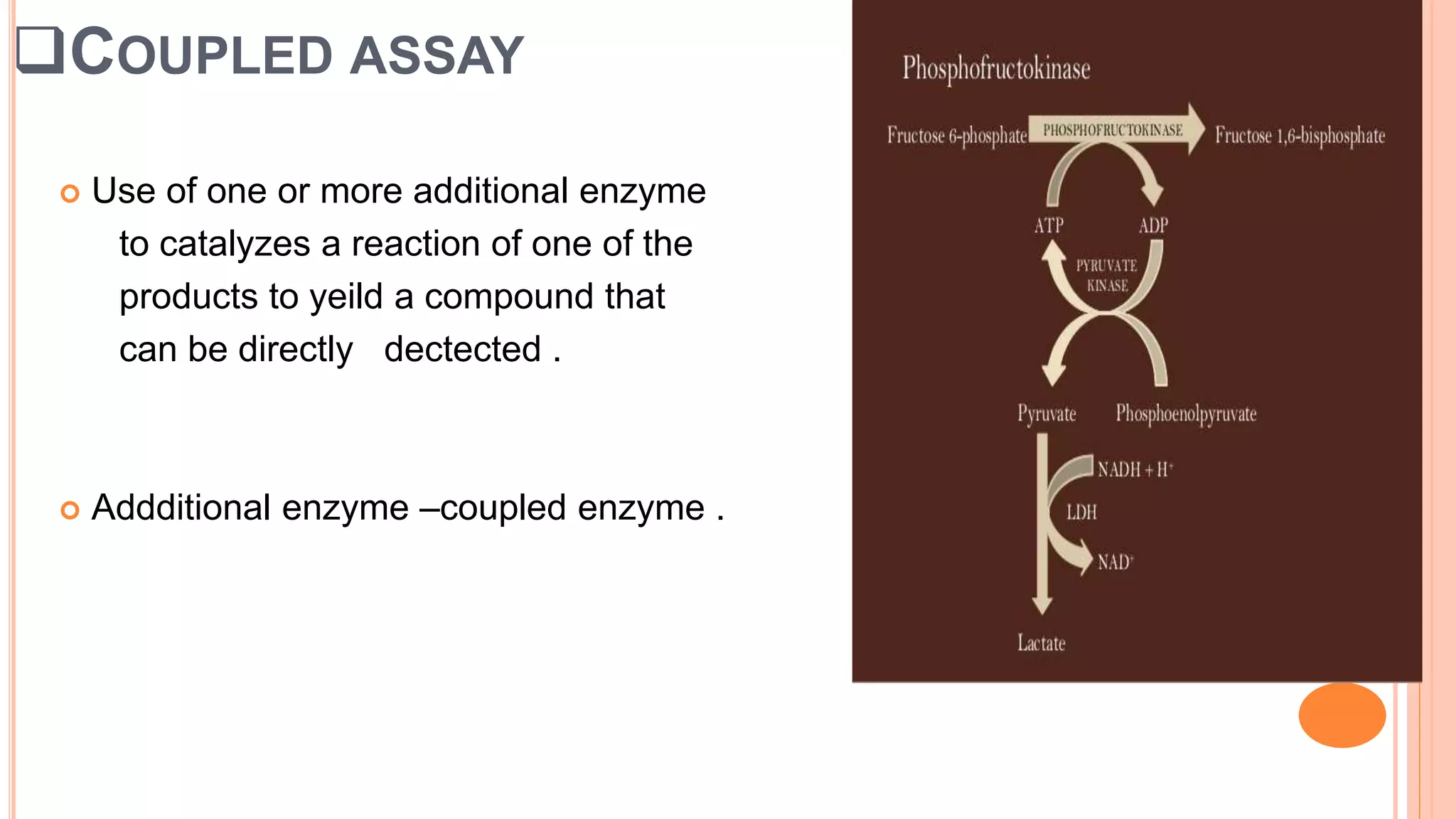
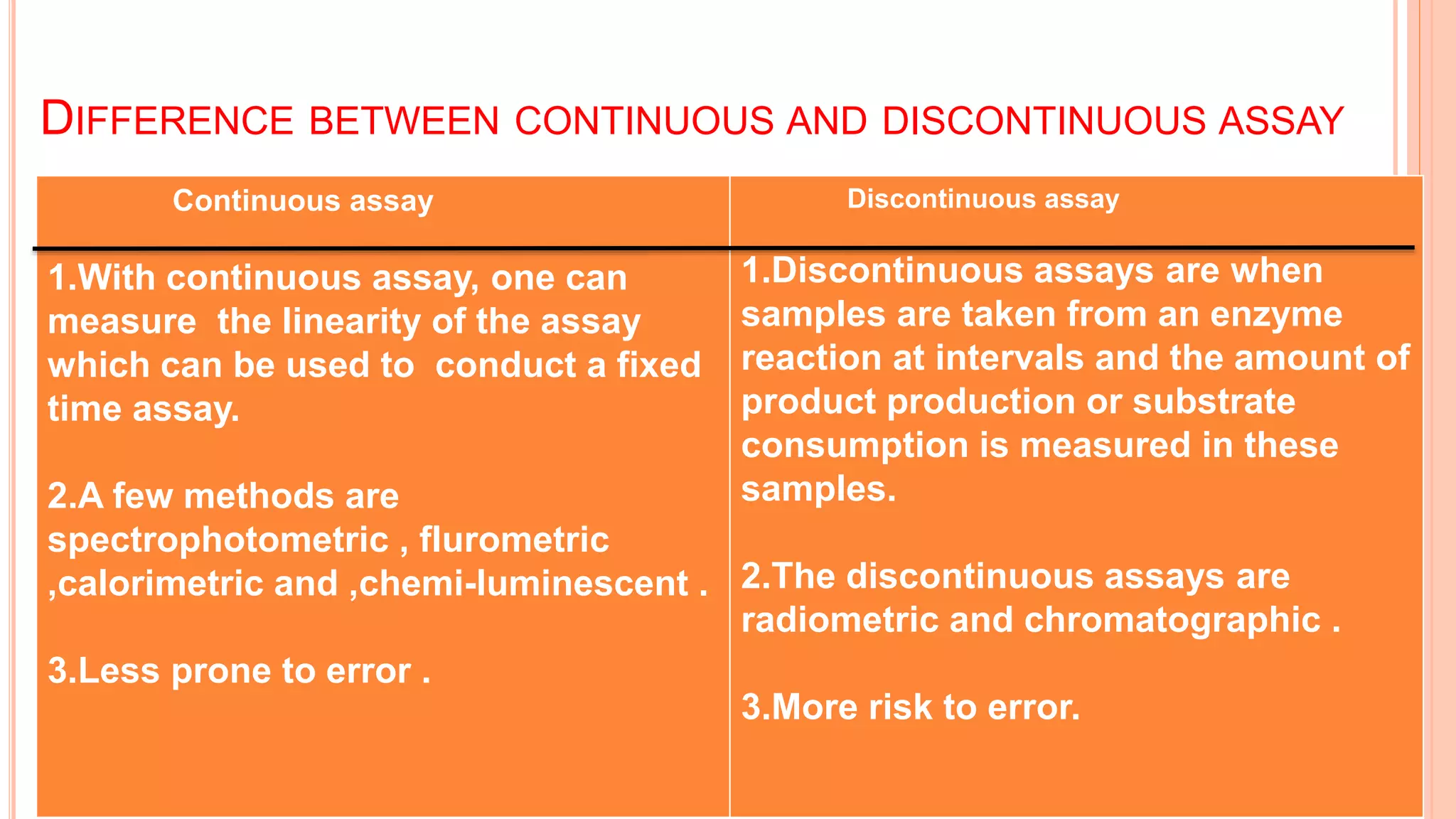
This document discusses enzyme assays, which are laboratory methods used to measure enzymatic activity. It describes different types of enzyme assays including continuous assays, where activity is measured continuously, and discontinuous assays, where samples are taken at intervals. Continuous assays discussed include spectrophotometric, fluorometric, polarimetric, electrode, manometric, and calorimetric methods. Discontinuous assays include radiometric and chromatographic methods. The document also covers the purposes of enzyme assays and factors to control in assay experiments.