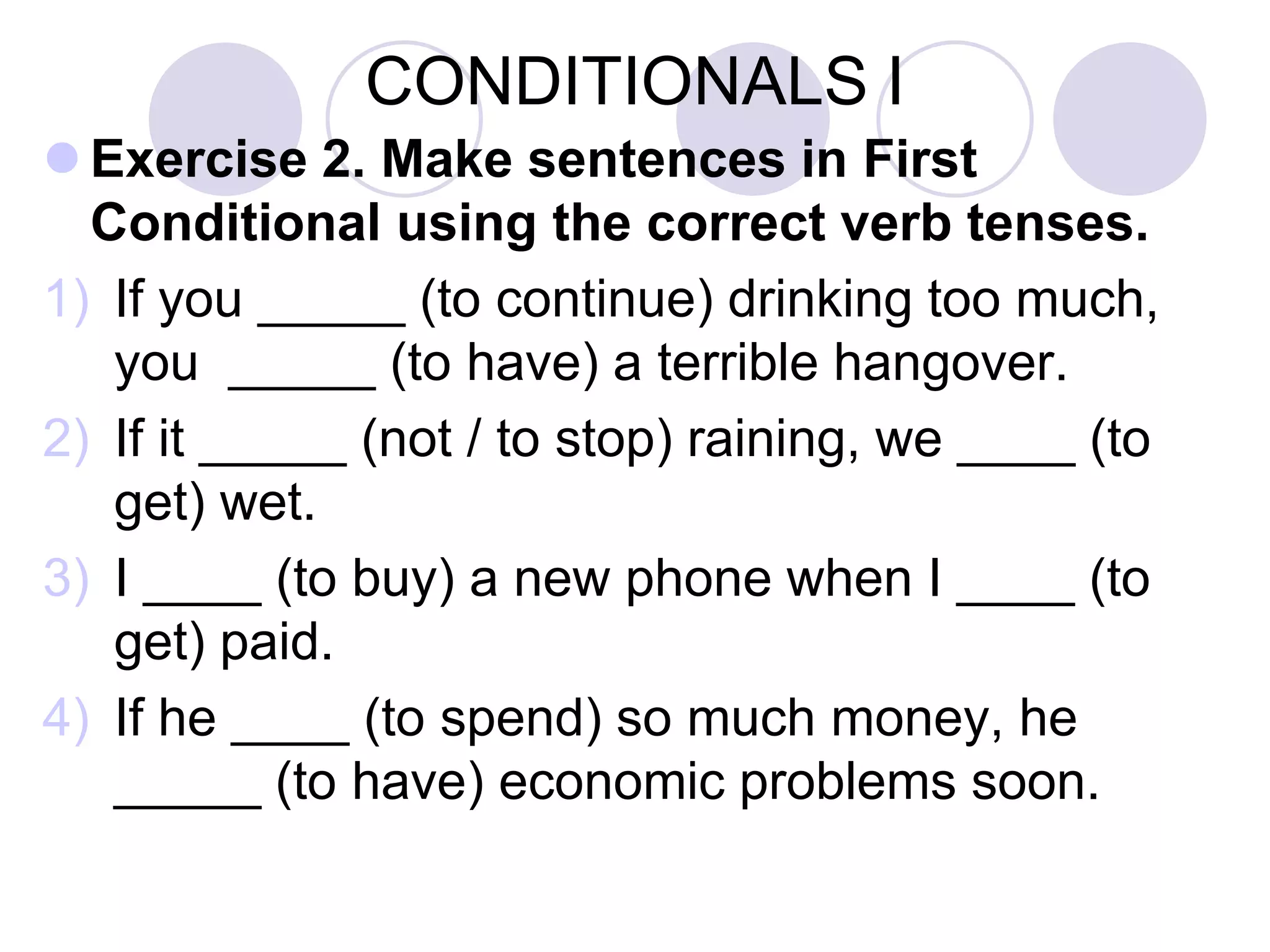
This document provides information on the use of "had better" and "would rather" in English. It explains that "had better" is used to advise something is preferable, using the present or future tense. "Would rather" expresses preference, using "would prefer" for specific preferences and "prefer" for general preferences. Examples of the structures and contractions of "had better" and "would rather" are given. The document also covers three types of conditionals in English - zero, first, and second conditionals - and provides examples of how to form sentences using each one. Exercises are included for learners to practice using "had better", "would rather", and the different conditional structures.