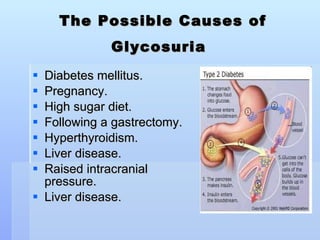
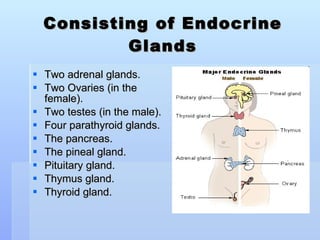
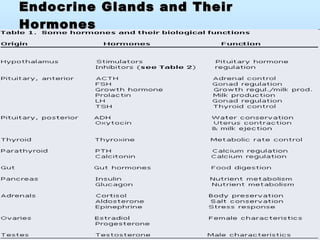
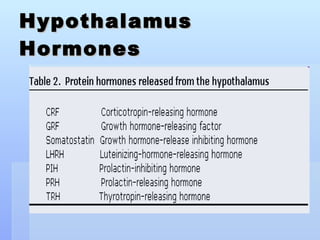
The document discusses various endocrine and medical terms related to the endocrine system. It defines glycosuria as glucose in the urine and describes possible causes such as diabetes, pregnancy, diet, or liver/thyroid issues. Polyuria is the excessive production of urine, with causes including diabetes, drinking issues, or kidney problems. The endocrine system secretes hormones to regulate processes like metabolism and consists of glands like the thyroid, pituitary, and adrenals.