This document provides biographical information about Mohanad AlBayati and summarizes key discoveries related to nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-derived vasodilators. It discusses:
1) The 1977-1986 discoveries by Furchgott, Murad, and Ignarro that acetylcholine causes relaxation via endothelium-derived NO and that NO is identical to endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF), earning them the 1998 Nobel Prize.
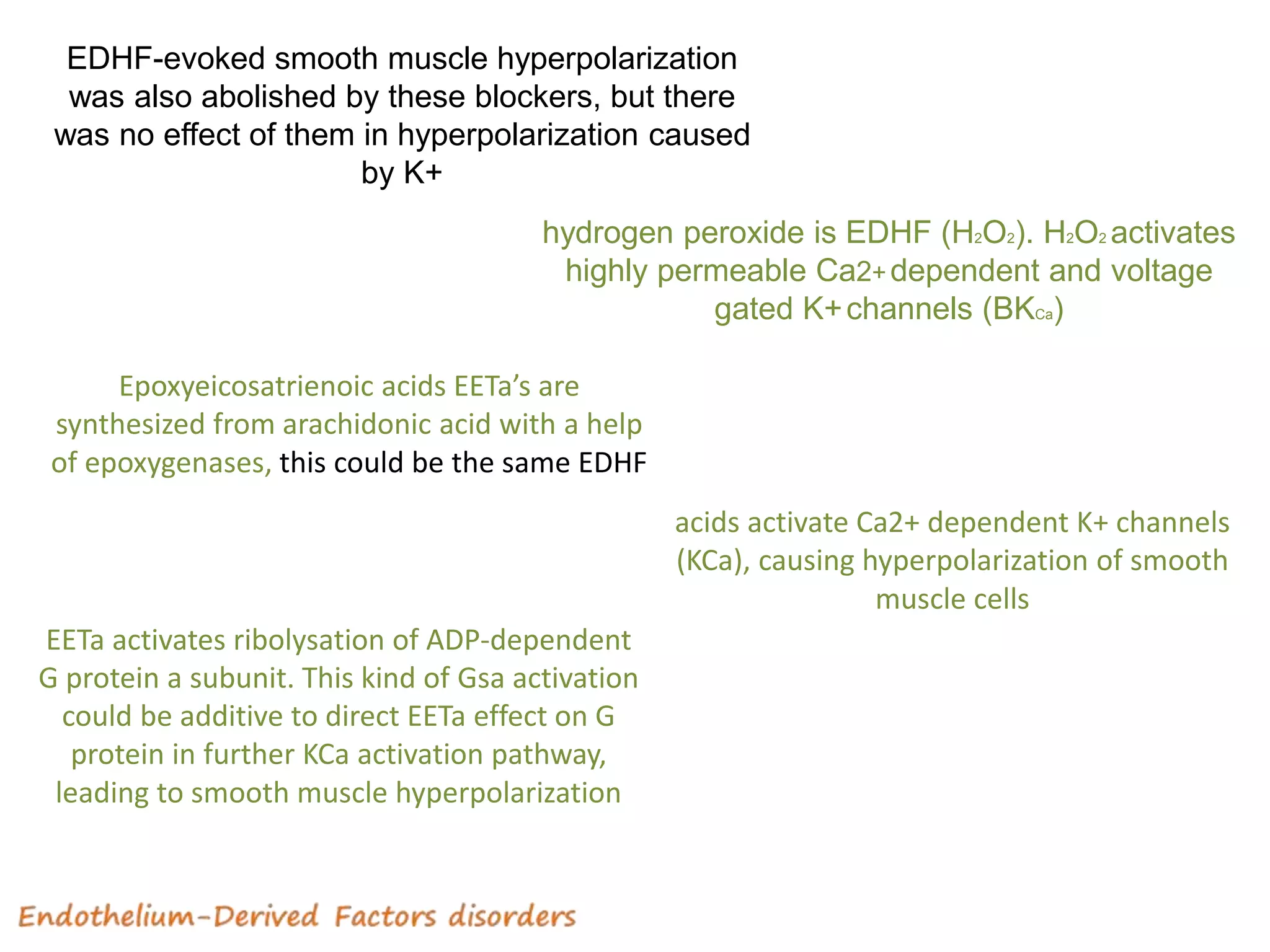
2) The endothelium releases vasodilators like NO and prostacyclin and vasoconstrictors like endothelin-1 and reactive oxygen species to regulate vascular tone.
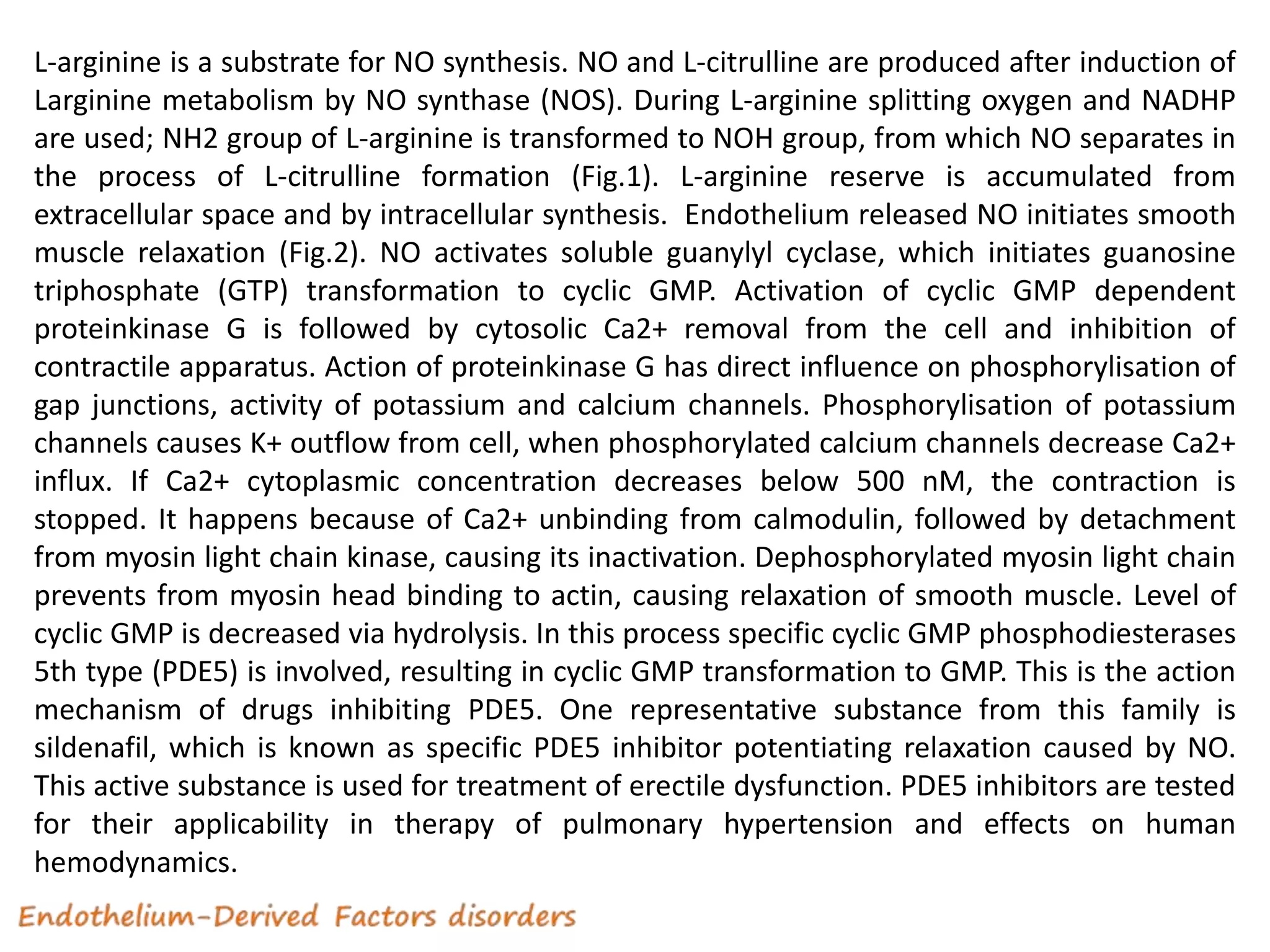
3) NO activates guanylate cyclase, increasing cGMP and