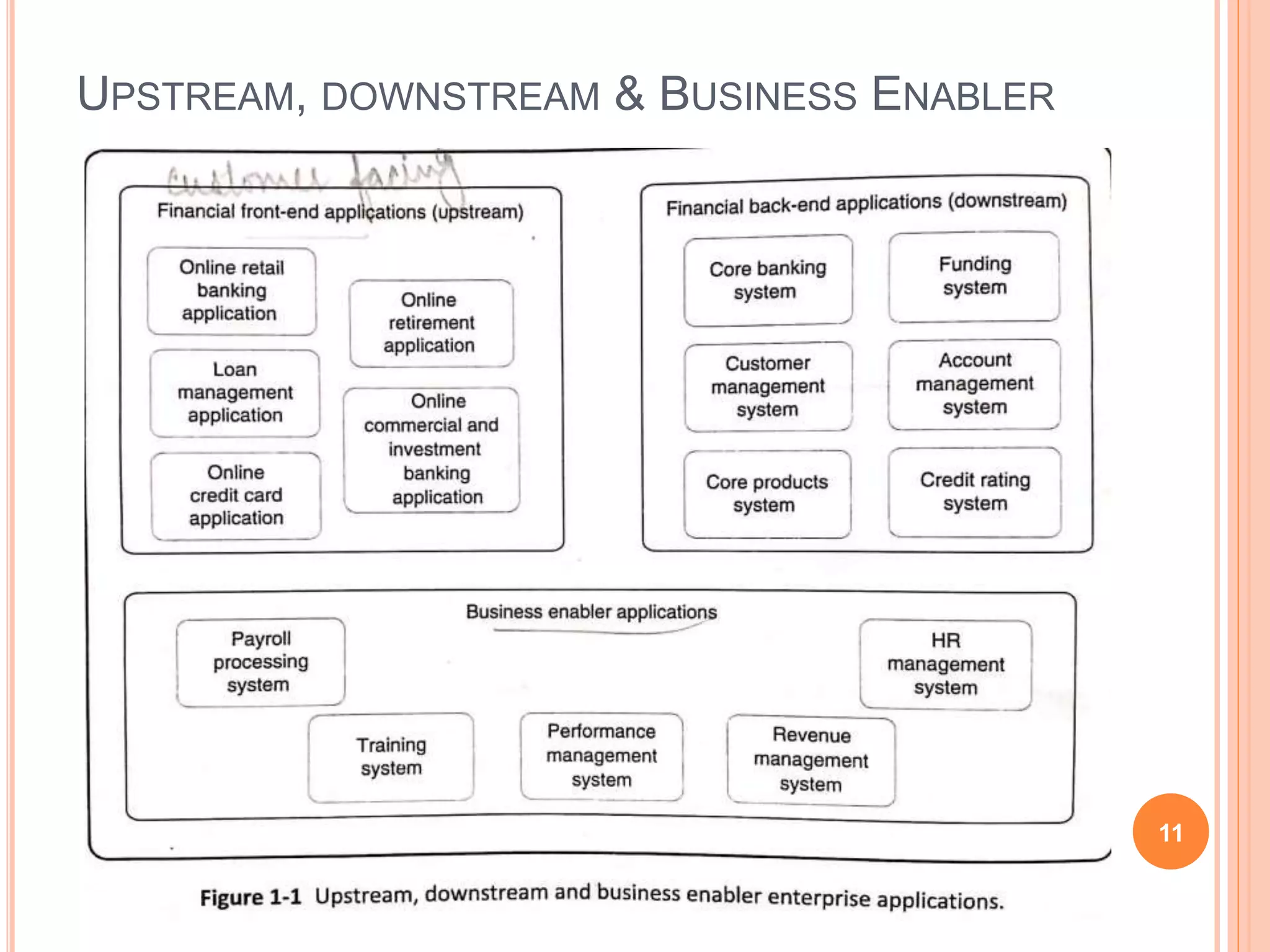
An enterprise is a large organization, and an enterprise application is software that helps an organization solve business problems. Enterprise applications can be categorized by their customer visibility (upstream, downstream, business enabler), the industry and business functions they support, how they process data (OLTP, OLAP), whether they are custom-built or commercial, and if they are host-centric or distributed. They must enhance efficiency, ensure security, handle large data volumes, and be easily maintained. Challenges for enterprise applications include automating business processes, integrating applications, maintaining security, and providing rich user experiences.