This document summarizes the findings of a post-mortem examination on a turtle. Key findings include:
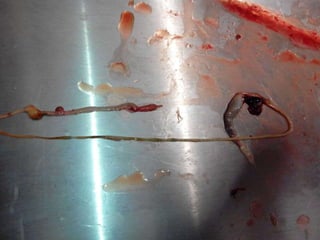
- Intestine contained small pebbles and parasites
- Liver, gallbladder and lungs appeared normal
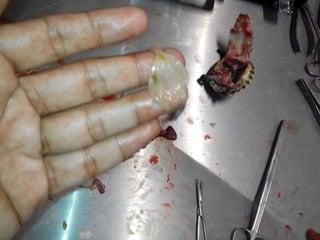
- Stomach contained a live roundworm and serosal hemorrhages
- Kidneys had necrotic foci
- Other organs like the esophagus, trachea, and spleen were also examined
The cause of death was determined to be multi-factorial, including parasitism, choking of the esophagus, and environmental changes as the turtle was a household pet. Recommendations are given to improve husbandry and deworm other turtles.