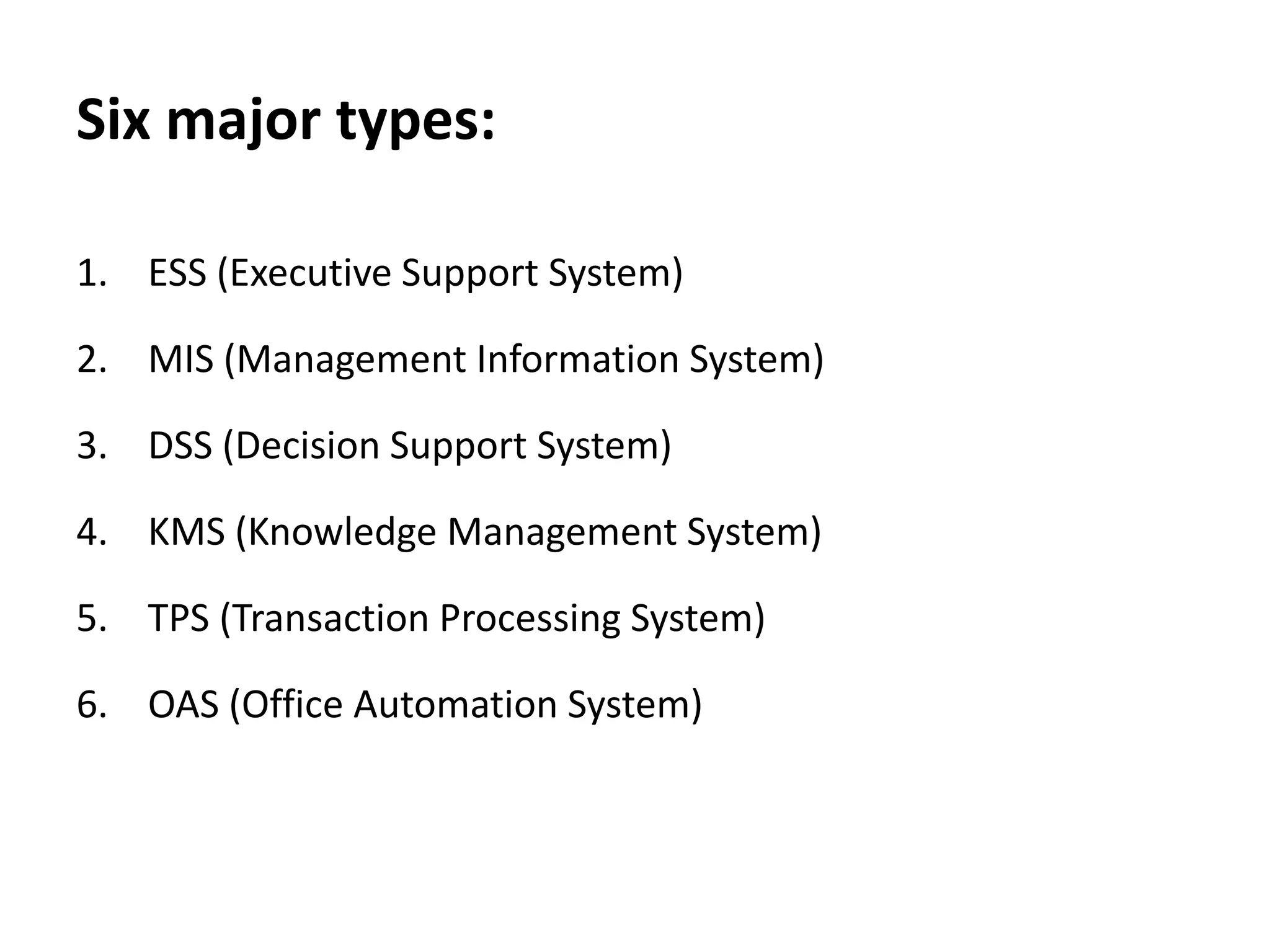
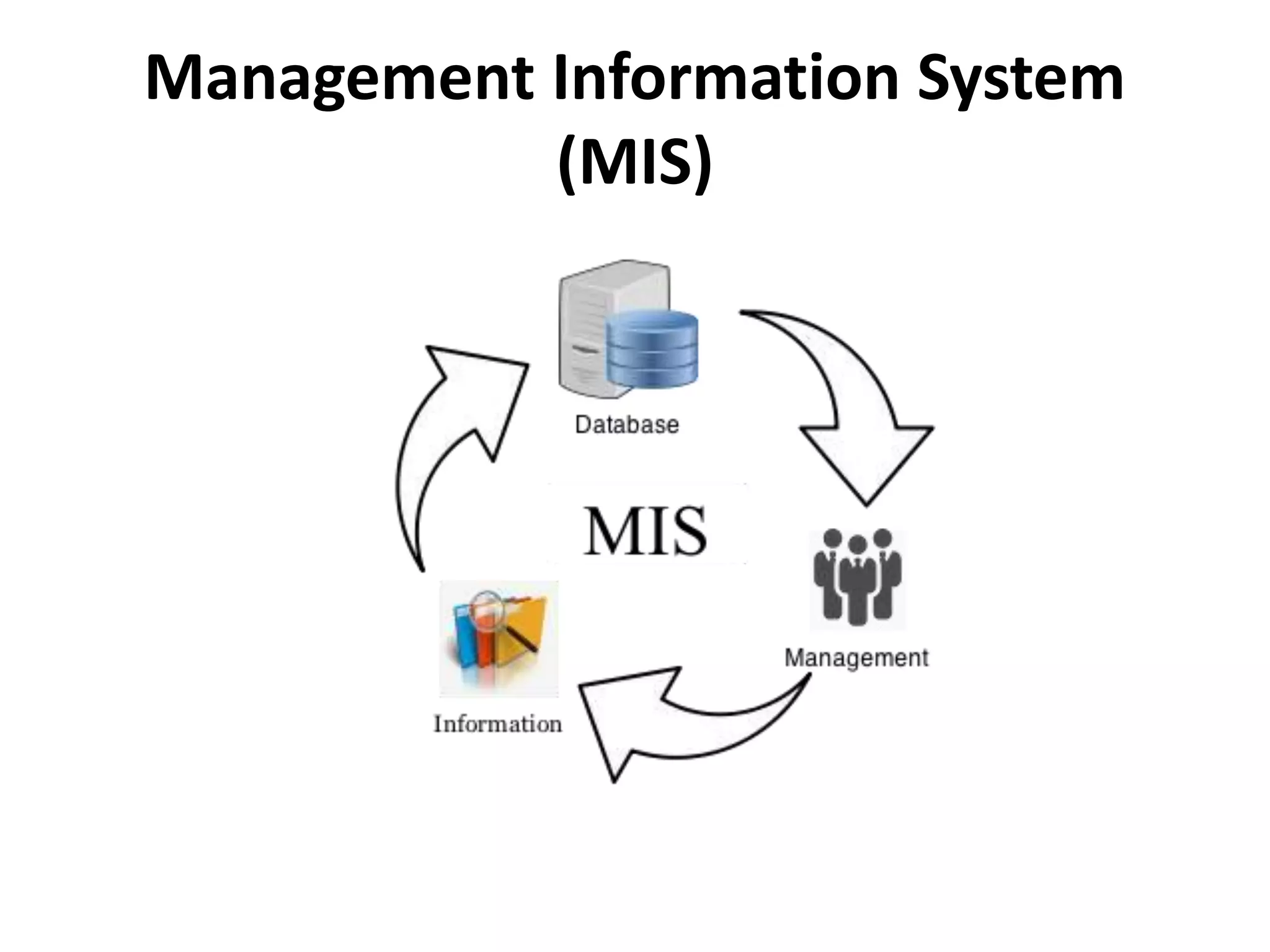
This document summarizes six major information systems: Executive Support System (ESS), Management Information System (MIS), Decision Support System (DSS), Knowledge Management System (KMS), Transaction Processing System (TPS), and Office Automation System (OAS). ESS helps senior executives make strategic decisions. MIS provides reports to support middle management decisions. DSS provides tools to support semi-structured decision making. KMS manages organizational knowledge and experiences. TPS processes business transactions and generates reports. OAS automates office tasks like communication and scheduling.