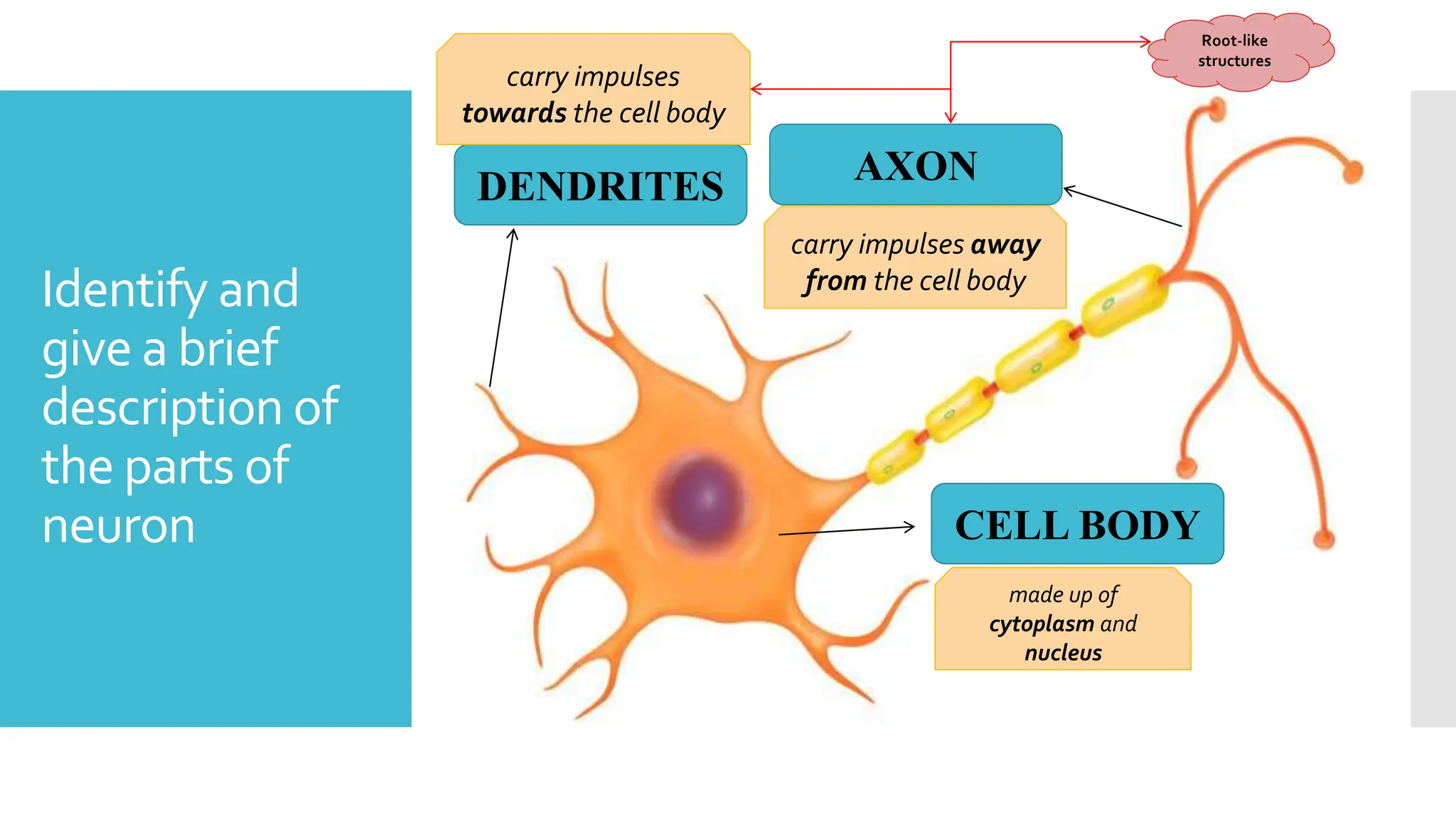
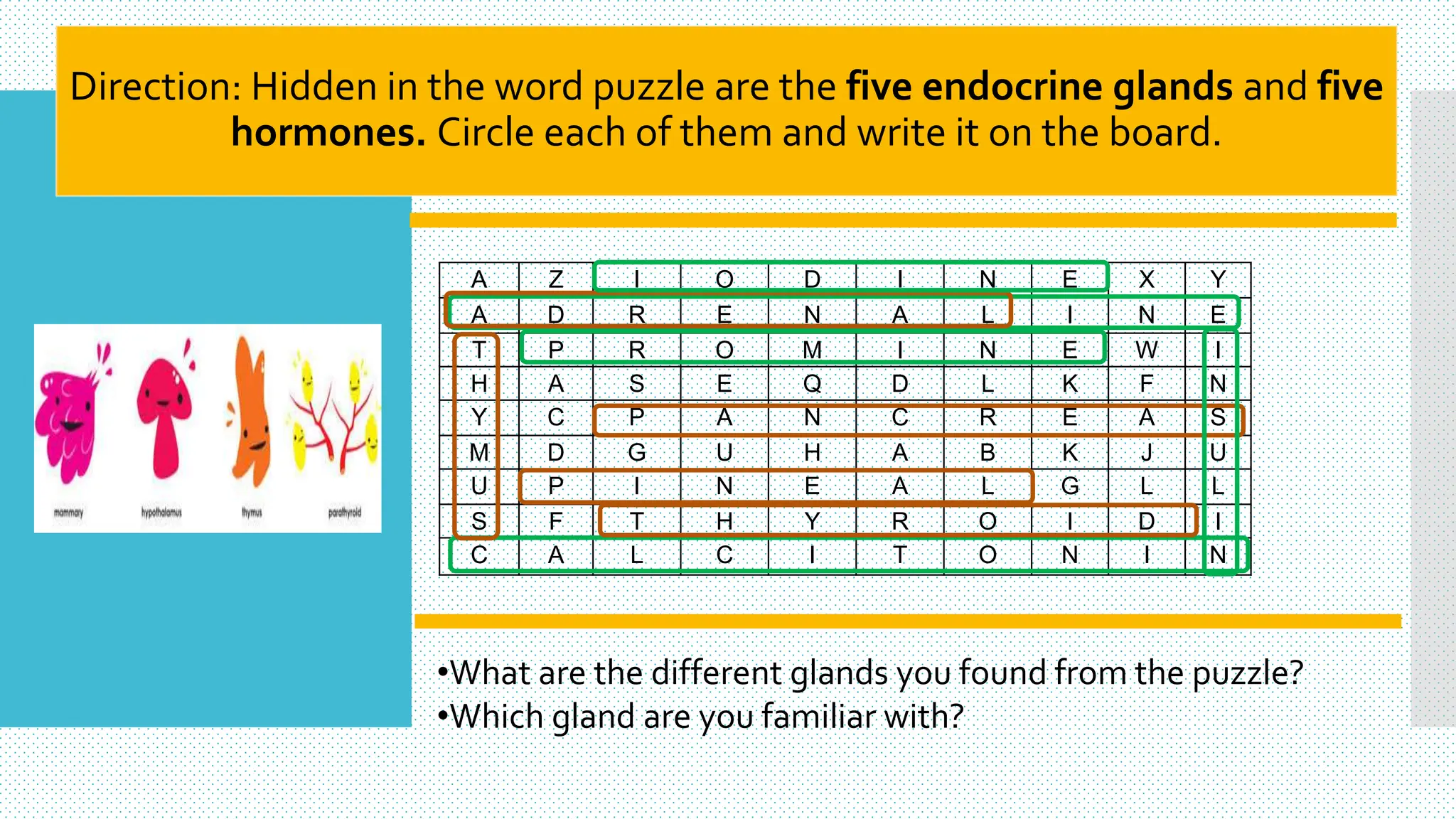
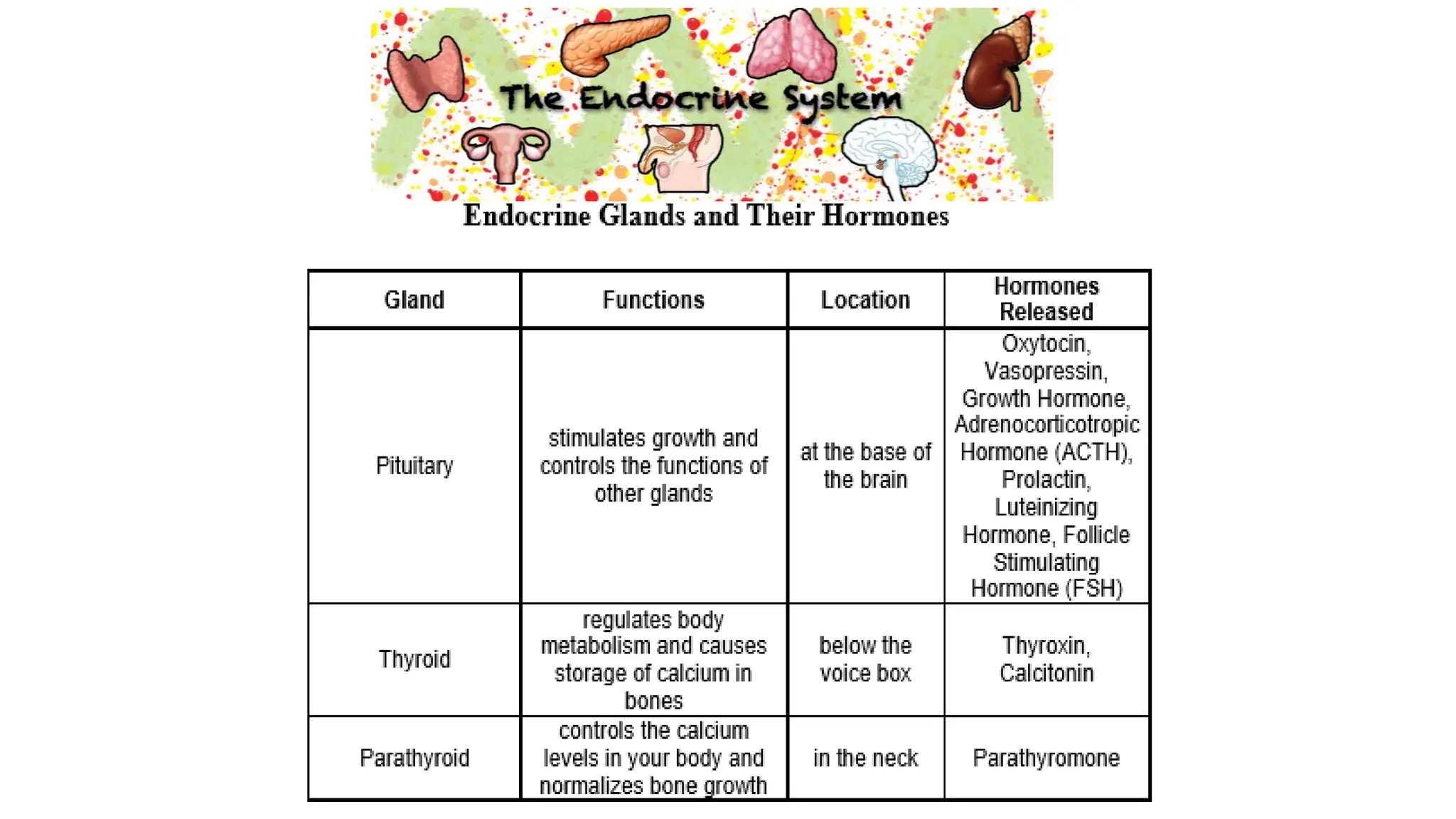
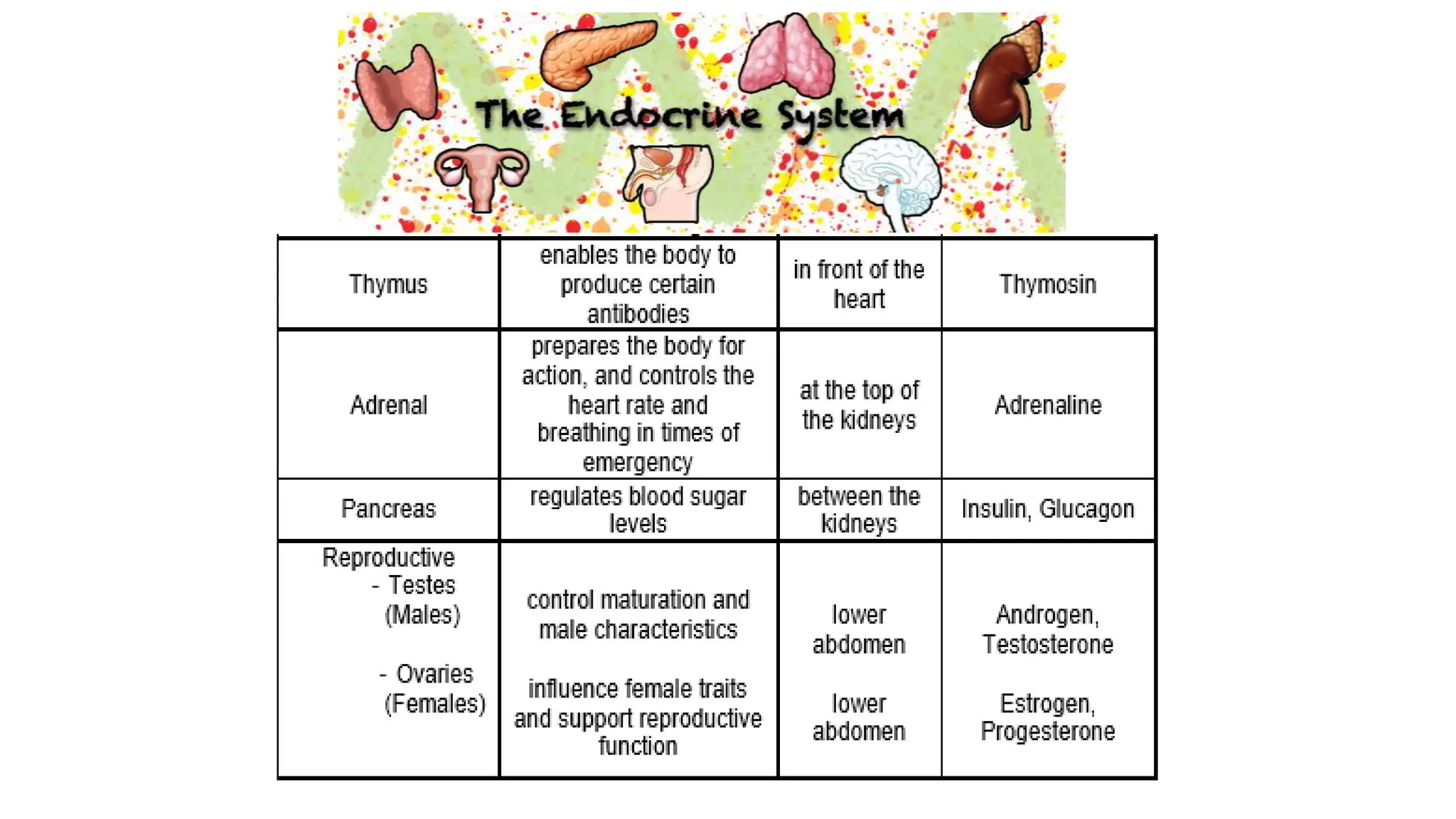
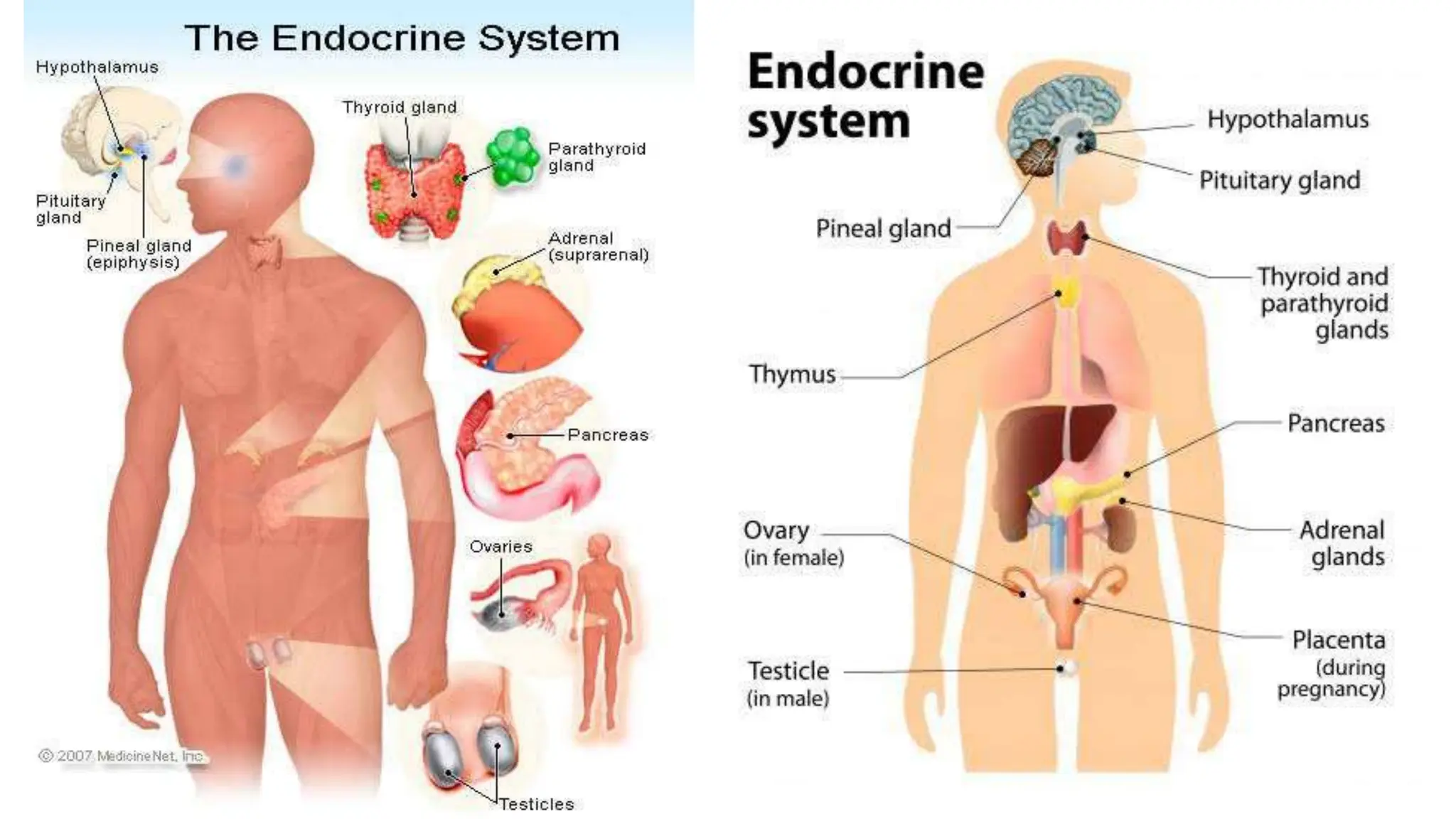
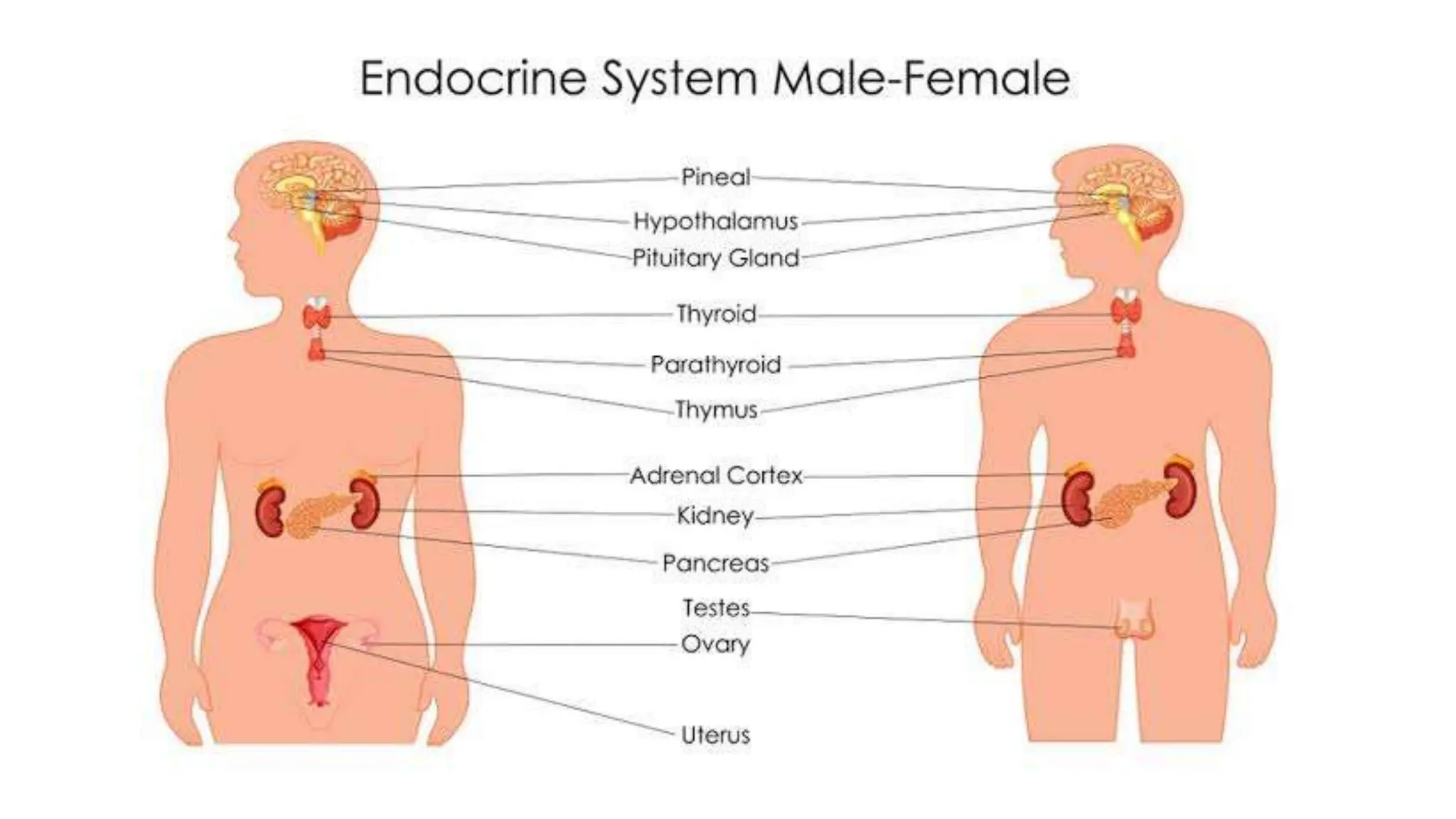
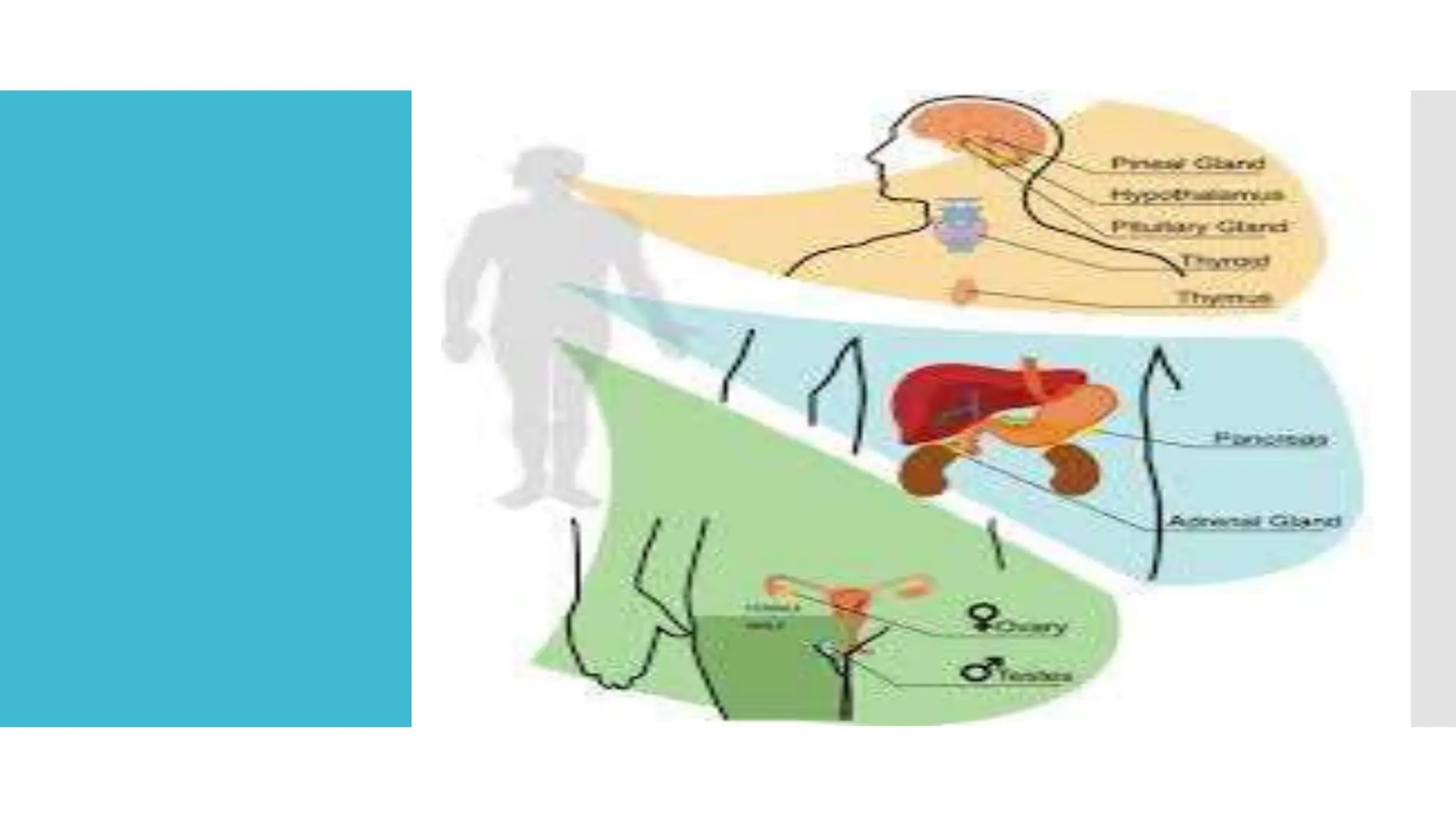
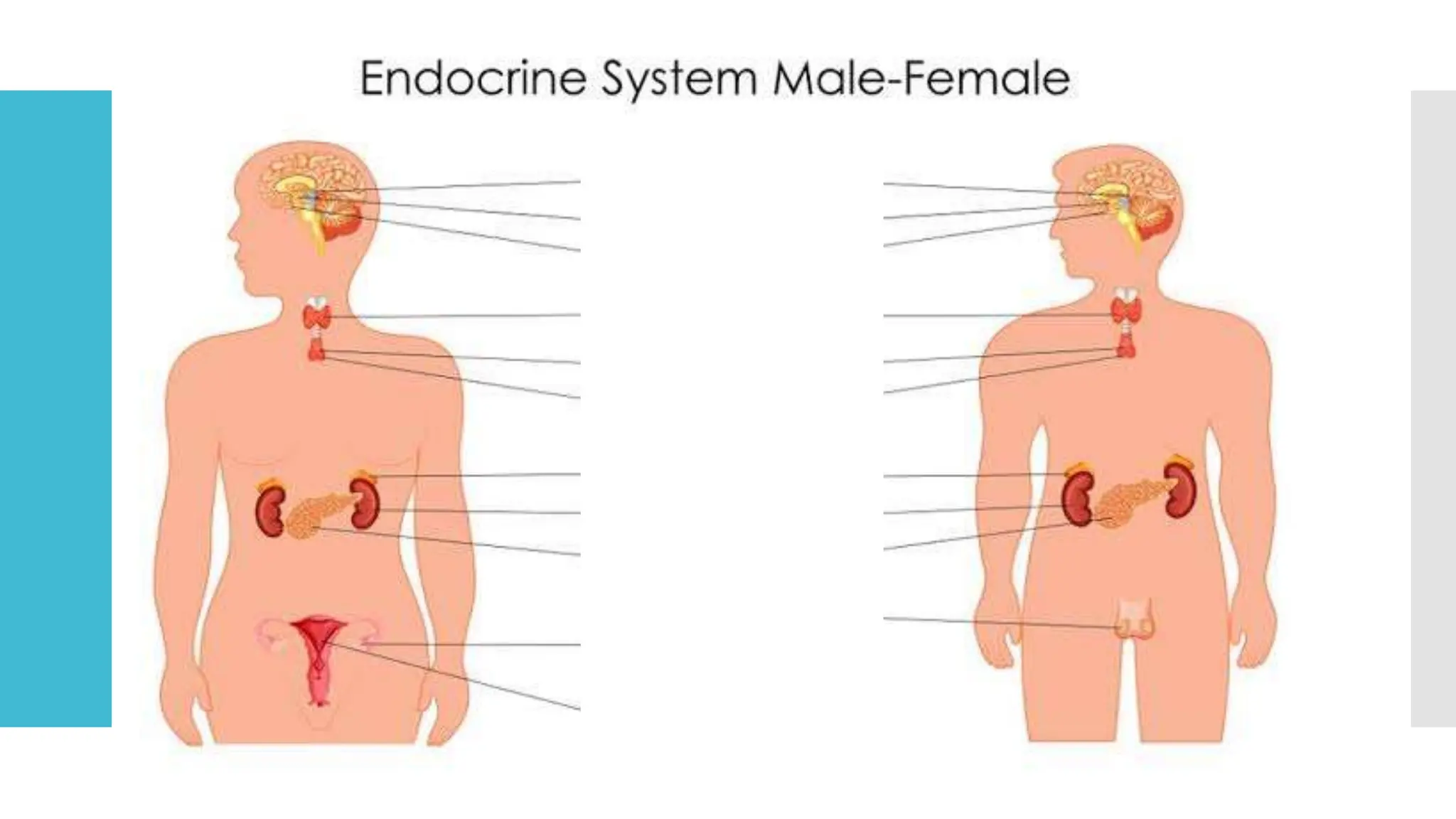
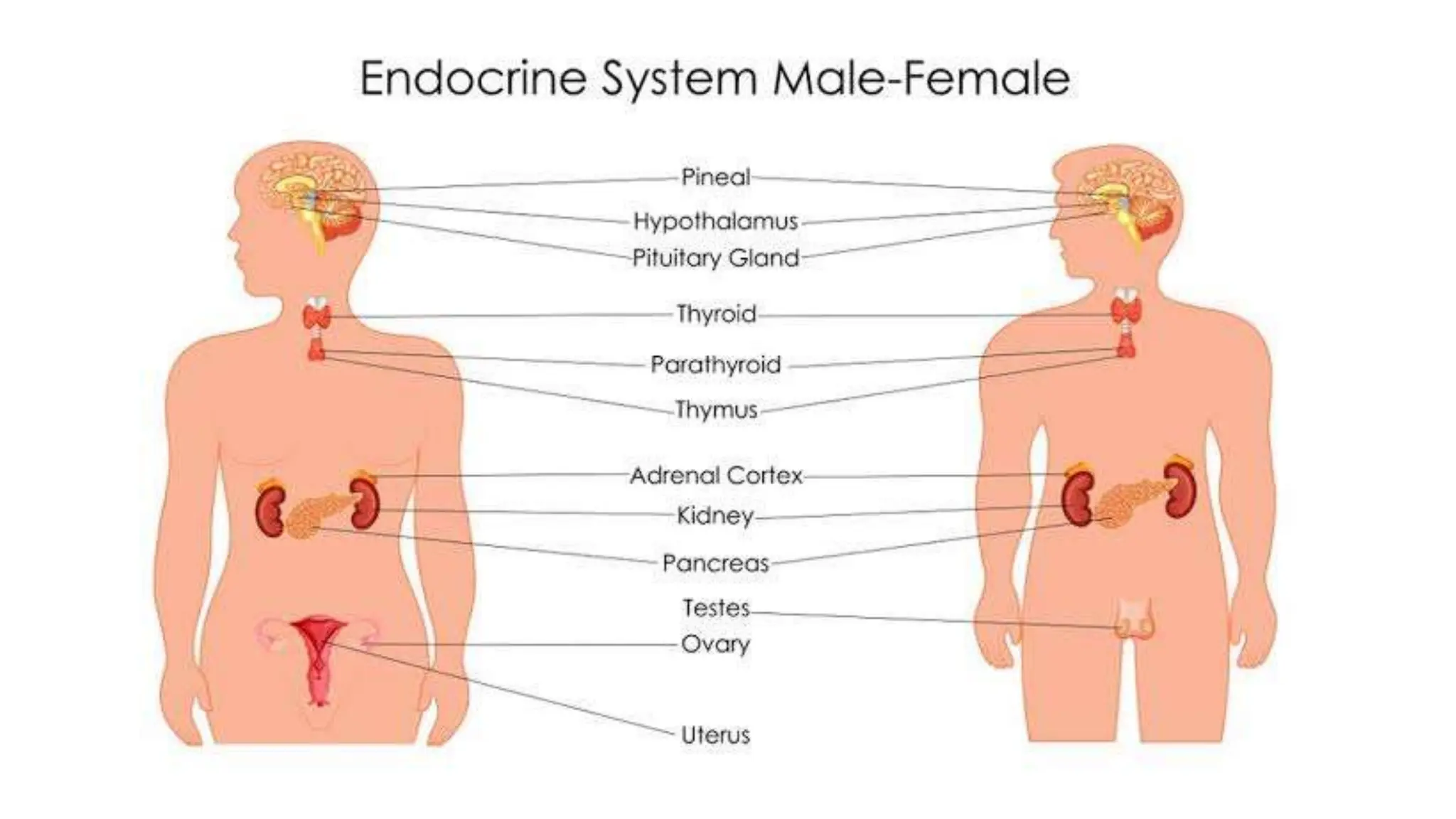
The document provides information about the endocrine system and its glands/hormones. It includes learning objectives about the endocrine glands and their functions. There are also activities that have students identify endocrine glands and hormones, describe their functions, and answer questions about various glands and conditions related to hormone imbalances or deficiencies.