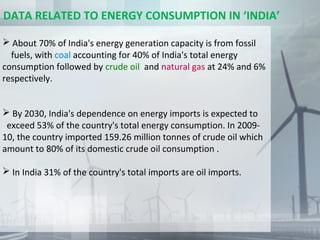
This document discusses various types of energy sources and the importance of energy conservation. It begins by explaining that energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed. It then describes different renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, and biomass. It also discusses non-renewable sources like coal and uranium. The document emphasizes the need for energy conservation given limited resources and increasing demand. It provides examples of conservation efforts in India like energy audits and appliance ratings. Overall, the document promotes reducing consumption and recycling to conserve energy.