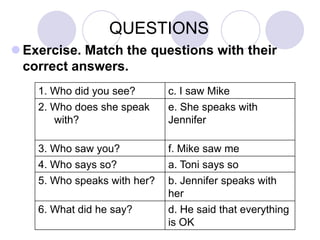
This document provides instruction on the use of imperatives and question structures in English. It begins by explaining that imperatives are used for commands, instructions, and requests, and are formed using the base verb without "to." It then discusses question structures, noting that auxiliary and modal verbs invert subject and verb order in questions. The document also distinguishes between who and what questions, and explains the use of like in questions. Several exercises are included to practice these structures.