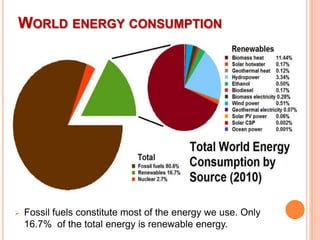
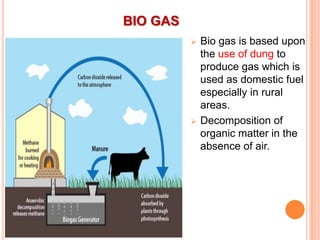
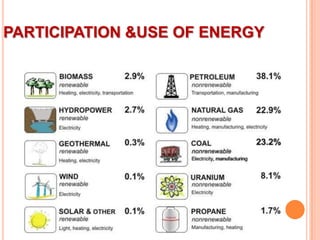
This document provides an overview of energy resources and conservation. It begins by defining energy and classifying resources as renewable and non-renewable. Fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas make up most of the world's energy consumption currently, though renewable sources like solar, wind and hydropower are growing. The document then discusses various non-renewable and renewable energy sources in more detail. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of energy conservation to use resources optimally and ensure availability for future generations.