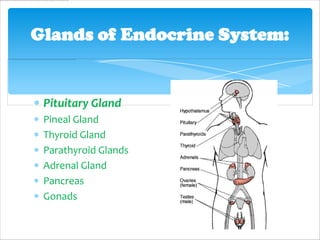
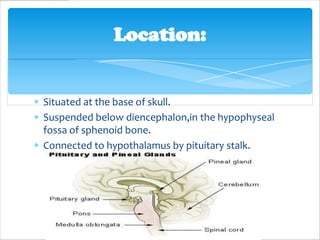
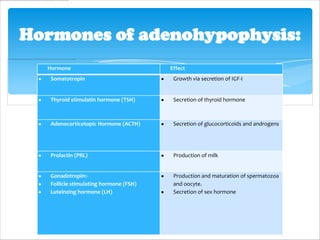
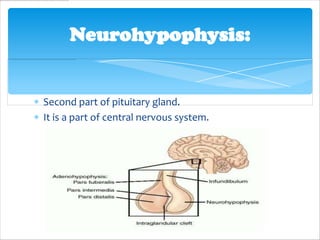
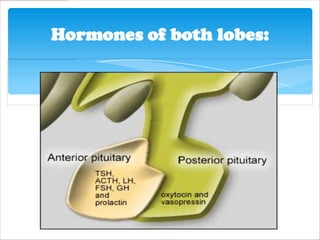
The pituitary gland, also known as the master gland, regulates other endocrine glands. It is located at the base of the skull and has three parts: the anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary, and intermediate lobe. The anterior pituitary secretes hormones that control growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The posterior pituitary stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus that influence milk production and water balance. The intermediate lobe's function is unclear in most mammals.