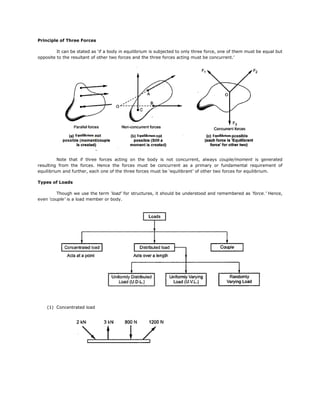
Equilibrium is the state of rest of a particle or body where the net force and net torque are zero. For a body to be in static equilibrium, the sum of the forces in the x and y directions and the sum of moments must equal zero. There are various types of loads that can act on structures including concentrated loads, uniformly distributed loads, and uniformly varying loads. Equilibrium problems of concurrent coplanar forces can be solved using the principle of two forces or three forces. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving for tensions, reactions, and other unknown forces in equilibrium problems.


![EQUILIBRIUM OF CONCURRENT COPLANAR FORCES
Example:
A boom AC hinged at A supports a 400 N load as shown. Find the force in cable BC, which is attached to
the wall at B. Neglect self weight of boom.
Solution:
FBD:
[∑ F x = 0] → +
−T cos 30 o + F cos 45 o = 0
cos 30 o
F = T
cos 45 o
eq. 1
[∑ F
y ]
=0 ↑+
T sin 30 o + F sin 45o − 400N = 0
eq. 2
Substititute eq. 1 to eq. 2:
cos 30o
T sin 30o + T
cos 45o
sin 45o − 400N = 0
T = 292.82 N
F = 358.63 N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engmech05equilibriumofconcurrentforcesystem-121013040059-phpapp02/85/Engmech-05-equilibrium_of_concurrent_force_system-4-320.jpg)
![Example:
A string supported at A and B carries a load of 20 kN at C and a load W at D as shown. Find the value of
W so that CD remains horizontal. Also find the tension in string segments AC, CD and DB.
Solution:
FBD:
Solving for T1 and T2 (Using FBD A)
[∑ F
y ]
=0 ↑+
T1 sin 30 o − 20 kN = 0
T1 = 40 kN
[∑ F
x = 0] → +
−T1 cos 30 o + T2 = 0
T2 = 34.64 kN
Solving for T3 and W(Using FBD B)
[∑ F
x = 0] → +
T3 cos 60 o − T2 = 0
T3 = 69.28 kN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engmech05equilibriumofconcurrentforcesystem-121013040059-phpapp02/85/Engmech-05-equilibrium_of_concurrent_force_system-5-320.jpg)
![[∑ Fy ]
=0 ↑+
T3 sin 60 o − W = 0
W = 60 kN
ASSIGNMENT:
1. A mass of 45 kg is suspended by a rope from ceiling. The mass is pulled by a horizontal force until the
rope makes an angle of 70o with the ceiling. Find the horizontal force and tension in the rope.
Ans. T = 469.78 N, F=160.67 N
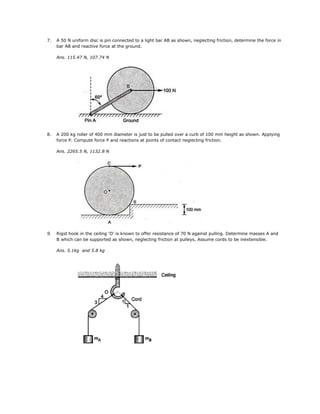
2. Bar AC 10 m long supports a load of 6000 N as shown. The cable BC is horizontal and 5 m long.
Determine forces in the cable and the bar.
Ans. F = 6928.2 N, T = 3464.1 N
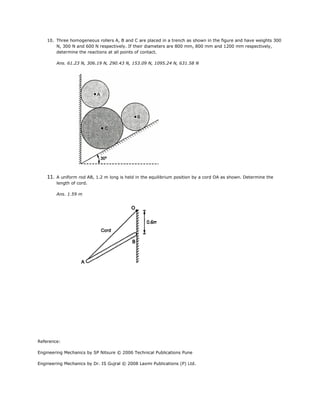
3. A sphere of weight W is kept at rest in V-groove as shown in the figure. If W = 750 N, find reactions at
point of contact.
Ans. R1 = 272.87 N @ 40 deg; R2 = 611.22 N @ 70 deg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engmech05equilibriumofconcurrentforcesystem-121013040059-phpapp02/85/Engmech-05-equilibrium_of_concurrent_force_system-6-320.jpg)